
If you’re studying matter properties and changes, it’s important to have a comprehensive answer key to help you understand and review the material. This answer key will provide you with the correct answers to various questions and exercises, allowing you to check your understanding and identify any areas that may require further study.
One of the first topics covered in matter properties and changes is the classification of matter. This answer key will provide accurate answers to questions related to the different types of matter, such as pure substances and mixtures, as well as the different classifications within these categories. By referring to the answer key, you’ll be able to verify your knowledge and ensure that you are correctly identifying the different types of matter in various scenarios.
Another important aspect of matter properties and changes is understanding physical and chemical properties. This answer key will include the correct answers to questions about physical properties, such as color, texture, and density, as well as chemical properties, such as reactivity and flammability. By consulting the answer key, you’ll be able to confirm your understanding of these properties and determine if you need to review any specific concepts.
Finally, the matter properties and changes answer key will provide you with the correct answers to questions about physical and chemical changes. This includes questions about the characteristics of physical changes, such as changes in state or size, as well as questions about the indicators of chemical changes, such as the production of gas or a change in color. By using the answer key, you can ensure that you are accurately identifying and describing these changes.
In summary, the matter properties and changes answer key serves as a valuable resource for students studying this topic. It provides accurate answers to questions about the classification of matter, physical and chemical properties, and physical and chemical changes. By utilizing the answer key, students can check their understanding, identify areas of weakness, and improve their overall comprehension of matter properties and changes.
Matter Properties and Changes Answer Key
In the study of matter properties and changes, it is important to have an answer key to help guide students in their understanding. This answer key provides a comprehensive list of correct responses for various questions and activities related to matter. With this resource, students can check their work and assess their understanding of the material.
The answer key is organized by topic, making it easy for students to locate the answers they need. Each topic includes a detailed explanation of the correct answer, as well as any relevant diagrams or examples. This allows students to not only find the correct response, but also to understand the reasoning behind it.
The answer key covers a wide range of topics, including properties of matter, physical and chemical changes, and conservation of mass. It also includes questions that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills, allowing students to apply their knowledge in different scenarios.
- Properties of matter: This section covers topics such as density, solubility, and conductivity. Students will need to identify the properties of different substances and explain their observations.
- Physical and chemical changes: Here, students will learn to differentiate between physical changes, such as melting or boiling, and chemical changes, such as burning or rusting. They will need to describe the changes that occur in different scenarios.
- Conservation of mass: This topic focuses on the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Students will need to balance chemical equations and calculate the mass of reactants and products.
Overall, the Matter Properties and Changes Answer Key is a valuable tool for students studying this topic. It provides them with the guidance and feedback they need to solidify their understanding of matter and its properties.
Definition of Matter

Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. It is the physical substance in the universe that makes up everything we see and interact with. Matter can exist in various forms, including solids, liquids, gases, and even plasma. It can be as small as a particle or as large as a planet. Matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms, which are the building blocks of all matter.
One key characteristic of matter is that it can undergo physical and chemical changes. Physical changes refer to changes in the physical properties of matter, such as its shape, size, or state, without altering its chemical composition. Examples of physical changes include melting ice into water or breaking a piece of wood into smaller pieces. On the other hand, chemical changes involve the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances with different chemical properties. Examples of chemical changes include burning wood to produce ash and smoke or combining hydrogen and oxygen to form water.
In summary, matter is the physical substance that makes up the universe. It has mass, occupies space, and can exist in various forms. Matter is composed of atoms and can undergo both physical and chemical changes.
Physical Properties of Matter
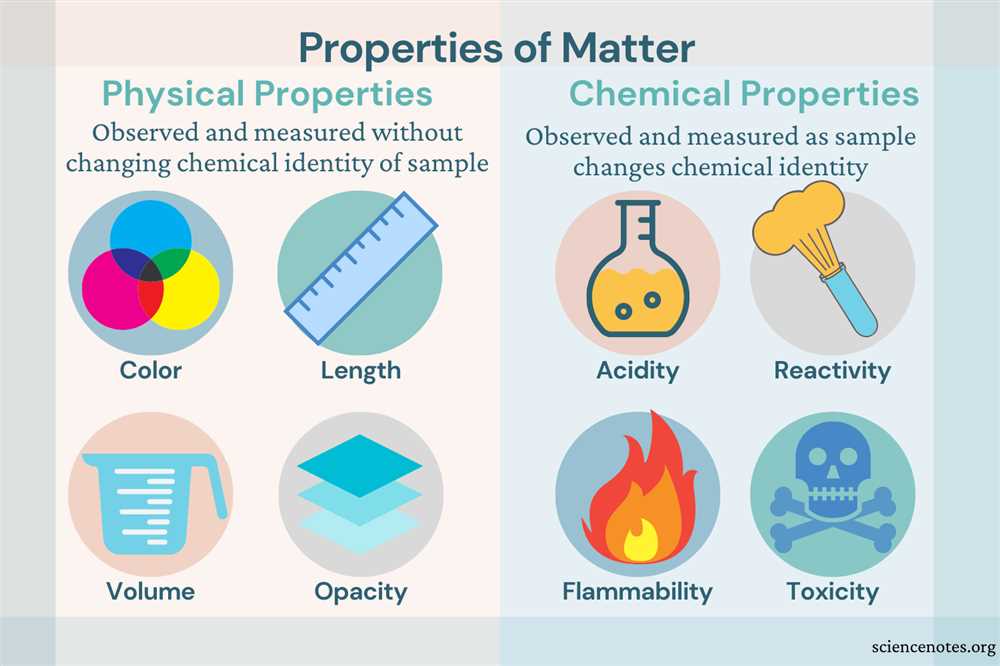
Physical properties of matter refer to the characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the composition or identity of the substance. These properties provide valuable information about the substance and help us differentiate one substance from another. There are several physical properties that can be used to describe matter, including color, shape, size, mass, density, texture, odor, taste, and boiling point.
