
In today’s rapidly advancing field of biology, stem cells have become a topic of great interest and debate. Stem cells have the unique ability to develop into many different cell types in the body, making them a valuable tool for medical research and potential treatment of various diseases. This webquest aims to provide answers to some key questions about stem cells and their potential.
One of the first questions addressed in this webquest is the definition of stem cells. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the potential to differentiate into specialized cell types. They are found in both embryonic and adult tissues, and can be classified into two main types: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, while adult stem cells are found in various tissues throughout the body.
The webquest also explores the different applications of stem cells in medical research and treatment. One of the key uses of stem cells is in regenerative medicine, where they can be used to repair or replace damaged tissues. For example, stem cells can be differentiated into nerve cells to treat neurological disorders, or into heart muscle cells to repair damaged cardiac tissue. Additionally, stem cells can be used to study diseases in a laboratory setting, leading to a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and potential new treatments.
However, the use of stem cells is not without controversy. The webquest addresses ethical concerns surrounding the use of embryonic stem cells, as their extraction typically involves the destruction of a human embryo. This has led to debates over the source of stem cells and the moral implications of their use. As a result, alternative sources of stem cells, such as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), have been developed to avoid these ethical considerations.
Stem Cell Webquest Answer Key
In the Stem Cell Webquest, you were given a set of questions that required you to research and gather information about stem cells. Here is the answer key to help you check your responses and expand your understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What are stem cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the ability to differentiate into specialized cell types. They are characterized by their ability to self-renew and divide, producing more stem cells, and differentiate into different cell types depending on the signals they receive from their environment.
Question 2: Where can stem cells be found in the human body?
Stem cells can be found in various parts of the human body, including bone marrow, blood, umbilical cord blood, adipose tissue, and organs such as the brain and liver. These different sources of stem cells have different capacities for differentiation and are used in various medical and research applications.
Question 3: What are the different types of stem cells?
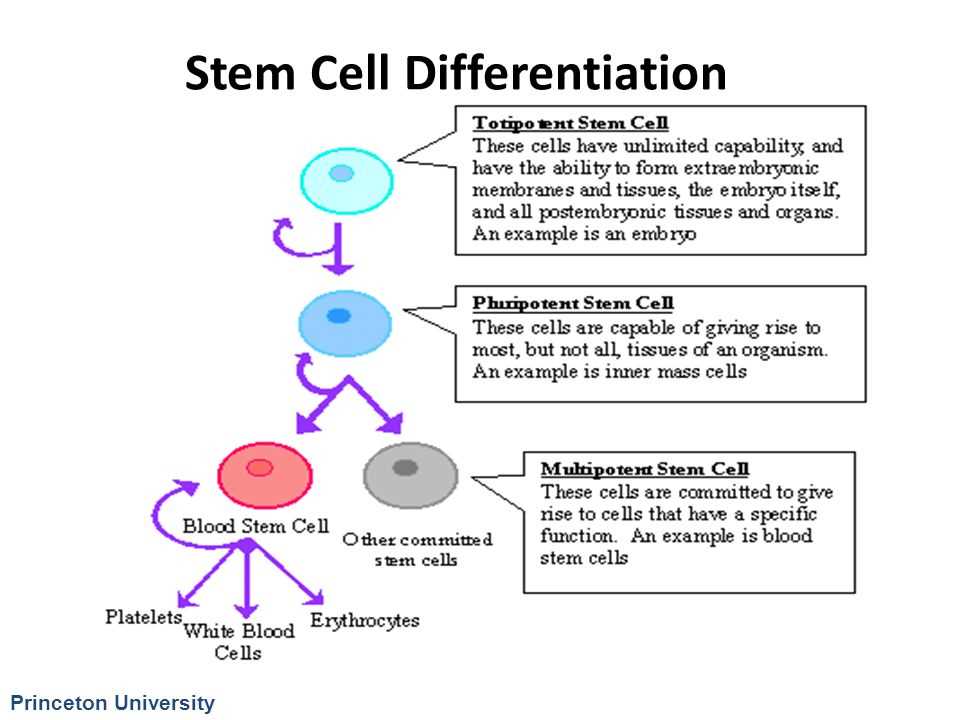
There are several types of stem cells, including embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and fetal stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of early embryos and have the potential to differentiate into any cell type. Adult stem cells are found in adult tissues and have limited differentiation capabilities. iPSCs are adult cells that are reprogrammed to have pluripotent properties similar to embryonic stem cells. Fetal stem cells are derived from the tissues of aborted fetuses.
Question 4: What are the potential uses of stem cells in medicine?
Stem cells have the potential to revolutionize medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types. They can be used to replace injured or damaged cells and tissues, regenerate new organs, and serve as a platform for drug discovery and testing. Stem cell therapy shows promise in treating a wide range of diseases and conditions, including heart disease, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, and cancer.
Question 5: What are the ethical considerations surrounding stem cell research?
