In today’s digital world, handling private details in educational assessments is critical. Whether dealing with quiz submissions, homework, or other evaluations, ensuring the safety of confidential data should be a priority. Without proper precautions, sensitive personal information can be exposed, leading to potential risks for individuals and organizations alike.
Understanding the importance of protecting personal data during evaluations requires an awareness of both the methods used to collect such information and the security measures necessary to keep it safe. This section will discuss strategies to prevent unauthorized access, as well as tools designed to monitor and secure vulnerable content throughout the evaluation process.
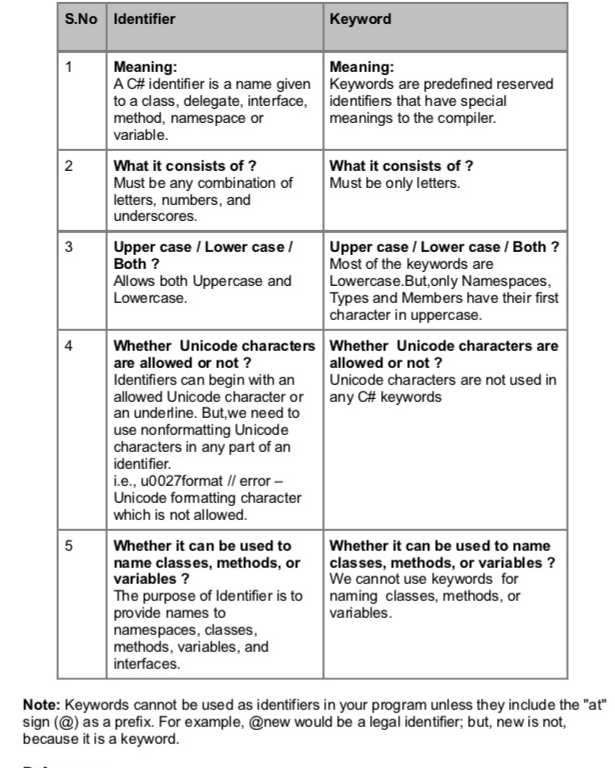
Understanding PII in Test Answers
In any educational or professional assessment, certain data can be classified as highly sensitive. These details, when improperly handled, pose serious security risks. It is essential to recognize what constitutes sensitive information and how it is involved in evaluation processes. Awareness of such data allows for more effective measures to ensure its privacy.
Personal information can range from basic identifiers, like names and contact details, to more specific elements such as addresses or financial records. These types of data are often integrated within test-related materials, whether in responses or personal identification fields. Understanding how this information is stored, shared, and processed is key to protecting it from misuse.
| Type of Data | Example |
|---|---|
| Personal Identifiers | Name, Date of Birth, Contact Information |
| Academic Details | Student ID, Grades, Course Enrollment |
| Financial Data | Payment Information, Scholarships |
Proper understanding of what qualifies as sensitive in these contexts is essential for reducing the chances of exposure. This awareness should guide both the storage and transmission practices to prevent unauthorized access.
Risks of Exposing Personal Data
Exposing sensitive information in any form, particularly during evaluations, can lead to a series of harmful consequences. When private details are improperly accessed, it creates opportunities for malicious individuals to exploit this data. Understanding the potential threats and their impact is crucial in developing protective measures.
Potential Threats
- Identity Theft: Unauthorized access to personal details can result in someone assuming another person’s identity to commit fraud or other illegal activities.
- Financial Loss: Leaked financial data, like bank details or credit card numbers, can lead to unauthorized transactions and significant financial damage.
- Reputation Damage: The release of private information can harm the individual’s reputation, especially if it includes confidential academic or professional details.
- Legal Consequences: Mishandling personal information can lead to legal actions, particularly in jurisdictions with strict privacy laws.
Long-Term Impact
- Loss of Trust: Once personal data is exposed, regaining the trust of those affected can be a lengthy and difficult process.
- Financial Penalties: Organizations that fail to protect personal data may face fines or penalties, especially in cases of negligence or non-compliance with regulations.
- Personal Stress: The psychological impact on individuals whose information is compromised can be severe, leading to anxiety or emotional distress.
