
The AP Statistics Chapter 8 Test is a crucial assessment that evaluates students’ understanding of statistical inference and hypothesis testing. In this chapter, students learn about different types of tests, such as z-tests and t-tests, and how to use them to analyze data and make inferences about a population. Through this test, students demonstrate their ability to apply statistical concepts and formulas to real-world scenarios.
One of the main objectives of Chapter 8 is to teach students how to formulate null and alternative hypotheses based on given research questions or problems. The test assesses their ability to correctly identify these hypotheses and explain their significance in statistical inference. Additionally, students are expected to be able to choose and perform an appropriate statistical test, interpret the test statistics, and draw valid conclusions based on the results.
Another important aspect of this test is students’ understanding of the conditions and assumptions required for different types of tests. They are expected to recognize when the conditions for a test are met and when they are violated, and adjust their analysis accordingly. Students should also demonstrate their knowledge of p-values and confidently interpret them in the context of a hypothesis test.
Overall, the AP Statistics Chapter 8 Test assesses students’ proficiency in statistical inference and hypothesis testing. It evaluates their ability to critically analyze data, conduct hypothesis tests, and make informed conclusions. By successfully completing this test, students demonstrate their readiness to apply statistical concepts to solve problems and make meaningful inferences in various fields of study.
What is AP Stats Chapter 8 Test?
AP Stats Chapter 8 test is a comprehensive examination that covers various concepts and topics related to statistics. It is designed to assess students’ understanding and application of statistical principles, methods, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions based on the data.
The test typically includes questions that require students to demonstrate their knowledge of key concepts such as confidence intervals, hypothesis testing, sampling distributions, and probability. Students are expected to apply these concepts to real-world scenarios and solve problems using statistical techniques.
Throughout Chapter 8, students learn about important statistical concepts and techniques, such as confidence intervals and hypothesis testing. These concepts form the basis of statistical analysis and decision-making. The test evaluates students’ ability to apply these concepts and interpret the results.
Additionally, the test may also include questions that assess students’ understanding of the different types of data, sampling methods, and experimental design. Students are expected to demonstrate their ability to collect, analyze, and interpret data accurately.
Overall, AP Stats Chapter 8 test is an important assessment that evaluates students’ mastery of statistical concepts and their ability to apply statistical techniques to real-world problems. It plays a crucial role in determining students’ understanding of statistics and their readiness for higher-level statistical analysis.
Overview of AP Stats test format
The AP Stats test is made up of two main sections: multiple-choice questions and free-response questions. The test is designed to assess students’ knowledge and understanding of statistical concepts and their ability to apply these concepts to real-world scenarios.
The multiple-choice section of the test consists of 40 questions, which account for 50% of the total score. These questions require students to analyze and interpret data, perform calculations, and make inferences based on statistical information. Some questions may also require students to read and interpret graphs, statistical charts, and data tables.
The free-response section of the test consists of six questions, which account for the remaining 50% of the total score. These questions are more complex and typically require students to demonstrate a deeper understanding of statistical concepts. Students may be asked to write a clear and concise explanation of a statistical concept, design and conduct an experiment, or analyze and interpret data from a real-world scenario.
To prepare for the AP Stats test, students should review key statistical concepts, practice solving problems and analyzing data sets, and familiarize themselves with the format and types of questions that may be asked on the test. It is also important for students to practice time management and make sure they allocate enough time to each section of the test.
How to prepare for AP Stats chapter 8 test?
To prepare for the AP Stats chapter 8 test, it is important to review the key concepts and statistical techniques covered in this chapter. Chapter 8 focuses on regression analysis, which involves analyzing the relationship between two quantitative variables. It is crucial to understand the concepts of correlation, scatterplots, least squares regression lines, and residual plots.
Here are some steps to effectively prepare for the AP Stats chapter 8 test:
- Review the chapter notes and textbook readings. Make sure you understand the definitions, formulas, and procedures related to regression analysis.
- Practice working with scatterplots and calculating correlation coefficients. Understand how to interpret the strength and direction of a linear relationship.
- Learn how to calculate and interpret the equation of a least squares regression line. Practice applying this line to make predictions and estimate values.
- Understand the concept of residuals and how to interpret residual plots. Practice identifying potential outliers and influential points.
- Complete practice problems and exercises related to regression analysis. Work through the example problems provided in the textbook or find additional practice resources online.
- Utilize online resources, such as instructional videos or interactive tutorials, to reinforce your understanding of regression analysis.