Stem cell research has raised ethical concerns due to the use of embryonic stem cells, which involves the destruction of human embryos. This has led to debates about the rights and moral status of embryos. However, alternative sources of stem cells, such as adult stem cells and iPSCs, have alleviated some of these concerns. Nonetheless, the ethical implications of stem cell research continue to be a topic of discussion.
- Embryonic stem cells
- Adult stem cells
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
- Fetal stem cells
In conclusion, stem cells are undifferentiated cells with immense therapeutic potential. They can be found in various parts of the human body and can be classified into different types. Stem cell research holds great promise for advancements in medicine, but also poses ethical considerations that need to be addressed.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the unique potential to develop into different types of cells in the body. They are characterized by their ability to self-renew and differentiate into specialized cell types, such as muscle cells, nerve cells, and blood cells. Stem cells can be found in various tissues and organs throughout the body, including bone marrow, blood, and adipose tissue.
There are two main types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are derived from early-stage embryos and have the potential to give rise to any type of cell in the body. Adult stem cells, on the other hand, are found in mature tissues and have a more limited range of differentiation. They are responsible for replenishing and repairing damaged cells in the body.
- Embryonic stem cells: These stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, a structure that forms early in embryonic development. They have the potential to differentiate into any type of cell in the body.
- Adult stem cells: These stem cells are found in mature tissues and organs throughout the body. They can differentiate into a limited range of specialized cells.
Stem cells hold great promise for medical research and regenerative medicine. They can be used to study the development and progression of diseases, as well as to test new drugs and therapies. Additionally, stem cell therapies have the potential to treat a wide range of conditions and injuries, such as spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s disease, and diabetes. However, there are still many ethical and scientific considerations surrounding the use of stem cells, and further research is needed to fully understand their capabilities and limitations.
Types of Stem Cells
There are several types of stem cells that exist in the human body, each with their own unique characteristics and potential applications in medical research and treatment. These include:
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): These stem cells are derived from human embryos that are typically around 5 days old. ESCs have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the body, making them incredibly versatile for research purposes.
- Adult Stem Cells (ASCs): These stem cells are found in various tissues and organs throughout the body, such as bone marrow, blood, and adipose tissue. While ASCs have a more limited differentiation potential compared to ESCs, they still play crucial roles in tissue regeneration and repair.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): iPSCs are created by reprogramming adult cells, such as skin cells, to revert back into a pluripotent state. This means that they regain the ability to differentiate into any cell type. iPSCs offer great potential for personalized medicine and disease modeling.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): MSCs are a type of adult stem cell that can be found in various tissues, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue. These cells have the ability to differentiate into bone, cartilage, and fat cells, among others. They also possess immunomodulatory properties, making them promising candidates for cell-based therapies.
The study and utilization of these different types of stem cells have opened up new avenues of research and treatment in regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and disease modeling. By understanding the unique characteristics and potential of each stem cell type, scientists can develop targeted therapies to address a wide range of medical conditions.
Importance of Stem Cells in Medical Research
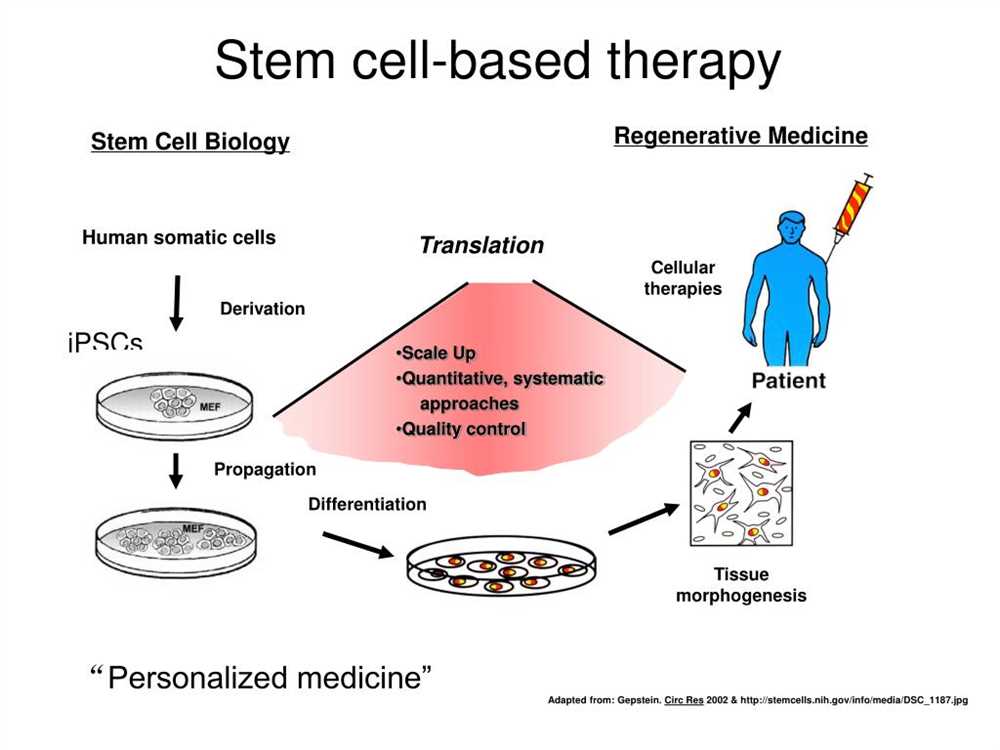
Stem cells play a crucial role in medical research due to their unique properties and potential for various therapeutic applications. These specialized cells have the remarkable ability to differentiate into different cell types and regenerate damaged tissues in the body. This makes them an invaluable resource for understanding disease mechanisms, developing new treatments, and improving patient outcomes.
