The Muslim world and Africa have a rich history of interconnectedness that spans centuries. The spread of Islam throughout Africa has had a profound impact on the continent, shaping its culture, politics, and society. This unit test aims to assess your understanding of the complex relationship between the Muslim world and Africa, covering topics such as the spread of Islam, the influence of Muslim scholars, and the cultural exchange between these two regions.
Throughout history, the Muslim world has played a significant role in shaping Africa’s religious and intellectual landscape. The spread of Islam across North Africa, the Sahel region, and the Swahili Coast has led to the flourishing of Islamic scholarship and the establishment of vibrant Muslim communities. This unit test will delve into the spread of Islam in these regions and examine the key historical figures and events that contributed to its growth.
Furthermore, this test will explore the cultural exchange between the Muslim world and Africa. The influence of Arabic language, Islamic architecture, and Islamic art can be found in various African societies. We will examine how this cultural exchange has shaped African identity and contributed to the diversity of the continent’s cultural heritage.
The Muslim World and Africa Unit Test
The Muslim world and Africa have had a significant historical and cultural connection throughout the centuries. Islam spread across Africa from the 7th century onwards, resulting in the formation of several Islamic empires and states. This unit test aims to assess your knowledge and understanding of the relationship between the Muslim world and Africa, including the impact of Islam in various aspects of African societies.
This unit test will cover topics such as the early spread of Islam in Africa, the rise of Islamic empires such as the Mali Empire and the Sokoto Caliphate, the influence of Islamic religion and culture on African societies, and the role of Africa in the global Muslim community. It will test your ability to analyze historical sources, interpret geographical maps, and evaluate the contributions of different African civilizations to the Islamic world.
- Identify and explain the factors that contributed to the spread of Islam in Africa.
- Analyze the impact of Islamic empires on the political, economic, and social development of African societies.
- Evaluate the role of prominent African Muslim scholars and leaders in shaping Islamic civilization.
- Interpret geographical maps to understand the extent of Islamic influence in Africa.
- Compare and contrast the development of Islam in different regions of Africa.
The test will consist of multiple-choice, short answer, and essay questions. It is important to review your notes, readings, and class discussions to prepare for the test. Pay attention to key concepts, historical events, and the cultural significance of Islam in Africa. By demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the material, you will be able to excel in this unit test and deepen your knowledge of the Muslim world and Africa.
Overview
The Muslim world and Africa have a rich and intertwined history that has shaped the cultural, political, and economic landscape of both regions. This unit test aims to assess your understanding of this complex relationship and its impact on various aspects of society.
The test will cover key topics such as the spread of Islam in Africa, the role of Muslim leaders and scholars, significant historical events, and the cultural exchange between the Muslim world and Africa. It will require a comprehensive understanding of the historical context and the ability to analyze and evaluate the impact of these interactions.
The spread of Islam in Africa
The spread of Islam in Africa had a profound impact on the continent, both culturally and politically. It began in the 7th century with the Arab conquest of North Africa and gradually spread southward through trade routes and peaceful conversions. The arrival of Islam introduced new religious and cultural practices, as well as political and economic systems, which influenced Africa’s societies and governments.
Role of Muslim leaders and scholars
Muslim leaders and scholars played a crucial role in shaping the Muslim world and Africa. They provided leadership, religious guidance, and intellectual contributions that influenced various spheres of life. These leaders and scholars acted as intermediaries between the Muslim world and Africa, promoting education, trade, and the spread of Islamic principles.
Significant historical events
The history of the Muslim world and Africa is replete with significant events that have had lasting consequences. Some notable events include Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage to Mecca, the reign of the Ottomans in North Africa, the Trans-Saharan trade routes, and the rise and fall of empires such as the Mali and Songhai Empires. Understanding these events is crucial in grasping the complexities of the relationships between the Muslim world and Africa.
