
Food safety is of utmost importance in the foodservice industry. In order to ensure a safe and healthy dining experience for guests, establishments must adhere to strict guidelines and regulations. ServSafe, a leading food safety training and certification program, offers Chapter 2 as an essential resource for understanding key concepts and practices. This article provides a comprehensive answer key to Chapter 2, offering a clear understanding of the measures necessary to maintain food safety.
Chapter 2 of ServSafe focuses on the four main types of hazards that can compromise the safety of food: biological, chemical, physical, and allergenic. The answer key delves into each type, outlining the potential risks and preventive measures that need to be implemented. By understanding the root causes and effects of these hazards, foodservice professionals can take proactive steps to mitigate risks and maintain a safe environment.
This answer key also covers important topics such as personal hygiene, cross-contamination, and proper cleaning and sanitizing procedures. ServSafe emphasizes the significance of these practices in preventing the spread of bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms. Additionally, the answer key provides detailed explanations and examples to help reinforce the importance of adhering to these guidelines.
Overall, ServSafe Chapter 2 answer key serves as a valuable tool for individuals working in the foodservice industry. By providing a comprehensive understanding of potential hazards and best practices, it equips professionals with the knowledge they need to ensure food safety. By implementing the guidelines outlined in this answer key, establishments can maintain a high level of cleanliness, protect the health of their guests, and establish a reputation for excellence in food safety.
ServSafe Chapter 2 Answer Key: Understanding Foodborne Illnesses
Foodborne illnesses are a major concern in the foodservice industry. It is crucial for foodservice workers to have a solid understanding of these illnesses in order to prevent them from occurring and ensure the safety of their customers. Chapter 2 of ServSafe provides an answer key to understanding foodborne illnesses and the risks associated with them.
One key concept covered in this chapter is the definition of a foodborne illness. According to ServSafe, a foodborne illness is a disease transmitted to people through food. These illnesses can be caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins. This definition emphasizes the importance of proper food handling and hygiene practices to prevent the transmission of these pathogens.
Common Foodborne Illnesses:
- Salmonella: This bacteria is commonly found in raw or undercooked poultry, eggs, and other meats. Symptoms of salmonella poisoning include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever.
- Norovirus: This virus is often spread through contaminated food or water. It causes symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- E. coli: This bacteria can be found in undercooked ground beef, raw fruits and vegetables, and unpasteurized milk. It can cause severe abdominal cramps and bloody diarrhea.
- Hepatitis A: This virus can contaminate food if it is handled by an infected person. Symptoms include fatigue, nausea, and yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Understanding the risks associated with these common foodborne illnesses is crucial for foodservice workers. By following proper food handling procedures, such as cooking foods to the correct temperature and practicing good personal hygiene, they can significantly reduce the risk of these illnesses occurring in their establishment.
The Importance of Understanding Foodborne Illnesses
Foodborne illnesses are a significant public health concern. They are caused by consuming contaminated food and can result in a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe illness and even death. It is essential for individuals, especially those working in the food service industry, to have a thorough understanding of foodborne illnesses to ensure the safety of their customers and prevent outbreaks.
One of the key reasons why understanding foodborne illnesses is crucial is that it allows individuals to identify potential sources of contamination and take appropriate preventive measures. By knowing the common causes of foodborne illnesses, such as undercooked meat, improper storage, or cross-contamination, food handlers can implement proper food safety practices to minimize the risk of contamination. This knowledge also enables them to recognize the symptoms of foodborne illnesses in themselves or others, allowing for early detection and prompt medical attention.
Understanding foodborne illnesses also helps in implementing proper sanitation and hygiene practices. Regular and effective handwashing, cleaning and sanitizing equipment, and maintaining a clean working environment are essential in preventing the spread of harmful bacteria and viruses that cause foodborne illnesses. By following strict sanitation protocols, individuals can ensure that their food preparation and handling practices are safe and minimize the risk of contamination.
Moreover, understanding foodborne illnesses is critical in compliance with food safety regulations and standards. In the food service industry, establishments are required to meet certain hygiene and safety standards to prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure the well-being of their customers. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in severe penalties and damage to the reputation of the business.
To sum up, a comprehensive understanding of foodborne illnesses is essential for individuals working in the food service industry. It allows them to identify potential sources of contamination, implement proper prevention strategies, and comply with food safety regulations. By prioritizing food safety, individuals can protect the health and well-being of their customers and mitigate the risk of foodborne illness outbreaks.
