
Measuring liquid volume is an important skill that is often taught in science classes. Whether you are a student learning about the properties of liquids or a teacher looking for answers to a worksheet, understanding how to accurately measure liquid volume is crucial.
In this article, we will provide answers to a liquid volume worksheet, walking you through the steps needed to find the correct measurements. Each question will be addressed, explaining the concept behind it and guiding you on the proper method of measurement.
By going through these answers, you will improve your understanding of liquid volume and become adept at measuring it accurately. Remember, practice and repetition are key to mastering any new skill.
How to Measure Liquid Volume: A Complete Guide
In many scientific experiments and everyday cooking, it is essential to accurately measure liquid volume. Whether you are measuring water for a recipe or conducting a chemistry experiment, precise measurements can make a significant difference in the outcome. This guide will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to measure liquid volume correctly.
1. Choose the appropriate measuring tool: Depending on the volume of liquid you need to measure, you may utilize different tools. For smaller amounts, a measuring spoon or cup will suffice, while larger volumes may require a measuring jug or beaker. Ensure that the measuring tool you choose has clear and accurate measurement markings.
2. Set up a level surface: For accurate measurement, it is essential to place your measuring tool on a level surface. This will prevent any tilting or spilling that could affect the measurements.
3. Pour the liquid into the measuring tool: Slowly pour the liquid into the measuring tool, taking care not to spill or splash. If you are using a measuring cup or spoon, make sure the liquid reaches the appropriate level indicated on the tool. For measuring jugs or beakers, ensure that the liquid reaches the desired volume without overflowing.
4. Check the measurement: Once the liquid is in the measuring tool, carefully read the measurement markings. For liquid volumes, it is crucial to read at eye level to ensure accuracy. If the volume is not a round number, you may need to estimate the additional amount based on the markings.
5. Use conversions if necessary: In some cases, you may need to convert liquid volumes from one measurement unit to another. Use conversion charts or online resources to accurately convert the volume if needed.
By following these steps, you can confidently measure liquid volumes for any experiment or recipe. Remember to be patient, take your time, and double-check your measurements to ensure accuracy.
Understanding the Importance of Accurate Liquid Volume Measurements
Accurate liquid volume measurements are crucial in numerous fields, including science, cooking, medicine, and manufacturing. Whether it’s ensuring the correct dosage of medication, formulating a recipe, or achieving consistent product quality, precise measurements are essential for success. Understanding the importance of accurate liquid volume measurements can help minimize errors, increase efficiency, and maintain quality standards.
Science: In scientific experiments, the precise measurement of liquid volumes is necessary for producing accurate results. Whether it’s measuring solutions for chemical reactions or determining the volume of a gas, accurate liquid volume measurements are crucial for obtaining reliable data. Mistakes in measurement can lead to incorrect interpretations and flawed conclusions.
Cooking: In the culinary world, accurate measurements of liquid volumes can make or break a recipe. Adding too much or too little liquid can significantly impact the taste, texture, and overall quality of a dish. From measuring water for boiling pasta to incorporating the right amount of liquid in a sauce, accurate volume measurements ensure consistent and delicious results.
Medicine: In the medical field, accurate liquid volume measurements are essential for administering the correct dosage of medications. Measuring liquid medicines with precision is crucial to ensure patient safety and efficacy. Incorrect measurements can result in under or overdosing, leading to potentially harmful consequences.
Manufacturing: In manufacturing industries, precise liquid volume measurements are essential to maintain product quality and consistency. Whether it’s measuring ingredients for food and beverage production, chemicals in industrial processes, or liquids in pharmaceutical manufacturing, accurate measurements ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications and standards.
In conclusion, accurate liquid volume measurements are vital in various fields. They are necessary for producing reliable scientific results, creating delicious culinary creations, ensuring proper medication administration, and maintaining product quality in manufacturing. The understanding of the importance of accurate liquid volume measurements allows individuals to perform their tasks more effectively, reduce errors, and achieve desired outcomes.
In order to accurately measure the volume of a liquid, it is important to use the appropriate units of measurement. These units allow scientists, engineers, and everyday individuals to communicate precisely about the amount of liquid being measured. There are several common units of liquid volume measurement that are used around the world.
One of the most commonly used units of liquid volume measurement is the liter (L). This unit is often used in the International System of Units (SI) and is equal to one cubic decimeter (dm³). It is a convenient unit for everyday use and is often used to measure quantities of liquids such as water, milk, and soda.
Gallons, quarts, pints, and cups

In the United States, the gallon (gal) is a commonly used unit of liquid volume measurement. One gallon is equal to 3.785 liters. The gallon is further divided into four quarts (qt), each quart being equal to 0.946 liters. Each quart is then divided into two pints (pt), and each pint is further divided into two cups (cup). This system of measurement is often used in recipes and for measuring liquids such as milk, oil, and gasoline.
