The Renaissance, a period of cultural and intellectual rebirth in Europe, marked a turning point in history. During this transformative era, new ideas and artistic expressions flourished, shaping the world as we know it today. But what were the key factors that fueled the birth of the Renaissance?
One of the key factors that propelled the Renaissance was the rediscovery of classical texts and ideas. Scholars and intellectuals began to delve into the works of ancient Greek and Roman philosophers, scientists, and writers, which had been preserved and studied in the Byzantine Empire and the Islamic world. This renewed interest in ancient knowledge led to a profound reevaluation of the human experience, sparking a desire for innovation, exploration, and progress.
Another crucial catalyst for the birth of the Renaissance was the economic prosperity of Italian city-states. Cities like Florence, Venice, and Genoa became thriving centers of trade and commerce, accumulating wealth and fostering a climate of innovation. The newfound affluence allowed patrons to support artists, architects, and scholars, creating a fertile ground for creativity and intellectual exchange.
Furthermore, the rise of humanism played a pivotal role in igniting the Renaissance. Humanists emphasized the importance of human achievements, focusing on the individual’s potential for greatness. This human-centered worldview challenged the prevailing religious dogmas of the time and encouraged a pursuit of knowledge and self-discovery. It laid the foundation for the development of art, literature, and philosophy that defined the Renaissance period.
In summary, the birth of the Renaissance was fueled by the rediscovery of classical texts, the economic prosperity of Italian city-states, and the rise of humanism. These key factors converged to create an environment conducive to intellectual and artistic flourishing, shaping the course of history and leaving a lasting impact on our world.
The Origins of the Renaissance
The Renaissance, meaning “rebirth,” was a period of cultural and intellectual awakening that began in Italy in the 14th century and spread throughout Europe during the 15th and 16th centuries. This movement marked a shift from the medieval period to the modern era, and it had a profound impact on art, literature, science, and philosophy.
One of the key factors that led to the birth of the Renaissance was the rediscovery of classical knowledge. During the Middle Ages, much of the wisdom of the ancient Greeks and Romans had been lost or forgotten. However, in the 14th century, scholars began to rediscover ancient texts that had been preserved in monasteries and libraries. These texts, which included works by Plato, Aristotle, and Cicero, provided new insights into philosophy, science, and the arts. They sparked a renewed interest in learning and inquiry, which laid the foundation for the Renaissance.
The economic prosperity of Italian city-states also played a significant role in the development of the Renaissance. Cities like Florence, Venice, and Genoa became wealthy through trade and banking, which allowed them to support a flourishing arts and culture scene. The wealthy patrons of these city-states, such as the Medici family in Florence, sponsored artists, architects, and scholars, further fueling the growth of the Renaissance. The patronage of the nobility and merchant class allowed artists and thinkers to focus on their work without financial constraints, leading to the creation of some of the most iconic works of the Renaissance.
- Rediscovery of classical knowledge
- Economic prosperity of Italian city-states
- Patronage of the nobility and merchant class
In conclusion, the origins of the Renaissance can be attributed to the rediscovery of classical knowledge, the economic prosperity of Italian city-states, and the patronage of the nobility and merchant class. These factors created a fertile environment for artistic, intellectual, and cultural innovation, which propelled the Renaissance forward and forever changed the course of history.
Early Influences on the Renaissance
The Renaissance was a period of cultural and intellectual rebirth that took place in Europe between the 14th and 17th centuries. During this time, there were several key influences that shaped the development of the Renaissance. These influences included the rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman texts, the rise of humanism, and the patronage of wealthy families and institutions.
One of the most important influences on the Renaissance was the rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman texts. During the Middle Ages, many of these texts were lost or forgotten, but they were reintroduced to Europe through the translation efforts of scholars and the establishment of libraries and academies. This rediscovery of classical literature sparked a renewed interest in the ideas and values of the ancient world, and it provided a foundation for the intellectual and artistic achievements of the Renaissance.
In addition to the rediscovery of classical texts, the rise of humanism also had a profound impact on the Renaissance. Humanism emphasized the worth and potential of human beings, and it encouraged the study of subjects such as literature, philosophy, and history. Humanist scholars focused on the individual and their role in society, and they sought to understand and celebrate the human experience. This emphasis on humanistic values and the pursuit of knowledge helped to fuel the intellectual and artistic creativity of the Renaissance.
