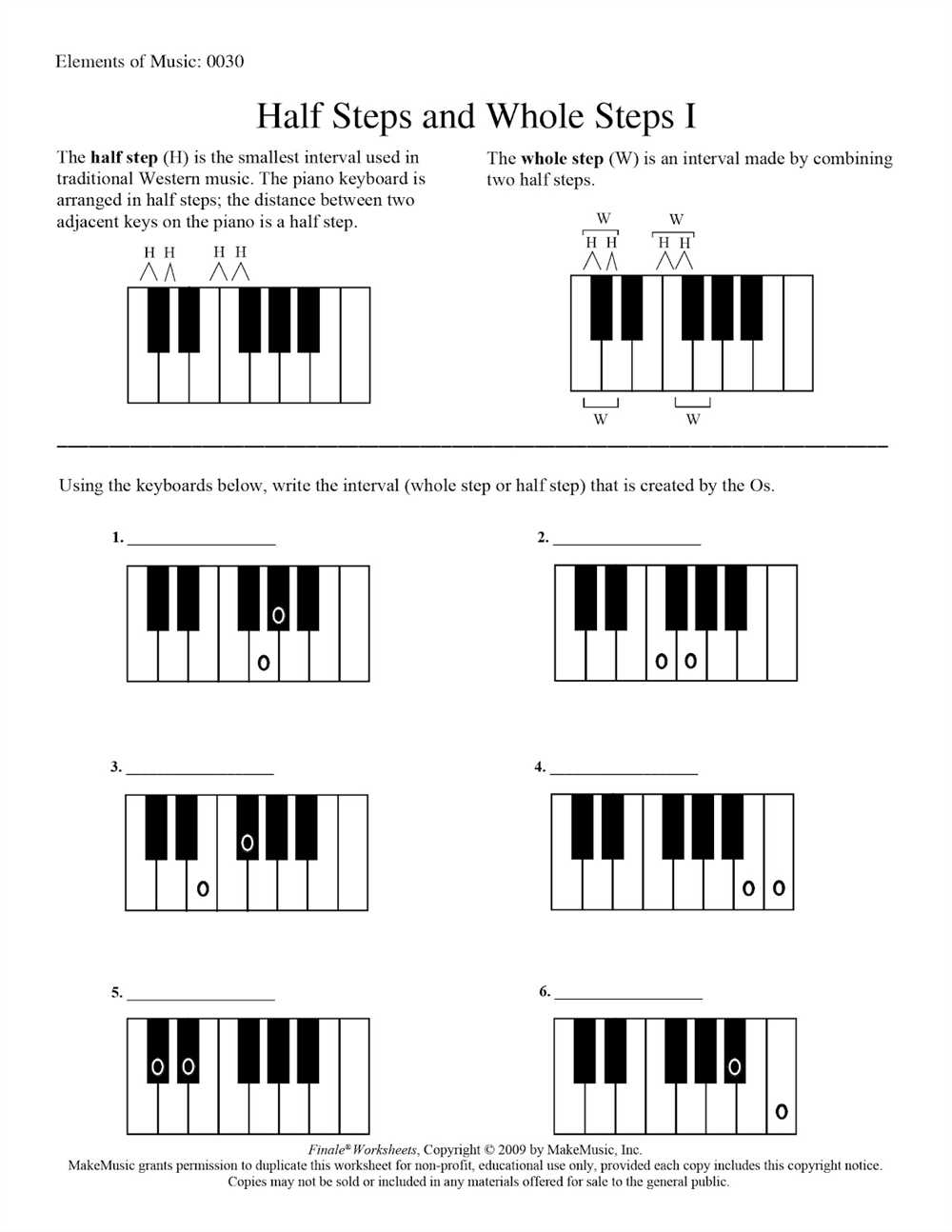
Understanding the concept of half steps and whole steps is crucial for any musician. These intervals are the building blocks of scales, chords, and melodies. To fully grasp this concept, it is essential to practice and familiarize yourself with the patterns of half and whole steps in different musical scales.
In this worksheet, you will find the answers to various exercises that require identifying the intervals between notes. By completing these exercises, you will enhance your ability to recognize and distinguish between half and whole steps in music. This will enable you to navigate the fretboard of an instrument or read sheet music more efficiently.
The worksheet includes examples of both ascending and descending scales in different keys. By analyzing these examples and comparing them to your answers, you will gain a deeper understanding of how half steps and whole steps relate to each other and how they form different scales.
Furthermore, this worksheet serves as a practice tool for identifying intervals in music theory. As you progress through the exercises, you will develop your listening skills and be able to identify and differentiate between half steps and whole steps in musical compositions. This skill is vital for musicians of all levels, as it allows for better interpretation and performance of music.