One of the primary reasons why stem cells are important in medical research is their ability to replace damaged or diseased tissues. For example, for patients with heart disease, stem cells derived from their own body may be used to regenerate damaged heart tissue and improve cardiac function. By understanding the mechanisms through which stem cells differentiate and repair damaged tissues, researchers can develop more effective therapies for a wide range of conditions, including neurological disorders, diabetes, and spinal cord injuries.
Another crucial aspect of stem cell research is their potential to provide personalized medicine. Each individual’s stem cells have a unique genetic makeup, which means that therapies developed using a patient’s own cells are less likely to be rejected by their immune system. This opens up new possibilities for targeted treatments and reduces the risk of complications associated with conventional transplantation methods.
Furthermore, stem cells provide valuable insights into the development of diseases and allow scientists to study disease progression in a controlled environment. By creating disease models using stem cells, researchers can observe how diseases develop at a cellular level and identify potential drug targets. This knowledge is instrumental in developing new drugs and treatment strategies to combat various diseases, such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s.
In conclusion, stem cells have revolutionized medical research and hold great promise for future advancements in healthcare. Their versatility, regenerative capabilities, and ability to model diseases make them an invaluable tool for understanding disease mechanisms, developing personalized treatments, and advancing medical knowledge. With continued research and innovation, stem cells are likely to play an increasingly important role in improving patient outcomes and revolutionizing medical treatment.
Potential Treatments Using Stem Cells
Stem cell research has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine by providing new treatments and therapies for a wide range of diseases and conditions. Stem cells, which have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, hold great promise in regenerative medicine.
One potential treatment using stem cells is for Parkinson’s disease. Scientists are investigating the use of stem cells to replace the dopamine-producing neurons that are lost in Parkinson’s patients. By transplanting dopamine-producing stem cells into the brain, it may be possible to restore normal dopamine levels and alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Spinal cord injury:
- Another potential treatment is for spinal cord injuries. Stem cells could be used to repair damaged nerve tissue and restore function. Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells to stimulate the growth of new nerve cells and support the regeneration of damaged cells in the spinal cord.
Heart disease:
- Stem cells may also hold the key to treating heart disease. By injecting stem cells into the damaged heart tissue, researchers hope to promote the regeneration of healthy heart muscle cells and improve overall heart function. This approach could potentially be used to repair damage caused by heart attacks and prevent the development of chronic heart conditions.
Diabetes:
- Stem cell therapy may offer a cure for diabetes by replacing the damaged or malfunctioning pancreatic cells responsible for producing insulin. By transplanting insulin-producing stem cells, researchers aim to restore normal glucose regulation in diabetic patients and eliminate the need for insulin injections.
In summary, stem cells have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of various diseases and conditions. From Parkinson’s disease to spinal cord injuries, heart disease to diabetes, stem cell therapy offers new hope for patients by promoting tissue regeneration and restoring normal function. Continued research and development in this field hold the promise of bringing about major advancements in medicine and improving the lives of countless individuals.
Ethical considerations surrounding stem cells
Stem cell research has sparked numerous ethical debates due to the potential sources of stem cells and their implications. One of the main ethical concerns is the destruction of embryos to obtain embryonic stem cells. Some argue that human embryos, even at the earliest stages of development, have the potential for personhood and should be granted the same rights and protection as fully developed individuals. They believe that using embryos for research purposes is morally wrong and unethical.
Another ethical consideration is the creation of chimeras and the potential for misuse in genetic modification. Stem cell research has the potential to create organisms that contain cells from different species, known as chimeras. This raises questions about the ethical boundaries of manipulating genetic material and the potential consequences of creating organisms that blur the lines between species.
Furthermore, the issue of informed consent and the potential for exploitation of vulnerable populations are also important ethical considerations. Stem cell research often involves the use of human subjects, and it is crucial to ensure that individuals fully understand the nature of the research and the potential risks involved. Vulnerable populations, such as those with disabilities or limited access to healthcare, may be more susceptible to coercion or exploitation.
Overall, the ethical considerations surrounding stem cells revolve around the balancing of potential benefits and harms, the protection of human rights and dignity, and the responsible use of scientific advancements. It is crucial to carefully weigh the ethical implications of stem cell research to ensure that it is conducted in a manner that upholds moral principles and respects the well-being of all individuals involved.