
Software testing is a crucial step in the development process, ensuring that the final product meets the highest standards of performance and efficiency. One of the most effective methods for evaluating software performance is the X and V Factor test. This test examines various factors that can impact the software’s functionality and performance, providing developers with valuable insights into potential issues and areas for improvement.
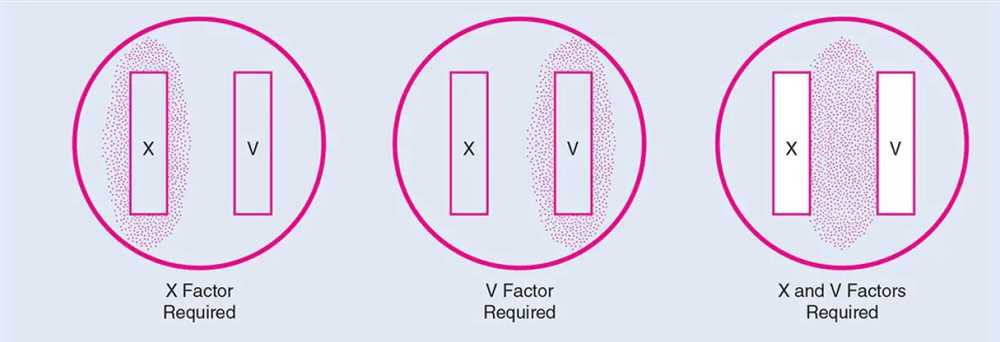
The X and V Factor test focuses on two key aspects: the X factor and the V factor. The X factor represents external factors that can influence the software’s performance, such as network conditions, hardware specifications, and user load. By simulating various scenarios and testing the software’s response, developers can identify potential bottlenecks and optimize the system accordingly.
The V factor, on the other hand, represents internal factors that can impact the software’s performance, such as code quality, algorithms, and database structures. By analyzing the software’s internal components and conducting performance tests, developers can pinpoint areas of improvement and enhance the overall efficiency of the system.
Overall, the X and V Factor test provides developers with a comprehensive evaluation of the software’s performance and efficiency. By considering both external and internal factors, this test offers a holistic perspective on the software’s capabilities and potential improvements. With the insights gained from the X and V Factor test, developers can optimize their software, ensuring that it delivers a seamless user experience and meets the demands of the modern digital landscape.
X Factor Test Procedure
The X factor test procedure is a systematic approach used in various industries to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of a particular product or process. It involves a series of tests and measurements that are designed to determine the presence and impact of the X factor, which can be any variable or factor of interest.
Before conducting the X factor test, it is essential to define the objectives and parameters of the test. This includes identifying the specific X factor being investigated and establishing the criteria for evaluation. Once the objectives are set, the next step is to design the test procedure, which includes selecting the appropriate testing methods, tools, and equipment.
- Data collection: The first step in the X factor test procedure is to collect relevant data. This can be done through various means, such as surveys, interviews, or observations. The data collected should be accurate, reliable, and representative of the population or process being evaluated.
- Experimental design: After collecting the data, an experimental design is developed to test the influence of the X factor. This includes determining the sample size, creating control groups, and selecting the appropriate statistical analysis methods.
- Test execution: Once the experimental design is finalized, the X factor test is conducted. This involves implementing the test procedure, measuring the variables of interest, and collecting the necessary data.
- Data analysis: The collected data is then analyzed using statistical methods and tools. This analysis helps determine the presence and magnitude of the X factor’s influence on the product or process being tested.
- Conclusion and recommendations: Based on the results of the data analysis, conclusions are drawn, and recommendations are made. These conclusions and recommendations provide insights into the effectiveness and potential improvements of the product or process being evaluated.
The X factor test procedure is an important tool in industries such as manufacturing, research and development, and quality control. It allows businesses to identify and understand the impact of various factors on their products or processes, enabling them to make informed decisions and improvements. By following a systematic and well-defined procedure, companies can ensure accurate and reliable test results that can drive innovation and success.
V Factor Test Procedure
The V factor test is a method used to identify a specific bacterial species called Haemophilus influenzae. This test relies on the utilization of the V factor or the coenzyme NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) by the bacteria. Haemophilus influenzae is an important human pathogen associated with respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia and meningitis. Therefore, the V factor test plays a crucial role in the identification and diagnosis of these infections.
The procedure for the V factor test involves inoculating the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae onto a selective medium known as chocolate agar. This agar contains hemoglobin, which acts as a source of the V factor. The inoculated plates are then incubated in a carbon dioxide-enriched environment, simulating the conditions of the human respiratory tract. Haemophilus influenzae requires the V factor for growth and, therefore, will grow only on the chocolate agar plates.
After incubation, the presence of Haemophilus influenzae can be confirmed through various methods. One of the common methods is the Gram stain, which allows the visualization and identification of the bacteria based on their cell wall characteristics. Additionally, further biochemical tests, such as oxidase and catalase tests, can be performed to confirm the identity of Haemophilus influenzae.
- The V factor test is essential in differentiating Haemophilus influenzae from other bacteria.
- It provides valuable information for the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory tract infections.
- The test utilizes the selective medium of chocolate agar, containing hemoglobin as the source of the V factor.
- Inoculated plates are incubated in a carbon dioxide-enriched environment to simulate the conditions of the respiratory tract.
- Confirmation of Haemophilus influenzae can be achieved through methods such as Gram staining and biochemical tests.