Finally, the patronage of wealthy families and institutions played a crucial role in the development of the Renaissance. These patrons provided financial support to artists, scholars, and scientists, enabling them to pursue their work and share their ideas. Without the support of patrons, many of the great achievements of the Renaissance may not have been possible. These patrons not only funded the creation of notable works of art, but they also established academies and institutions that fostered innovation and creativity. Their patronage created an environment that encouraged and rewarded the pursuit of knowledge and artistic expression.
In conclusion, the Renaissance was shaped by a combination of influences, including the rediscovery of classical texts, the rise of humanism, and the patronage of wealthy families and institutions. These influences helped to fuel the intellectual and artistic achievements of the period, and they continue to impact our understanding of the Renaissance today.
The Fall of the Roman Empire and its Impact on the Renaissance
The fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century had a significant impact on the development of the Renaissance. The collapse of this powerful empire led to a period of political instability, economic decline, and social upheaval in Europe. However, out of the chaos emerged a new era of intellectual and cultural resurgence that would shape the course of history.
One of the most significant effects of the fall of the Roman Empire was the disruption of trade and commerce. With the collapse of the empire’s vast network of roads, bridges, and ports, Europe experienced a decline in long-distance trade and the loss of economic stability. This economic decline led to a decline in urbanization, as cities and towns were abandoned or left in ruins. However, this decline in urban life also paved the way for a new focus on rural life, agriculture, and self-sufficiency.
In addition to the economic impact, the fall of the Roman Empire also had profound effects on the political and social structures of Europe. With the collapse of centralized authority, Europe was fragmented into a patchwork of small kingdoms and city-states. This fragmentation gave rise to a system of feudalism, in which local lords and nobles held power over their lands and the people who worked them. This feudal system laid the foundation for the hierarchical social structure of the medieval period.
Despite the hardships and challenges brought about by the fall of the Roman Empire, this period of upheaval also created fertile ground for intellectual and cultural innovation. As Europe struggled to rebuild and redefine itself, scholars and artists began to look to the past for inspiration. The revival of classical learning, known as the Renaissance, was born out of a desire to recreate the glory and achievements of ancient Rome. This renewed interest in the humanities, philosophy, and the arts laid the groundwork for the intellectual and cultural movements that would define the Renaissance era.
In conclusion, the fall of the Roman Empire had a profound impact on the development of the Renaissance. It led to economic decline, political fragmentation, and social changes in Europe. However, out of this period of instability and upheaval emerged a renewed interest in the classics and a flourishing of intellectual and cultural achievements that would shape the course of history.
The Role of Italian City-States
The Italian city-states played a crucial role in the birth of the Renaissance. These city-states, such as Florence, Milan, and Venice, were independent political entities that were ruled by powerful families or oligarchies. They became centers of wealth, trade, and intellectual activity, attracting artists, thinkers, and scholars from all over Europe.
One of the key factors that contributed to the flourishing of the Renaissance in the Italian city-states was their wealth and prosperous economy. The city-states were located in strategic positions that allowed them to dominate trade routes and control important resources. This economic prosperity provided the necessary financial support for the patronage of artists and scholars, leading to the creation of magnificent works of art and the advancement of knowledge in various fields.
The city-states also fostered an environment of intellectual exchange and competition. The competition among the city-states, particularly Florence and Milan, fueled a spirit of innovation and creativity. Artists and scholars in these city-states were encouraged to push the boundaries of traditional art and knowledge, resulting in groundbreaking discoveries and artistic masterpieces.
The city-states were also known for their strong emphasis on education. They established universities and academies that provided opportunities for intellectual growth and the pursuit of knowledge. These institutions attracted scholars and students from all over Europe, creating a vibrant intellectual community where ideas and knowledge were shared and exchanged.
In conclusion, the Italian city-states played a pivotal role in the birth of the Renaissance. Their economic prosperity, intellectual exchange, and emphasis on education provided the ideal conditions for the flourishing of art, science, and culture. The legacy of the Italian city-states can still be seen today in the magnificent works of art and the intellectual achievements of the Renaissance period.