Ounces and milliliters
In addition to liters and gallons, smaller units of liquid volume measurement are often used. The ounce (oz) is a unit commonly used in the United States and is equal to 29.574 milliliters. The milliliter (ml) is a standard unit used in the International System of Units and is equal to one cubic centimeter (cm³). Milliliters are often used to measure smaller quantities of liquid, such as medicine or perfume.
How to Read Liquid Volume Measurements

When working with liquids, it is important to be able to accurately measure their volume. Liquid volume is commonly measured in units such as ounces, milliliters, and liters. Understanding how to read liquid volume measurements is essential in various fields, including cooking, chemical experiments, and medical dosing.
Step 1: Choose the appropriate measuring tool. Depending on the amount of liquid you need to measure, you may use different tools. For small amounts, a graduated cylinder or a measuring spoon can be used. For larger volumes, a measuring cup or a beaker is more suitable. Ensure that the measuring tool is clean and dry before use.
Step 2: Fill the measuring tool with the liquid. Carefully pour the liquid into the measuring tool, being mindful not to spill or splash. Slowly add the liquid until it reaches the desired volume. It is important to keep the measuring tool on a flat surface to ensure accurate readings.
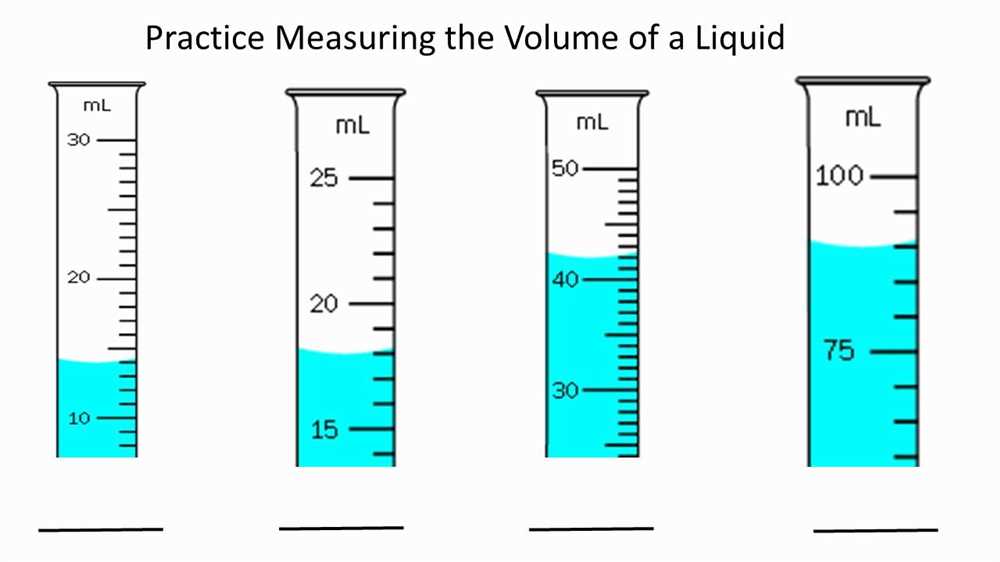
Step 3: Read the measurement. Look at the scale or markings on the measuring tool to determine the volume of the liquid. In a graduated cylinder, for example, each marked line represents a specific volume. Read the measurement at eye level, ensuring that the meniscus (the curved surface of the liquid) is at the correct level. Make note of the measurement in the appropriate unit of measurement.
Step 4: Consider the uncertainty. Depending on the measuring tool used, there may be some uncertainty in the measurement. This uncertainty can be due to the width of the measuring markings, the accuracy of the tool, or other factors. Take this uncertainty into account when using the liquid measurement in any calculations or applications.
By following these steps and practicing with various liquid measuring tools, you can become proficient in reading liquid volume measurements and ensure accurate results in your experiments, cooking, or any other tasks that involve liquids.
Practical Tips for Measuring Liquid Volume

Measuring liquid volume accurately is an essential skill in various fields, such as cooking, science experiments, and medical applications. Using the correct techniques and tools can ensure precise measurements and reliable results. Here are some practical tips to help you measure liquid volume effectively:
1. Use a graduated cylinder:
A graduated cylinder is a cylindrical glass or plastic container with calibrated markings for measuring liquid volume. It is the most accurate tool for measuring liquids. Make sure to use the appropriate size graduated cylinder that can accommodate the volume of liquid you need to measure. Place the cylinder on a flat surface, align your eyes with the level of the liquid, and read the measurement at the bottom of the meniscus, the curved surface of the liquid.
2. Be mindful of units:
Pay close attention to the units used in the graduated cylinder or any other measuring tool you are using. Most common units for liquid volume measurement include milliliters (mL) and liters (L). Ensure that you are using the correct unit and convert if necessary to match the requirements of your experiment or recipe.
3. Use a digital scale:
If you need to measure the volume of a liquid that is not suitable for a graduated cylinder, you can use a digital scale. Place a container on the scale, tare it (zero it out), and carefully pour the liquid until you reach the desired volume. This method is particularly useful for measuring viscous liquids or substances with irregular shapes.