Cultural exchange
The Muslim world and Africa have engaged in extensive cultural exchange throughout history. This exchange has facilitated the spread of languages, arts, architecture, and culinary traditions. Additionally, it has fostered a unique fusion of African and Islamic cultural elements, resulting in the development of vibrant and diverse societies.
Background
The Muslim world and Africa have a long and complex history that spans centuries. Islam first arrived in Africa with the expansion of the Arab Empire in the 7th century. Muslim traders, scholars, and rulers played a significant role in shaping Africa’s political, social, and cultural landscape, leaving a lasting impact on the continent.
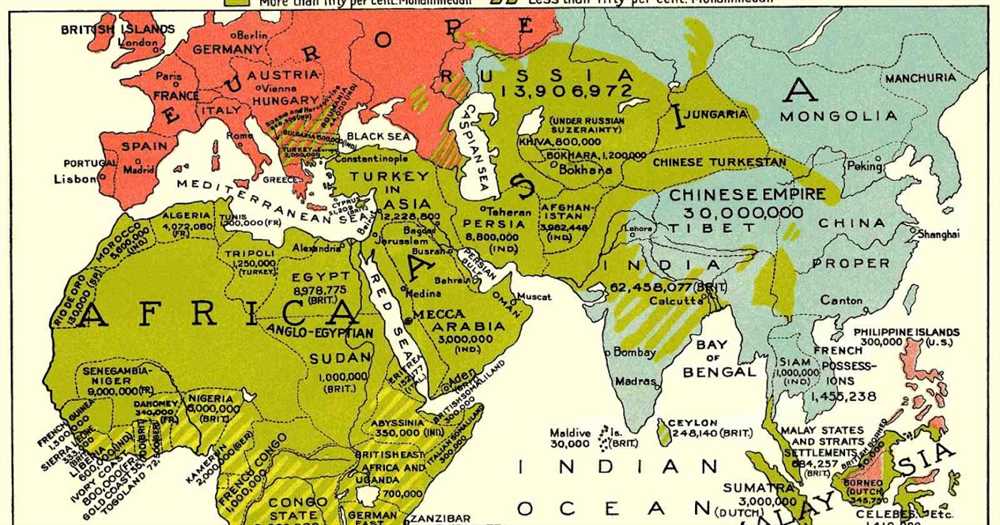
One key aspect of the Muslim presence in Africa is the spread of Islam across the continent. Through trade networks and peaceful missionary efforts, Islam gradually gained followers and established itself as a major religion in many regions of Africa. It became particularly influential in the northern parts of the continent, such as present-day Morocco, Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and Somalia. Over time, Muslim traders and scholars also ventured further into the interior of Africa, spreading their faith and knowledge.
Another important factor in the history of the Muslim world and Africa is the trans-Saharan trade. This trade network connected the Mediterranean region with West Africa and facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and people. Muslim merchants played a crucial role in this trade, using camel caravans to transport valuable commodities like gold, salt, and slaves across the vast Sahara Desert. This trade route not only enriched the economies of the regions involved but also fostered cultural exchange and the spread of Islam.
Furthermore, Muslim states and empires emerged in Africa, such as the Kingdom of Ghana, the Mali Empire, and the Songhai Empire. These powerful states embraced Islam as their official religion and integrated it into their political and legal structures. They also became important centers of Islamic learning and attracted scholars and students from across the Muslim world.
In summary, the history of the Muslim world and Africa is a complex tapestry of trade, cultural exchange, and political influence. Islam’s arrival in Africa brought about significant changes, shaping the continent’s religious, social, and economic landscape. The trans-Saharan trade, the spread of Islam, and the rise of Muslim states all played crucial roles in this historical relationship.
The Spread of Islam in Africa
The spread of Islam in Africa had a profound impact on the continent, both culturally and politically. This process began in the 7th century when Arab Muslim traders brought Islam to North Africa. From there, it gradually spread across the Sahara Desert and into the sub-Saharan regions. Islam’s spread in Africa was facilitated by a variety of factors including trade networks, military conquests, and the appeal of Islamic beliefs and practices to African populations.