Ultimately, the risks associated with exposing private data are far-reaching. Taking steps to prevent such incidents is vital to protecting individuals and organizations from the potentially devastating consequences of data breaches.
Best Practices for Data Protection

Ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive information requires a combination of strategies aimed at minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. By implementing effective security measures, organizations can prevent data breaches and protect individual privacy during any process involving personal details. These practices focus on strengthening security systems, monitoring data usage, and educating individuals on how to handle sensitive information responsibly.
To achieve maximum protection, it is essential to employ a multi-layered approach, combining technical safeguards, organizational protocols, and employee awareness programs. Encrypting sensitive files, restricting access to authorized personnel, and regularly auditing systems are just a few measures that can help in maintaining a secure environment.
Regular updates to security tools and staying informed on new threats are also crucial to address emerging vulnerabilities and prevent potential exploits. Creating a culture of security within an organization can ensure that everyone is vigilant and proactive about data protection.
Tools for Securing Sensitive Information
Securing private data requires the use of specialized tools designed to protect against unauthorized access and prevent breaches. These tools help safeguard critical information from being exposed, stolen, or misused. By employing various security technologies, organizations can reduce risks and enhance their ability to defend sensitive content throughout its lifecycle.
Encryption Tools
Encryption is one of the most effective methods for securing data. It converts information into an unreadable format, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be easily accessed or understood. Popular encryption tools include:
- BitLocker: A full disk encryption tool for Windows devices.
- VeraCrypt: Open-source software for encrypting files and entire drives.
- PGP (Pretty Good Privacy): Used to encrypt emails and other communications.
Access Control Systems
Access control tools help restrict who can view or manipulate sensitive information. By granting access only to authorized individuals, organizations can prevent unauthorized data access and minimize exposure. Common tools include:
- Okta: A platform for identity and access management.
- Auth0: Provides secure authentication and authorization services for applications.
- Windows Active Directory: Manages user permissions and access rights within an enterprise network.
These tools work together to create a comprehensive security strategy, combining encryption, access control, and other protective technologies to ensure sensitive data remains secure at all times.
Legal Implications of PII Disclosure
Unauthorized exposure of sensitive personal information can have significant legal consequences for both individuals and organizations. Laws and regulations are in place to protect individuals’ privacy, and violations can result in serious penalties. The legal landscape surrounding the mishandling of private data is complex and varies across jurisdictions, but it generally includes provisions for fines, lawsuits, and other legal actions.
Organizations found guilty of exposing private details may face substantial financial penalties, especially if they are deemed negligent in their security practices. Individuals whose data is disclosed may also have the right to pursue legal action for damages. Furthermore, non-compliance with data protection laws can lead to regulatory scrutiny, audits, and reputational damage that can have long-lasting effects on businesses.
In addition to penalties, there are obligations for businesses to notify affected parties and regulators in case of a breach. Failure to do so promptly can lead to further legal complications. Understanding the legal framework and its implications is essential for ensuring that private information is handled responsibly and in accordance with applicable laws.
How to Detect PII in Test Responses

Recognizing sensitive information in evaluation submissions is a critical task for any organization handling private data. When personal details are embedded in responses, it is vital to have methods in place to detect and protect them. These strategies involve both manual and automated techniques to identify data that may need additional security or privacy measures.
Manual Detection Methods
One way to detect sensitive details in submissions is through manual review. This method involves carefully examining each submission for common types of personal information such as:
- Full names
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Physical addresses
- Identification numbers (e.g., social security numbers)
While manual checks can be effective, they are time-consuming and prone to human error, especially in larger datasets. It is important to develop a systematic approach when reviewing responses to minimize oversight.
Automated Detection Tools
To complement manual methods, automated tools can be used to scan responses for sensitive information. These tools leverage algorithms and pattern recognition to detect data that fits certain criteria. Examples of such tools include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) software: Analyzes text for context and detects patterns that match personal identifiers.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools: Monitors submissions and flags content that appears to contain confidential information.
- AI-driven scanners: Use machine learning to continuously improve detection accuracy over time.
By integrating both manual and automated detection approaches, organizations can ensure that sensitive details are quickly identified and protected during the evaluation process.