By using this half steps and whole steps worksheet, you are taking a significant step towards mastering the fundamentals of music theory. With practice and dedication, you will soon develop a strong understanding of intervals and be able to apply this knowledge to your playing or composition. So, grab your instrument and start exploring the world of half steps and whole steps!
What are half steps and whole steps?
In music theory, half steps and whole steps are terms used to describe the distance between two adjacent pitches or notes. They are the building blocks of scales and chords, and understanding their relationship is fundamental to understanding music theory.
A half step, also known as a semitone, is the smallest interval in Western music. It is the distance between two adjacent keys on a piano or two neighboring frets on a guitar. It can also be thought of as the distance between two consecutive letters on the musical alphabet. For example, the distance from C to C# is a half step.
A whole step, also known as a whole tone, is equivalent to two half steps. It is the distance between two keys that have one key in between them on a piano or two frets apart on a guitar. It can also be thought of as skipping one letter on the musical alphabet. For example, the distance from C to D is a whole step.
In a musical scale, such as the major scale, there is a pattern of whole steps and half steps that determines the sequence of pitches. The specific pattern of whole and half steps gives each scale its unique sound and character.
Understanding half steps and whole steps is essential for musicians in areas such as playing by ear, transposing music, and building chords and scales. By knowing the distances between notes, musicians can navigate the musical landscape with precision and creativity.
How to Determine Half Steps and Whole Steps
Understanding the concept of half steps and whole steps is essential in music theory. It allows you to navigate the different notes and intervals on a musical scale. To determine whether a step is a half step or a whole step, you need to consider the distance between two consecutive notes on the scale.
A half step, also known as a semitone, is the smallest interval between two notes. It represents the distance of one key on a piano keyboard. For example, the distance from C to C# is a half step. You can also think of it as moving up or down by one fret on a guitar.
A whole step, on the other hand, is twice the distance of a half step. It represents the distance of two keys on a piano keyboard or two frets on a guitar. For example, the distance from C to D is a whole step.
To determine whether a step is a half step or a whole step, you can use the following rule: if the two notes have one letter name in between (e.g., C to D), it is a whole step. If the two notes only have a half letter name in between (e.g., C to C#), it is a half step.
It is important to note that this rule applies to most scales but not all. Some scales have different patterns of intervals, and the distance between notes may vary. However, understanding the concept of half steps and whole steps will provide you with a solid foundation for understanding music theory and building your musical knowledge.
Understanding the music theory behind half steps and whole steps
When it comes to understanding music theory, one fundamental concept to grasp is the distinction between half steps and whole steps. These terms refer to the smallest intervals between two adjacent notes in Western music. By understanding this concept, musicians can better analyze melodies, understand chord progressions, and navigate scales and key signatures.
A half step, sometimes called a semitone, is the smallest interval in Western music. It is the distance between two adjacent notes on a keyboard, regardless of whether they are white or black keys. For example, the distance between C and C# (or Db) is a half step. Another example is the distance between E and F. The half step is crucial in creating tension and dissonance in music, as it creates a sense of proximity and unresolved movement.
A whole step, also known as a whole tone, is equal to two half steps. It represents a larger interval between two adjacent notes. For example, the distance between C and D is a whole step, as is the distance between F and G. Whole steps are often used to create a sense of stability and resolution in music, as they provide a more pronounced sense of distance between notes.
Understanding the distinction between half steps and whole steps is essential for musicians when it comes to building scales and understanding key signatures. In a major scale, for example, the pattern of intervals is whole step, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step, whole step, half step. By knowing this pattern, musicians can construct any major scale on any starting note.
Overall, the concept of half steps and whole steps lays the foundation for understanding the harmonic and melodic structure of music. By mastering this fundamental concept, musicians can better analyze and compose music while appreciating the intricate details of how notes interact and create tension and resolution.
Why are half steps and whole steps important?
Half steps and whole steps are fundamental building blocks in music theory and are crucial in understanding how scales, chords, and melodies are constructed. By understanding and being able to identify half steps and whole steps, musicians are able to navigate the musical landscape with confidence and precision.
A half step is the distance between two adjacent keys on a piano, regardless of whether they are white or black keys. This small interval of half steps plays a significant role in creating tension and resolution within a piece of music. By using half steps strategically, composers and songwriters can create melodic and harmonic movement that captures the listener’s attention and evokes a range of emotions.