Trade played a significant role in the spread of Islam in Africa. Arab merchants established trade routes across the Sahara Desert, exchanging goods such as gold, salt, and slaves. Along these routes, they also spread Islamic teachings and established Muslim communities. These trade networks served as conduits for the diffusion of Islamic beliefs and practices, allowing them to reach far-flung areas of Africa.
Military conquests were another important factor in the spread of Islam in Africa. Islamic armies, led by caliphs and generals, conquered various regions in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. The defeated populations were often compelled to convert to Islam, either out of choice or as a means of gaining favor with their conquerors. This process resulted in the formation of Islamic states and empires, such as the Fatimid Caliphate in Egypt and the Almoravid Empire in West Africa.
The appeal of Islamic beliefs also contributed to the spread of Islam in Africa. The tenets of Islam, such as monotheism, social justice, and the equality of all believers, resonated with many Africans who were disenchanted with traditional African religions or oppressed by societal hierarchies. Additionally, the adoption of Islam often provided access to new trading opportunities, education, and legal protections, further incentivizing its spread.
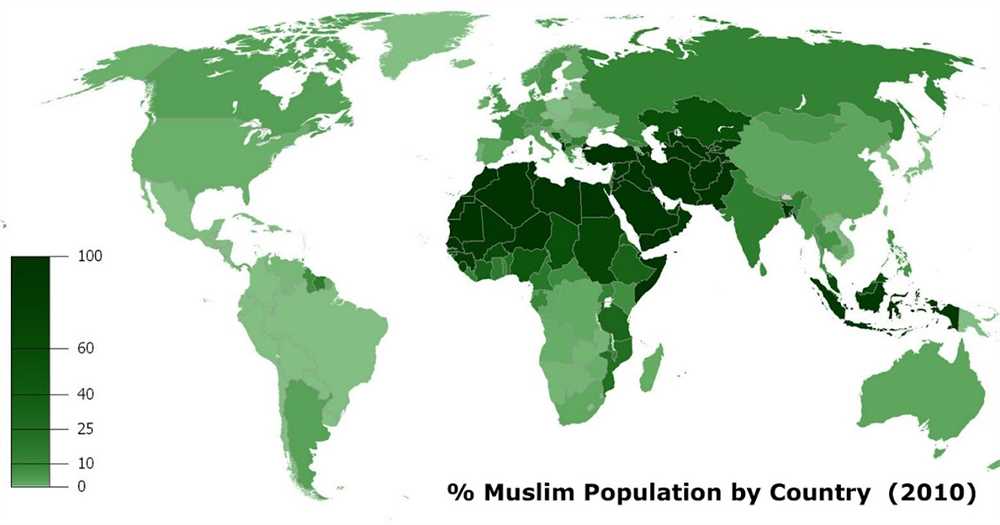
Overall, the spread of Islam in Africa had a complex and multi-faceted history. It transformed political structures, created new cultural and religious syncretisms, and left a lasting legacy on the continent’s diverse societies. Today, Islam remains one of the largest religions in Africa, with millions of Muslims spread across the continent.
Cultural Exchange between the Muslim World and Africa
The cultural exchange between the Muslim world and Africa has been significant and has played a crucial role in shaping the history, traditions, and beliefs of both regions. This exchange has occurred through various means such as trade, migration, and the spread of Islam. It has resulted in the blending of cultures, the adoption of new practices, and the development of unique art forms and architectural styles.
One of the key aspects of the cultural exchange between the Muslim world and Africa is the spread of Islam. The arrival of Muslim traders and scholars in Africa led to the conversion of many African communities to Islam. This religious conversion not only brought about changes in religious beliefs but also influenced other aspects of African culture such as language, dress, and food. The blend of African and Islamic cultures is evident in the architecture of mosques and Islamic religious practices in various regions of Africa.