Color: Color is a physical property that helps distinguish substances based on their appearance. Different substances have different colors, ranging from transparent to opaque, and from bright to dull.
Shape: The shape of a substance refers to the external form or appearance it takes. Some substances, such as liquids and gases, adapt to the shape of their container, while others, like solids, maintain a specific shape regardless of their container’s shape.
Size: Size is a physical property that refers to the dimensions or magnitude of an object. It can be measured in terms of length, width, height, or volume.
Mass: Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It determines an object’s resistance to changes in motion and is commonly measured using a balance or scale.
Density: Density is the ratio of mass to volume and is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given space. It helps identify substances and can be used to determine if a substance will float or sink in another substance.
Texture: Texture describes how a substance feels when touched or interacted with. It can be categorized as rough, smooth, soft, hard, etc.
Odor: Odor refers to the characteristic smell or scent of a substance. Different substances have distinct odors, which can be used to identify them.
Taste: Taste is the sensation perceived by the tongue when a substance is in contact with taste buds. It can be categorized as sweet, sour, salty, bitter, or umami.
Boiling Point: The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes from a liquid to a gas. It is a characteristic physical property that can help identify substances.
These are just a few examples of physical properties that can be used to describe matter. By understanding and observing these properties, scientists and researchers can gain insights into the behavior, composition, and identification of substances.
Chemical Properties of Matter
The chemical properties of matter refer to its ability to undergo chemical reactions or changes. Unlike physical properties, which can be observed or measured without altering the substance, chemical properties involve a transformation of the original substance into a new substance with different chemical properties.
One important chemical property of matter is reactivity. This refers to the ability of a substance to react with other substances and undergo a chemical change. For example, iron is a reactive metal that easily combines with oxygen in the air to form rust. This reaction is a chemical change because the composition of the iron has changed, resulting in a new substance with different properties.
Another chemical property is flammability. Flammable substances have the ability to undergo combustion, or burn, when exposed to a flame or spark. This is a chemical change because the substance is being transformed into new substances, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor, as a result of the combustion process.
Chemical properties can also determine the stability or instability of a substance. Some substances are highly stable and do not easily undergo chemical changes, while others are more reactive and prone to chemical reactions. Understanding the chemical properties of matter is important in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science, as it allows scientists to predict how substances will behave in different conditions and how they can be used or controlled.
In summary, the chemical properties of matter involve its ability to undergo chemical reactions or changes, such as reactivity and flammability. These properties can determine the stability or instability of a substance and have important implications in various scientific disciplines. By studying and understanding these properties, scientists can gain insights into the behavior of matter and how it can be manipulated or controlled for various applications.