- Form or join a study group to discuss and review concepts with fellow classmates. Teaching others can also enhance your own understanding.
- Create flashcards or summary sheets to help memorize key formulas and concepts. Review these regularly leading up to the test.
By following these steps and consistently practicing regression analysis, you will be well-prepared for the AP Stats chapter 8 test. Remember to allocate enough time for studying, seek help if needed, and stay organized with your notes and practice materials. Good luck!
Reviewing Key Concepts and Formulas
As you prepare for your AP Stats Chapter 8 test, it’s important to review key concepts and formulas that you’ve learned throughout the chapter. This will help solidify your understanding and ensure that you’re well-prepared for any questions or problems that may arise on the test.
One key concept in Chapter 8 is the idea of sampling variability. This refers to the fact that different samples from the same population will yield slightly different results. Understanding this concept is crucial for interpreting data and making accurate statistical inferences. The formula for standard deviation for a sample mean is also an important formula to remember, as it allows us to quantify the spread of the sample means.
Formula: standard deviation for a sample mean = standard deviation of the population / square root of the sample size
Another important concept in this chapter is the Central Limit Theorem. This theorem states that the distribution of sample means will be approximately normal, regardless of the shape of the original population, as long as the sample size is large enough. Understanding this theorem is essential for conducting hypothesis tests and constructing confidence intervals.
One formula that is commonly used in hypothesis testing is the z-score formula. This formula allows us to determine the number of standard deviations a sample mean is away from the population mean. It is used to calculate the p-value, which is a measure of the strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis.
Formula: z-score = (sample mean – population mean) / (standard deviation / square root of the sample size)
- Sampling variability and the formula for standard deviation for a sample mean
- The Central Limit Theorem and its implications for sample means
- The z-score formula and its role in hypothesis testing and calculating p-values
By familiarizing yourself with these key concepts and formulas, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle the AP Stats Chapter 8 test with confidence. Remember to practice applying these concepts to real-world examples and sample problems to further reinforce your understanding.
Practicing with sample problems
One of the most effective strategies for preparing for the AP Statistics Chapter 8 test is to practice with sample problems. By working through a variety of problems, you can gain a better understanding of the concepts and techniques covered in the chapter, and improve your ability to apply them in different scenarios. The sample problems allow you to simulate the test environment and get a sense of the types of questions you may encounter on the actual exam.
When practicing with sample problems, it is important to focus on the key concepts and skills covered in Chapter 8. This includes understanding and interpreting scatterplots, calculating and interpreting correlation coefficients, identifying the type and strength of relationships between variables, and using regression models to make predictions and analyze data. By honing these skills, you will be well-prepared to demonstrate your understanding on the test.
Here are some sample problems to help you practice:
- Given a scatterplot with points forming a linear pattern, calculate the correlation coefficient and interpret its meaning in terms of the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables.
- Use a regression model to predict the value of a dependent variable based on the value of an independent variable. Interpret the meaning of the predicted value in the context of the problem.
- Given a scatterplot with points forming a nonlinear pattern, discuss why the correlation coefficient may not accurately represent the relationship between the variables.
- Identify a scenario where a high correlation coefficient does not necessarily imply a causal relationship between the variables.
- Calculate the coefficient of determination for a regression model and interpret its meaning in terms of the proportion of variation in the dependent variable that can be explained by the independent variable.
By practicing with these sample problems and similar ones, you can build your confidence and improve your ability to tackle the AP Statistics Chapter 8 test. Remember to review the key concepts and techniques, and seek additional help or resources if needed. Good luck with your preparation!
Common topics covered in AP Stats chapter 8 test
The AP Stats chapter 8 test covers various topics related to inference for proportions. Understanding these concepts and being able to apply them correctly is essential for students taking the AP Statistics exam. Here are some common topics that students can expect to see on the chapter 8 test:
1. Confidence intervals for proportions:

Students will likely be asked to calculate and interpret confidence intervals for proportions. This involves using formulas, understanding the relationship between sample size, sample proportion, and confidence level, and interpreting the meaning of the interval within a given context.