Whole steps, on the other hand, are two half steps combined. This larger interval allows for greater tonal movement and can create a sense of stability and direction within a musical passage. Understanding how whole steps function within scales and chords provides musicians with the knowledge needed to compose and improvise musical phrases that flow seamlessly.
In addition to their role in creating musical tension and resolution, half steps and whole steps are crucial in understanding scales and their modes. Scales are collections of pitches that follow specific patterns of whole steps and half steps, and by understanding these patterns, musicians can easily identify and play scales in any key. Similarly, chords are built using intervals of whole steps and half steps, and knowing how these intervals are constructed is essential for building and analyzing chords.
Overall, half steps and whole steps are important foundations in music theory. They provide a framework for understanding musical structure, creating tension and resolution, and navigating the complexities of scales and chords. By mastering these concepts, musicians can enhance their musicality, creativity, and ability to communicate through their art.
Common exercises for practicing half steps and whole steps
When learning about half steps and whole steps in music theory, it is important to practice these concepts in order to develop a solid understanding. There are several common exercises that can help musicians improve their ability to identify and play these intervals accurately.
1. Scale exercises: One of the most effective ways to practice half steps and whole steps is by playing scales. Start with a simple major scale, such as C major, and practice playing the scale one note at a time, paying attention to the intervals between each note. Make sure to identify the half steps and whole steps in the scale and practice playing them accurately. Once comfortable with the major scale, try playing other scales, such as minor scales, melodic minor scales, and harmonic minor scales, to further reinforce the concept of half steps and whole steps.
2. Interval exercises: Another exercise that can help develop an understanding of half steps and whole steps is practicing intervals. Begin by playing and identifying different intervals, such as a major third or a perfect fifth. Pay close attention to the distance between each note and determine whether it is a half step or a whole step. This exercise can be done both melodically and harmonically, by playing intervals in succession or simultaneously. Gradually increase the complexity of the intervals to challenge yourself and further reinforce the concept.
3. Ear training exercises: In addition to playing scales and intervals, it is also important to develop your ear for half steps and whole steps. One way to do this is by using ear training exercises. These exercises involve listening to a series of notes and identifying the intervals between them. As you become more proficient, you can start to identify the half steps and whole steps more quickly and accurately. Ear training exercises can be done both with a keyboard or instrument and by listening to recorded examples.
By consistently practicing these common exercises, musicians can improve their ability to identify, play, and understand half steps and whole steps. As these concepts are fundamental to music theory and composition, mastering them will provide a strong foundation for any musician.
Tips for mastering half steps and whole steps
Understanding and mastering half steps and whole steps is essential for any musician, whether you play an instrument or sing. These fundamental concepts of music theory help create melodies, harmonies, and chords, and provide the foundation for understanding scales and keys. Here are some tips to help you become confident with half steps and whole steps:
1. Memorize the pattern
The first step in mastering half steps and whole steps is to memorize the pattern. A half step is the smallest interval in Western music, and it is the distance between adjacent keys on a piano keyboard. In a whole step, there is one key in between. By memorizing this pattern and visualizing it on an instrument, you can start to grasp how they sound and feel.
2. Practice with scales
One of the best ways to get comfortable with half steps and whole steps is to practice scales. Scales are a sequence of notes that follow a specific pattern of intervals. By playing scales in different keys, you can train your ear to recognize the half steps and whole steps within them. Start with major scales, as they are the most commonly used, and then move on to other scales such as harmonic minor or melodic minor.
3. Use mnemonics
Another useful technique for remembering the pattern of half steps and whole steps is to use mnemonics. Mnemonics are memory aids that use words or phrases to help recall information. For example, you can use phrases like “W-W-H-W-W-W-H” to remember the pattern of whole steps and half steps in a major scale. Creating your own mnemonics can personalize the learning process and make it easier to remember.
4. Analyze musical pieces

Analyzing musical pieces can provide practical examples of how half steps and whole steps are used in actual music. Take a song you are familiar with and try to identify the intervals between each note. Pay attention to when half steps are used to create tension or resolve, and when whole steps are used to create a sense of stability. By analyzing different pieces, you can start to recognize patterns and understand how these intervals contribute to the overall musical structure.
5. Experiment with chord progressions

Chord progressions are sequences of chords that create the harmonic foundation for a piece of music. By experimenting with different chord progressions and paying attention to the intervals between chords, you can deepen your understanding of how half steps and whole steps contribute to the overall harmony. This hands-on approach allows you to apply the concepts you’ve learned and develop a more intuitive understanding of these intervals.
Mastering half steps and whole steps requires practice and patience. By following these tips and dedicating time to study and practice, you can develop a strong foundation in music theory and improve your overall musicianship.