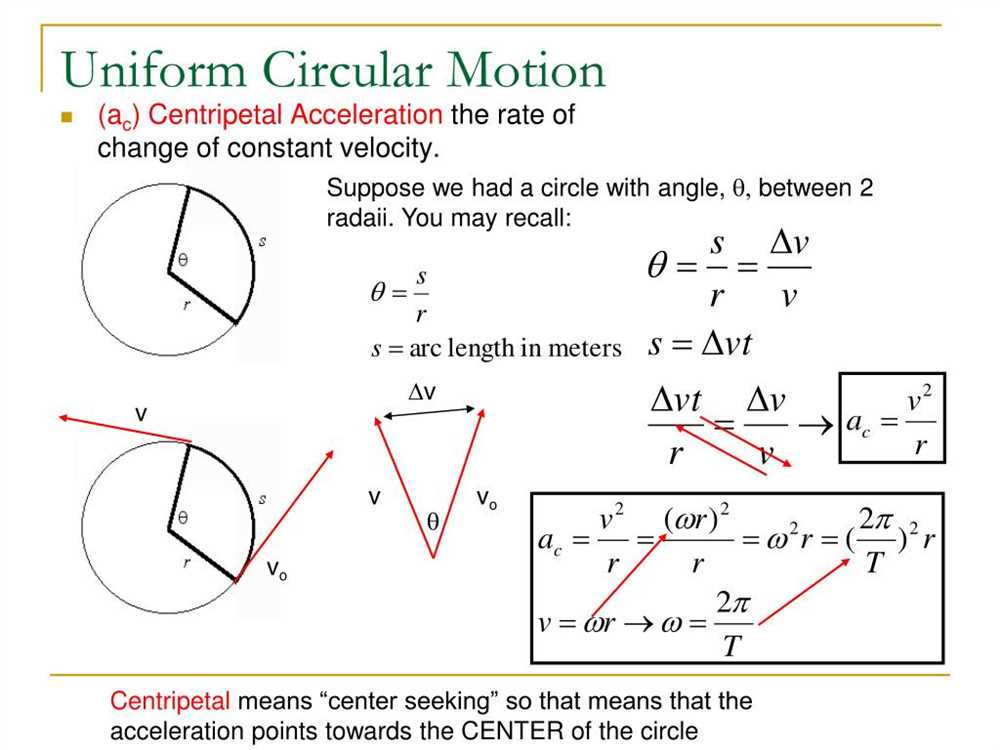
In the study of physics, one of the fundamental concepts is uniform circular motion. This type of motion occurs when an object travels along a circular path at a constant speed. To better understand this concept and its key principles, the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo has been developed as an interactive tool for students.
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo provides students with a hands-on experience to explore the effects of changing various parameters on a circular motion. By adjusting factors such as the mass of the object, the radius of the circle, and the speed of the object, students can observe how these changes impact the motion of the object.
The answer key for the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo serves as a guide for students to check their understanding and verify their results. It provides detailed explanations and calculations for each scenario, allowing students to compare their answers and ensure they have grasped the underlying principles of uniform circular motion.
Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo Answer Key

Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object moves in a perfect circle at a constant speed. The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows students to explore the concepts and equations related to this type of motion. With the answer key for the Gizmo, students can check their understanding and ensure they have correctly completed the activities and questions.
The answer key for the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo provides the correct answers and explanations for each question and activity in the simulation. This allows students to compare their own answers and learn from any mistakes they may have made. It can also serve as a valuable resource for teachers, providing them with a tool to assess their students’ understanding of the material and identify areas for further instruction or review.
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo covers a range of topics related to this type of motion, including the relationship between the radius and speed of an object in circular motion, the centripetal force required to keep an object in circular motion, and the period and frequency of the motion. The answer key provides detailed explanations for each concept, helping students to grasp the underlying principles and apply them to new situations.
Overall, the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo answer key is an essential resource for both students and teachers. It offers a comprehensive guide to completing the Gizmo activities and ensures that students understand the key concepts and equations related to uniform circular motion. By using the answer key, students can enhance their learning and improve their problem-solving skills in this important area of physics.
Understanding the Concept of Uniform Circular Motion
In physics, uniform circular motion refers to the motion of an object traveling in a circular path with a constant speed. This type of motion is characterized by the object moving at a constant speed around a fixed center, causing it to continuously change direction. Understanding uniform circular motion is essential in various fields of science, such as astronomy, mechanics, and engineering.
In uniform circular motion, the object experiences a centripetal force directed towards the center of the circle. This force keeps the object moving in the circular path and prevents it from moving away in a straight line. The magnitude of the centripetal force depends on the mass of the object, the speed at which it is moving, and the radius of the circular path. This force can be calculated using the formula: Fc = (m * v^2) / r, where Fc is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object, v is the velocity, and r is the radius of the circular path.