2. Hypothesis testing for proportions:
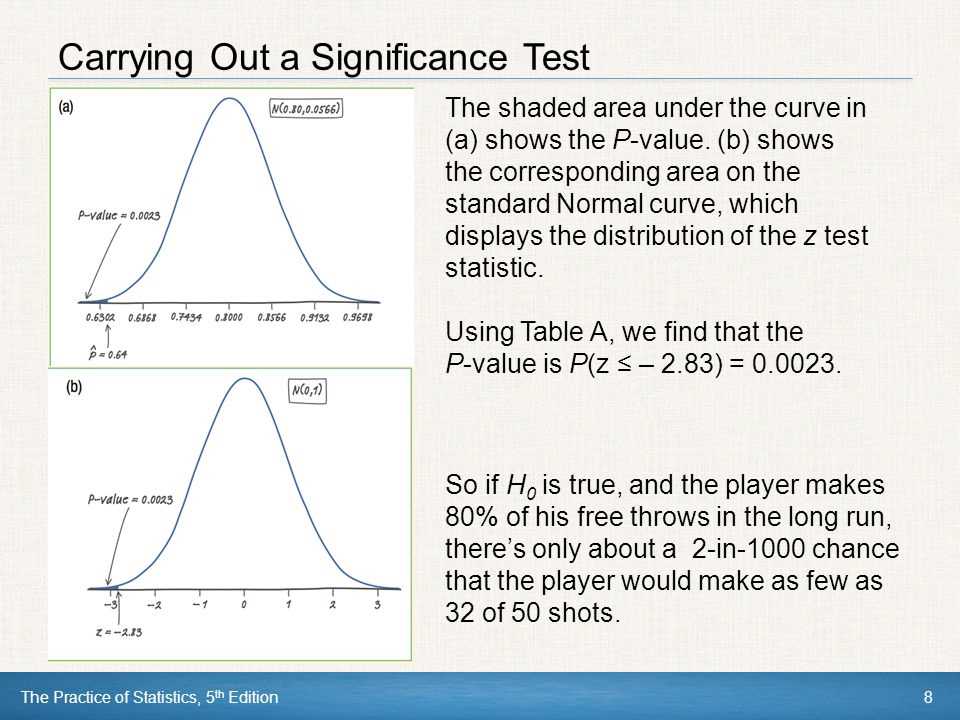
Another important topic covered in chapter 8 is hypothesis testing for proportions. Students will learn how to set up null and alternative hypotheses, calculate test statistics, determine p-values, and make appropriate conclusions based on the results. They may also be asked to interpret the practical significance of the findings.
3. Sampling distribution of sample proportions:
Understanding the sampling distribution of sample proportions is crucial for inference in this chapter. Students will learn about the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution, the central limit theorem, and the conditions required for using normal approximation. They may also explore the concept of margin of error and its impact on the precision of estimates.
4. Comparing proportions:
Students may encounter questions that involve comparing proportions between different groups or conditions. This could include conducting hypothesis tests for the difference in proportions, calculating confidence intervals for the difference, or analyzing contingency tables. Students should be familiar with the methods for testing and comparing proportions using appropriate statistical techniques.
These topics highlight some of the major concepts that are typically covered in the AP Stats chapter 8 test. It is important for students to review these topics thoroughly, practice solving related problems, and seek clarification on any areas of confusion before taking the test.
Sampling Distributions
A sampling distribution refers to the distribution of a statistic obtained from multiple random samples of the same population. This concept is crucial in statistics because it allows us to make inferences about the population based on a smaller sample.
When sampling from a population, there will always be some variability in the statistic we obtain from each sample. The sampling distribution shows us how this variability is distributed and allows us to estimate the population parameter.
Central Limit Theorem: One important concept in sampling distributions is the Central Limit Theorem. It states that for large enough sample sizes, the sampling distribution of the mean will be approximately normal, regardless of the shape of the population distribution. This is true even if the population distribution is not normally distributed.
For example, if we repeatedly take random samples of size n from a population and calculate the mean of each sample, the sampling distribution of those means will be approximately normal. This allows us to make confident inferences about the population mean based on the sample mean.
Sampling distributions are important in hypothesis testing and constructing confidence intervals. By understanding the properties of sampling distributions, we can make more accurate and reliable statistical inferences. Without sampling distributions, we would not be able to generalize our findings from a sample to the larger population.
Sampling distribution of the proportion: In addition to the sampling distribution of the mean, we can also consider the sampling distribution of proportions. This distribution describes the variability of the proportion in different samples.
| Type of Sampling Distribution | Statistic | Formula |
| Sampling distribution of the mean | Mean | x̂ = Σx / n |
| Sampling distribution of the proportion | Proportion | p̂ = x / n |
Overall, understanding sampling distributions is crucial in statistics as it allows us to confidently analyze and make inferences about a population based on a smaller sample.