Changes in Matter
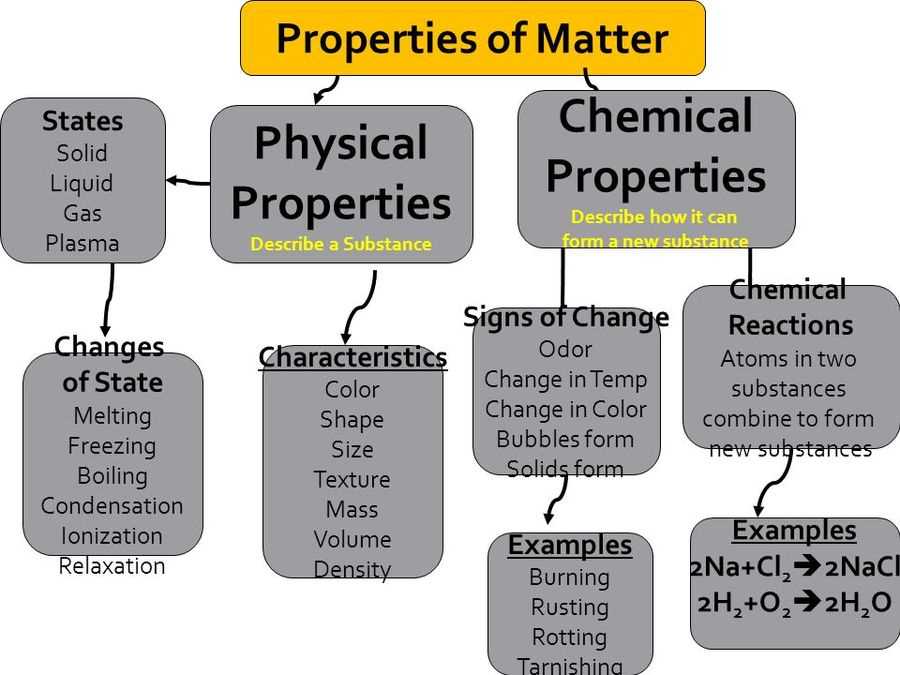
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It can exist in different states, such as solid, liquid, or gas. One of the fundamental concepts in the study of matter is that it can undergo various changes. These changes can be classified into two main categories: physical changes and chemical changes.
Physical changes are changes in the physical properties of matter, such as shape, size, or state, without altering its chemical composition. For example, melting ice into water is a physical change because the substance remains water and can be easily reversed by freezing it again. Other examples of physical changes include cutting a piece of paper, dissolving salt in water, or boiling water. These changes can be observed and measured without any new substances being formed.
Chemical changes, on the other hand, involve the formation of new substances with different properties. During a chemical change, the atoms of the substances rearrange themselves, resulting in the formation of new molecules. For example, burning paper is a chemical change because it produces new gases, ash, and smoke. Other examples of chemical changes include rusting of iron, baking a cake, or digestion of food. Chemical changes are usually accompanied by the release or absorption of energy, such as heat or light.
In conclusion, matter undergoes different types of changes. Physical changes involve alterations in the physical properties of matter without changing its chemical composition. Chemical changes, on the other hand, result in the formation of new substances with different properties. Understanding these changes is essential in various fields, from chemistry to everyday life.
Physical Changes in Matter
Physical changes in matter refer to any alterations that occur in the physical characteristics of a substance, without changing its chemical composition. These changes can involve properties such as shape, size, color, or state of matter. Physical changes do not produce new substances and are generally reversible.
One common example of a physical change is the melting of ice. When heat is applied, the solid ice undergoes a phase change and becomes liquid water. The chemical composition of water remains the same, but its state changes from solid to liquid. Similarly, freezing water reverses this physical change, turning liquid water back into solid ice.
Physical changes can also involve changes in the size or shape of a substance. For example, cutting a piece of paper into smaller shapes or stretching a rubber band are physical changes that do not alter the chemical composition of the paper or rubber. These changes only affect the physical appearance of the materials.
In conclusion, physical changes in matter involve alterations in the physical characteristics of a substance without changing its chemical composition. These changes can include changes in state, size, shape, or color. Understanding physical changes is important in various fields, such as chemistry, physics, and materials science.
Chemical Changes in Matter
Chemical changes in matter occur when substances undergo a chemical reaction, resulting in the formation of new substances with different properties. These changes involve the breaking and formation of chemical bonds, leading to the rearrangement of atoms to create entirely new molecules.
One example of a chemical change is the combustion of a substance, such as wood or gasoline. When these substances come into contact with oxygen and are heated, they undergo a chemical reaction known as combustion. This process produces carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy in the form of heat and light. The original substance, whether it be wood or gasoline, is completely transformed into new substances during this chemical change.
Chemical changes in matter can also be observed in common everyday activities, such as cooking. When food is cooked, chemical reactions occur that transform the flavors, textures, and colors of the ingredients. For example, when bread is toasted, the heat causes the Maillard reaction to take place, resulting in the browning of the bread and the formation of new, more complex flavors. Similarly, when meat is cooked, the proteins undergo denaturation, leading to changes in texture and taste.
It is important to note that chemical changes in matter are often accompanied by physical changes, such as changes in temperature, color, or odor. These physical changes are indicators of the chemical reactions taking place. Additionally, chemical changes are typically irreversible, meaning that the original substances cannot be easily recovered after the reaction has occurred.
In conclusion, chemical changes in matter involve the formation of new substances through the breaking and formation of chemical bonds. These changes can be observed in various everyday activities and are often accompanied by physical changes. Understanding and recognizing chemical changes in matter is crucial in fields such as chemistry and cooking, as it allows us to manipulate matter to create new and desired outcomes.