One important concept in uniform circular motion is the period, which refers to the time it takes for an object to complete one full revolution around the circular path. The period is denoted by the symbol T and is inversely proportional to the frequency, denoted by f. The period can be calculated using the formula: T = 1 / f. Another related concept is the angular velocity, denoted by ω, which represents the rate of change of the angle as the object moves along the circular path.
Understanding the concept of uniform circular motion is crucial in various practical applications. For example, it is used in designing amusement park rides, such as roller coasters and Ferris wheels, where the ride needs to ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience for the passengers. It is also important in understanding the motion of celestial bodies, such as planets and satellites, as they orbit around their respective centers. Engineers and physicists rely on the principles of uniform circular motion to design and analyze the motion of various objects and systems.
Exploring the Components of Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo is a virtual tool that allows students to explore and understand the components of circular motion. This Gizmo provides a hands-on experience in learning the principles of circular motion, such as centripetal force, tangential velocity, and radius. By manipulating these variables, students can observe the effects on the motion of an object moving in a circular path.
One of the key components of the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo is the centripetal force. Students can adjust the magnitude and direction of the centripetal force to see its impact on the circular motion. By increasing or decreasing the centripetal force, students can observe how it affects the speed and radius of the object’s path. This allows them to understand the relationship between centripetal force, speed, and radius in circular motion.
In addition to centripetal force, the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo also allows students to explore the concept of tangential velocity. Tangential velocity refers to the speed of an object moving along the tangent line of its circular path. By adjusting the tangential velocity, students can observe how it affects the object’s motion. They can also see how the tangential velocity changes with the change in radius or centripetal force. This helps students understand the relationship between tangential velocity, radius, and centripetal force in circular motion.
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo provides a valuable tool for students to visualize and manipulate the components of circular motion. By experimenting with the centripetal force and tangential velocity, students can develop a deep understanding of how these variables affect the motion of an object in a circular path. This interactive learning experience enhances their understanding of fundamental principles and prepares them for further studies in physics.
Applying Newton’s Laws to Uniform Circular Motion
In uniform circular motion, an object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. This motion requires a centripetal force to keep the object moving in its circular path. To understand the physics behind uniform circular motion, we can apply Newton’s laws.
Newton’s first law states that an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant speed unless acted upon by an external force. In the case of uniform circular motion, the object is constantly changing direction, so there must be a force acting on it. This force is called the centripetal force and is directed toward the center of the circle.
According to Newton’s second law, the net force on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration. In uniform circular motion, the acceleration is directed toward the center of the circle. Therefore, we can use this equation to calculate the centripetal force: F = m * a, where F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object, and a is its acceleration.
Newton’s third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In the case of uniform circular motion, the centripetal force is provided by an external force, such as tension in a string or the force of gravity. This external force is balanced by the equal and opposite reaction force exerted by the object on its surroundings.
In conclusion, by applying Newton’s laws to uniform circular motion, we can understand the concept of centripetal force and how it keeps an object moving in a circular path. The centripetal force is provided by an external force and is necessary to overcome the object’s tendency to move in a straight line. Through the use of Newton’s laws, we can calculate the centripetal force and analyze the dynamics of objects in uniform circular motion.
Analyzing the Key Features of Uniform Circular Motion
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion where an object moves along a circular path at a constant speed. It is characterized by several key features that help us understand and analyze this type of motion.
1. Constant speed:
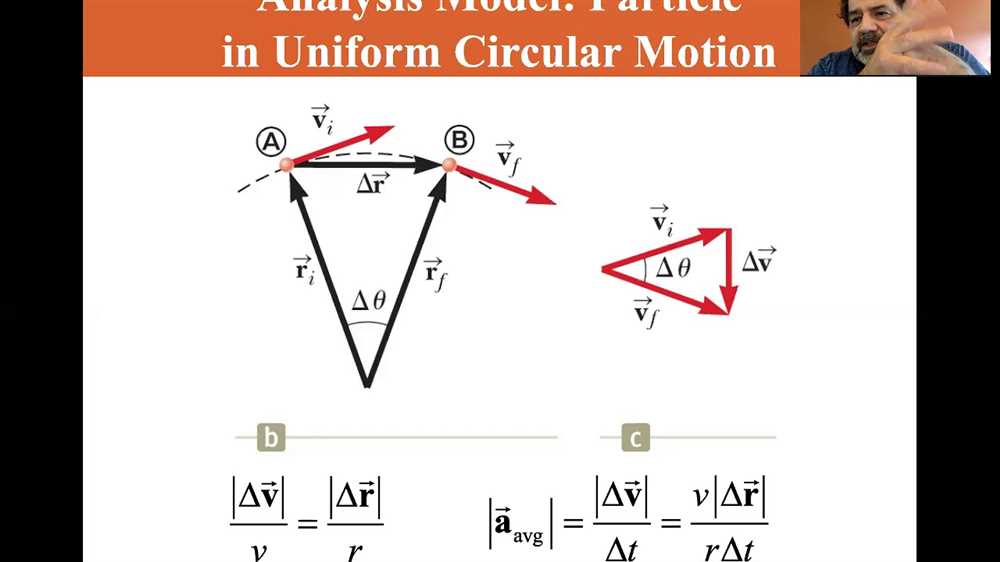
One key feature of uniform circular motion is that the object moves at a constant speed throughout the motion. This means that the magnitude of the object’s velocity remains constant. However, the direction of the velocity vector changes continuously as the object moves around the circular path.