The cultural exchange between the Muslim world and Africa also extended to the fields of art and literature. African artists and craftsmen were greatly influenced by Islamic art forms, leading to the development of unique artistic styles that incorporated both African traditions and Islamic aesthetics. The art of calligraphy, intricate geometric patterns, and the use of vibrant colors are some of the notable elements that emerged from this cultural exchange. In literature, Arabic and Arab-Islamic writings influenced the development of African written and oral traditions, leading to the creation of new literary forms that were influenced by both cultures.
In conclusion, the cultural exchange between the Muslim world and Africa has been extensive and has had a profound impact on both regions. This exchange has fostered the blending of cultures, the adoption of new practices, and the development of unique art forms and architectural styles. It has enriched the cultural diversity of both the Muslim world and Africa, and continues to shape their identities and histories.
Africa’s Role in the Islamic Empires
The continent of Africa played a significant role in the development and expansion of the Islamic empires. The spread of Islam across Africa brought about cultural, economic, and political changes that shaped the history of the region. The Islamic empires, such as the Umayyad, Abbasid, and Fatimid dynasties, had a profound impact on the African societies they encountered, leaving lasting legacies.
One of the key contributions of Africa to the Islamic empires was its abundant resources. Africa was rich in natural resources such as gold, ivory, and slaves, which were highly sought after by the Islamic empires. The trans-Saharan trade routes, connecting West Africa with North Africa and the Middle East, played a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between these regions. This trade route not only enriched the Islamic empires economically but also fostered cultural exchange and the spread of Islam in Africa.
Moreover, Africa’s geographical location made it an important hub for trade and commerce. The Islamic empires established trade networks and flourishing cities along the African coast, such as Alexandria in Egypt and Mogadishu in Somalia. These urban centers became centers of learning, where scholars and traders from different parts of the Islamic world exchanged knowledge and goods. The coastal regions of Africa, with their access to the Indian Ocean, also facilitated the trade between the Islamic empires and other Asian societies.
Africa’s role in the Islamic empires was not limited to trade and commerce. The spread of Islam in Africa led to the formation of powerful African Muslim states, such as the Songhai Empire in West Africa and the Sultanate of Zanzibar in East Africa. These African states adopted Islamic administration, laws, and customs, blending them with their own indigenous traditions. The Islamic empires provided political and military support to these African states, helping them strengthen their rule and expand their influence in the region.
In conclusion, Africa played a crucial role in the Islamic empires by providing valuable resources, serving as a trading hub, and contributing to the formation of African Muslim states. The interactions between the Islamic empires and Africa resulted in cultural exchange, economic prosperity, and political alliances that shaped the history of both regions.
The Impact of Islam on African Societies
Islam has had a profound impact on African societies throughout history, shaping their culture, economy, and social structure. With the arrival of Islam in Africa, new religious beliefs and practices were introduced, which often blended with existing traditional African religions. This fusion of Islamic teachings and indigenous customs led to the development of unique African Islamic cultures.
The spread of Islam also brought about significant changes in African societies, particularly in terms of governance and law. Many African states adopted Islamic legal systems, such as Sharia, which influenced the way justice was administered and social norms were upheld. Islamic education also played a crucial role in shaping African societies, as Islamic schools and scholars became centers of learning and knowledge dissemination.
Furthermore, Islam played a crucial role in the economic development of African societies. The establishment of trade networks and the growth of Islamic cities facilitated economic exchanges, leading to increased prosperity in regions such as West Africa. The trans-Saharan trade route, for example, connected African merchants with those from the Middle East and North Africa, promoting commerce and cultural exchange.
Overall, the impact of Islam on African societies cannot be understated. It brought about changes in religious beliefs, social norms, governance, education, and trade, shaping the course of African history and leaving a lasting legacy that is still evident today.