4. Avoid estimating:
Estimating liquid volume by eye can lead to significant errors. Always use appropriate measuring tools instead of relying on visual estimations. Even slight variations in volume can affect the accuracy and outcome of your experiments or recipes.
5. Practice good technique:
When pouring liquids, hold the measuring tool at eye level to ensure accurate readings. Allow the liquid to settle before taking measurements, and avoid shaking or tilting the container during the process. Take your time and be patient to obtain precise results.
By following these practical tips, you can improve your liquid volume measurement skills and ensure reliable and accurate results. Remember, precision is crucial when it comes to scientific experiments and culinary pursuits that rely on precise measurements.
Measuring Liquid Volume Using Different Tools
Measuring the volume of liquid accurately is important in various fields, including science, cooking, and medicine. Different tools are available to measure liquid volume, each designed for specific purposes and levels of precision.
Graduated cylinders are commonly used tools for measuring liquid volume in science experiments. These cylindrical containers have markings along the sides, which allow for precise measurements. To use a graduated cylinder, simply pour the liquid into it and read the volume at the bottom of the meniscus, which is the curved surface of the liquid. Graduated cylinders are available in various sizes, allowing for measurements of different volumes.
Beakers are another commonly used tool for measuring liquid volume. Unlike graduated cylinders, they have a wide-mouthed design and do not have precise markings for volume measurements. Instead, beakers often have approximate markings to give a rough estimate of the volume. They are ideal for measuring larger volumes of liquid, such as during cooking or mixing ingredients for a recipe. Beakers are available in various sizes, making them versatile tools for measuring liquid volume.
Pipettes or droppers are used for more precise measurements of small liquid volumes. They have a narrow and elongated design, with markings on the side to indicate volume. To use a pipette, squeeze the rubber bulb at the top to create suction, then immerse the pipette tip into the liquid. Release the bulb slowly to draw the liquid into the pipette, and then transfer the liquid to a container or another vessel. Pipettes are commonly used in laboratories and medical settings for accurate measurement of liquids.
Overall, the choice of tool for measuring liquid volume depends on the specific application and the level of precision required. Whether it’s a graduated cylinder for precise measurements, a beaker for rough estimates, or a pipette for small volumes, using the right tool ensures accurate and consistent results in various scientific, culinary, and medical endeavors.
Common Errors and Troubleshooting in Liquid Volume Measurements
Accurate measurement of liquid volume is crucial in many scientific and practical applications. However, errors can occur during the process that can lead to inaccurate results. Understanding and troubleshooting these common errors can help improve the accuracy of liquid volume measurements.
Inadequate calibration of measuring tools
One common error is the inadequate calibration of measuring tools. It is essential to ensure that the measuring tools, such as graduated cylinders or beakers, are properly calibrated before use. This involves confirming the accuracy of the measurement scale and adjusting it if necessary. Failure to calibrate the instruments can result in significant errors in liquid volume measurements.
Misreading the meniscus
Another common error is misreading the meniscus. When measuring liquid volume in a cylindrical container, such as a graduated cylinder, it is important to read the bottom of the meniscus at eye level. The meniscus is the curved surface of the liquid, and misreading it can lead to an incorrect volume measurement. It is crucial to ensure accurate readings by aligning the bottom of the meniscus with the appropriate measurement mark.
Using the wrong measuring instrument
Using the wrong measuring instrument can also lead to errors in liquid volume measurements. Different liquids require different measuring instruments depending on their viscosity and volume. For example, a graduated cylinder may be suitable for measuring small volumes, while a volumetric flask is more appropriate for precise measurements of specific volumes. Using the wrong instrument can result in inaccurate measurements due to the limitations and inaccuracies of the tool.
Temperature effects
Temperature effects can also introduce errors in liquid volume measurements. As temperature increases, the volume of a liquid may expand, leading to an overestimation of the actual volume. Conversely, as temperature decreases, the volume may contract, resulting in an underestimation of the actual volume. To mitigate this error, it is important to measure the liquid volume at a consistent temperature or apply appropriate temperature correction factors.
Precision of measurements
Precision in liquid volume measurements depends on the resolution and accuracy of the measuring instrument. Instruments with higher resolution and accuracy allow for more precise measurements. Using instruments with lower precision can introduce errors in the measurements and affect the overall accuracy of the results. It is important to select measuring tools with the appropriate precision for the desired level of accuracy.
Inadequate technique
Inadequate technique during the measurement process can also contribute to errors. This can include not properly aligning the eye with the meniscus, not ensuring that the measuring tool is vertically aligned, or not allowing sufficient time for the liquid to settle before taking a reading. Practicing proper technique and being mindful of these potential errors can help improve accuracy in liquid volume measurements.
By addressing and troubleshooting these common errors in liquid volume measurements, one can enhance the accuracy and reliability of their results. Accurate liquid volume measurements are essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and engineering, where precise measurements are crucial for research, experiments, and quality control.