2. Centripetal acceleration:
In uniform circular motion, there is always an inward acceleration towards the center of the circle, called the centripetal acceleration. This acceleration is responsible for keeping the object on its circular path. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration is directly proportional to the square of the object’s speed and inversely proportional to the radius of the circular path.
3. Centripetal force:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, there must be a net force acting on an object to produce acceleration. In uniform circular motion, the net force acting on the object is the centripetal force, which is always directed towards the center of the circle. The magnitude of the centripetal force is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the centripetal acceleration.
4. Period and frequency:
Uniform circular motion can be described in terms of its period and frequency. The period is the time it takes for the object to complete one full revolution around the circular path, while the frequency is the number of revolutions per unit of time. These two quantities are inversely proportional to each other, meaning that a shorter period corresponds to a higher frequency, and vice versa.
5. Tangential velocity:
In addition to the centripetal acceleration, an object in uniform circular motion also has a tangential velocity. This is the velocity component that is tangent to the circular path at any given point. The magnitude of the tangential velocity remains constant throughout the motion, as long as the object maintains a constant speed.
By analyzing these key features of uniform circular motion, we can gain a deeper understanding of how objects move along circular paths and the forces that govern their motion. These principles are essential in various fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy, where circular motion plays a significant role.
Solving Problems using the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo is an interactive tool that allows students to explore and understand the concepts of uniform circular motion. It provides a virtual laboratory environment where students can simulate different scenarios and solve problems related to circular motion. By using this Gizmo, students can gain a deeper understanding of the principles governing circular motion and improve their problem-solving skills.
When solving problems using the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo, it is important to follow a systematic approach. The first step is to carefully read and analyze the given problem statement. Identify the known quantities and the unknown quantity that needs to be determined. In the context of circular motion, these quantities typically include the radius of the circle, the velocity of the object, and the period or frequency of the motion.
Next, use the Gizmo to set up the virtual experiment. Adjust the values of the known quantities and observe how they affect the motion of the object. The Gizmo provides real-time feedback and visualizations, allowing students to see the effects of changing variables. By manipulating the radius, velocity, or period in the Gizmo, students can gain an intuitive understanding of how these factors influence the motion of the object.
Once the virtual experiment is set up, students can use the Gizmo to collect data. Measure the quantities that are relevant to the problem, such as the time taken for the object to complete one revolution or the angle through which it rotates. Use this data to calculate the unknown quantity using the relevant formulas and equations. The Gizmo provides guidance and hints to help students apply the correct formulas and solve the problem efficiently.
In conclusion, the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo is a powerful tool for solving problems related to circular motion. By systematically analyzing the problem, setting up virtual experiments, and collecting data, students can develop a deep understanding of circular motion principles and sharpen their problem-solving skills. The interactive nature of the Gizmo enhances the learning experience and allows students to explore different scenarios and gain hands-on experience in a virtual laboratory environment.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting Tips with the Gizmo
In using the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo, there are several common mistakes that students often make. One of the most common mistakes is not setting the radius correctly. The radius is a crucial parameter in circular motion, as it determines the size of the circle. It is important to double-check the value entered for the radius and ensure it is accurate.
Another mistake that students frequently make is not properly adjusting the speed. The speed of an object in uniform circular motion is directly related to the radius. If the speed is too high or too low, it can lead to inaccurate results. It is important to carefully adjust the speed to match the given radius and ensure that it is set correctly.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Double-check the radius: Before starting the Gizmo, make sure to verify the entered value for the radius. This will help ensure that the size of the circle is accurate.
- Adjust the speed: If the results obtained from the Gizmo do not match the expected values, try adjusting the speed. Increase or decrease the speed gradually until the desired results are achieved.
- Reset the Gizmo: If all else fails, try resetting the Gizmo to its default settings. This can help eliminate any errors or incorrect inputs that may be causing issues.
- Ask for assistance: If you are still experiencing difficulties with the Gizmo, don’t hesitate to seek help from your teacher or classmates. They may be able to provide insight or guidance on how to troubleshoot the issue.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following the troubleshooting tips, you can ensure a more accurate and successful experience with the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo. Remember to always double-check your inputs and make adjustments as necessary to achieve the desired results.