Key Figures of the Renaissance
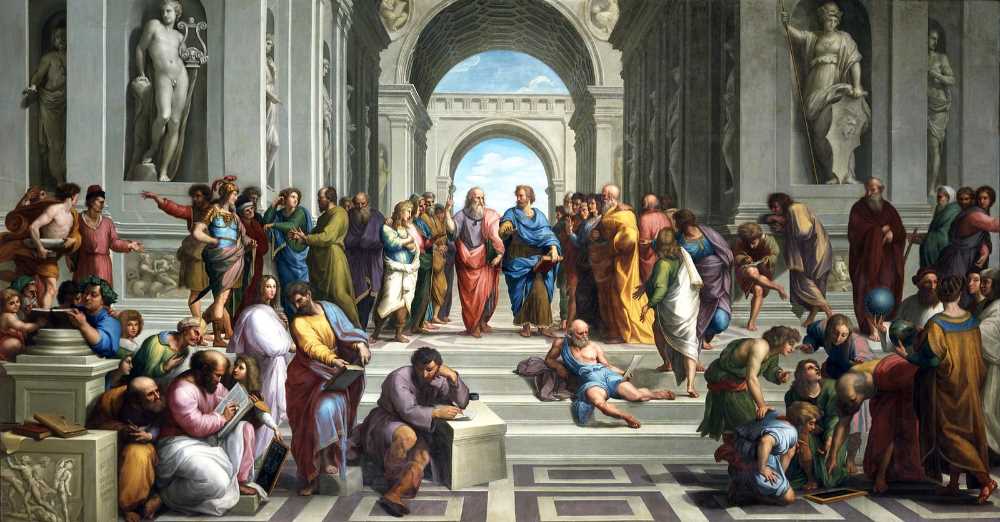

The Renaissance period was marked by an incredible surge of creativity and achievement, with numerous key figures emerging during this time who had a profound impact on art, literature, science, and more. These individuals were at the forefront of the intellectual and cultural movements that defined the period, and their innovations continue to shape the world today.
One of the most iconic figures of the Renaissance was Leonardo da Vinci, a true Renaissance man who excelled in various fields. Leonardo was not only a renowned painter, responsible for masterpieces such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, but he was also an inventor, engineer, and scientist. His numerous sketches and writings demonstrate his curiosity and innovation in areas such as anatomy, engineering, and flight. Leonardo’s work embodies the spirit of the Renaissance, with its emphasis on humanism and the belief in the limitless potential of the individual.
Another key figure of the Renaissance was Michelangelo Buonarroti, who achieved fame as a sculptor and painter. Michelangelo’s sculptures, including the iconic David and the Pietà, are characterized by their realism and emotional expression. He also played a crucial role in the construction of the Sistine Chapel, where his frescoes, most notably The Creation of Adam, remain some of the greatest achievements in Western art. Michelangelo’s mastery of the human form and his ability to capture the human condition in his work made him a dominant figure of the Renaissance.
The world of literature was also transformed during the Renaissance, with figures such as William Shakespeare revolutionizing the art of playwriting. Shakespeare’s plays explored an array of human emotions and experiences, and his innovative use of language and poetic techniques set new standards for dramatic writing. His works, such as Romeo and Juliet, Hamlet, and Macbeth, continue to be performed and studied worldwide, making Shakespeare a central figure in the literary heritage of the Renaissance.
These are just a few of the key figures who shaped the Renaissance era and left a lasting impact on the world. Their pioneering ideas, artistic achievements, and scientific advancements continue to inspire and influence generations, making the Renaissance a truly transformative period in history.
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci was a renowned Italian artist, scientist, inventor, and polymath of the Renaissance period. Born on April 15, 1452, in Vinci, Italy, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest painters and thinkers of all time. Da Vinci’s works spanned various disciplines, including art, engineering, anatomy, and architecture, and his contributions significantly influenced the development of Western art and science.
Leonardo da Vinci is best known for his iconic works of art, such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper. His meticulous attention to detail, innovative use of perspective, and his ability to capture the human form with unprecedented realism set him apart from other artists of his time. Da Vinci’s paintings are characterized by their exquisite craftsmanship, soft tones, and deep emotional expressions.
In addition to his artistic achievements, Leonardo da Vinci was also a brilliant scientist and inventor. He made groundbreaking discoveries in various fields, including anatomy, astronomy, geology, and physics. In his “Anatomical Manuscripts,” da Vinci dissected human bodies and accurately depicted the inner workings of the human anatomy. His scientific observations and theories were far ahead of his time.
Leonardo da Vinci’s legacy extends beyond his artistic and scientific contributions. His ingenious inventions, such as flying machines, armored vehicles, and musical instruments, demonstrate his innovative thinking and foresight. Da Vinci’s notebooks, filled with sketches, diagrams, and scientific observations, provide a glimpse into the mind of a true genius.
Leonardo da Vinci’s multidisciplinary approach to knowledge and creativity continues to inspire and captivate people around the world. His ability to seamlessly bridge the gap between art and science serves as a testament to the limitless potential of the human mind. Da Vinci’s work continues to be studied and admired, making him an eternal symbol of intellectual curiosity and artistic excellence.