Definition and Causes of Foodborne Illnesses
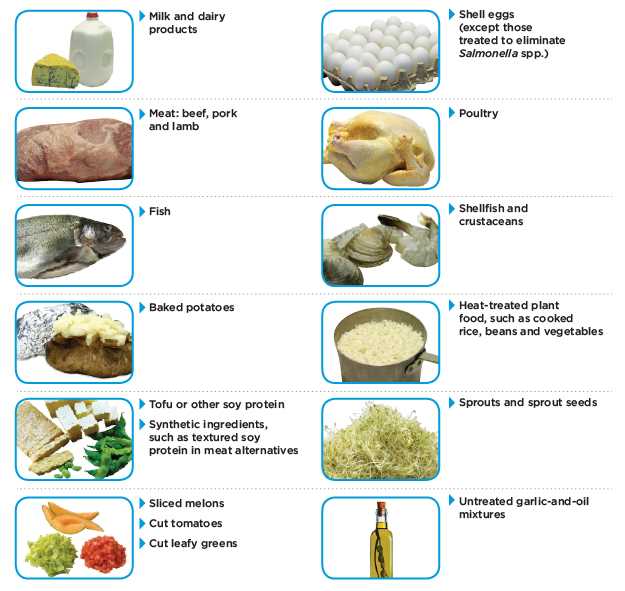
Foodborne illnesses, also known as food poisoning or foodborne diseases, are conditions caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages. These illnesses can result from consuming food that is contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins produced by these microorganisms.
The causes of foodborne illnesses vary and can include improper food handling and storage, inadequate cooking temperatures, poor personal hygiene of food handlers, cross-contamination of foods, and consumption of raw or undercooked foods. Additionally, contaminated water and unsanitary food preparation environments can also contribute to the occurrence of foodborne illnesses.
Improper food handling and storage: Food can become contaminated if it is not handled and stored properly. This can occur when food is left at unsafe temperatures, such as in the “danger zone” between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C), where bacteria can grow rapidly. Cross-contamination from raw to cooked foods or from contaminated surfaces can also occur during handling and storage.
Inadequate cooking temperatures: Cooking food to the proper internal temperature is crucial in killing harmful microorganisms. If food is not cooked to the recommended temperature, bacteria or other pathogens may survive and cause illness when consumed.
Poor personal hygiene: Food handlers who do not practice good personal hygiene can contribute to the transmission of pathogens. This includes not washing hands properly, not wearing gloves when necessary, and working while sick with a contagious illness.
Cross-contamination: Cross-contamination occurs when pathogens from one food item are transferred to another, typically through contact with contaminated surfaces, utensils, or hands. For example, using the same cutting board for raw meat and ready-to-eat foods without proper cleaning and sanitation can result in cross-contamination.
Raw or undercooked foods: Consuming raw or undercooked foods, such as raw eggs, unpasteurized milk, or raw seafood, can increase the risk of foodborne illnesses. These foods may contain harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites that can cause illness when ingested.
It is important to understand and follow proper food safety practices in order to prevent foodborne illnesses. These practices include maintaining proper storage temperatures, cooking foods to the recommended internal temperatures, practicing good personal hygiene, preventing cross-contamination, and avoiding the consumption of raw or undercooked foods.
Common Types of Foodborne Illnesses
Foodborne illnesses, also known as food poisoning, are caused by consuming contaminated food or drinks. These illnesses can range from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to severe complications and even death. There are several common types of foodborne illnesses, each caused by different pathogens or toxins.
One of the most common types of foodborne illnesses is salmonellosis, which is caused by the bacteria Salmonella. Symptoms of salmonellosis include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever. This illness is typically transmitted through contaminated food such as raw or undercooked poultry, eggs, or unpasteurized dairy products.
Another common type of foodborne illness is norovirus infection. Noroviruses are highly contagious and can be spread through contaminated food, water, or surfaces. Symptoms of norovirus infection include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. This illness is often associated with outbreaks in settings like cruise ships, schools, and restaurants.
E. coli infection is also a frequent cause of foodborne illnesses. The bacterium Escherichia coli, commonly found in the intestines of animals, can contaminate food through fecal matter. Consumption of undercooked ground beef or contaminated produce can lead to symptoms such as severe abdominal cramps, bloody diarrhea, and kidney failure.
Prevention and Control
- Proper food handling and preparation: It is crucial to follow good hygiene practices during food preparation, such as washing hands frequently, separating raw and cooked foods, and cooking food to the appropriate temperatures.
- Safe food storage: Food should be stored at the correct temperatures to prevent the growth of bacteria. Refrigerate perishable items promptly and discard any food that has been left at room temperature for too long.
- Regular cleaning and sanitizing: Clean and sanitize food preparation surfaces, utensils, and equipment regularly to prevent cross-contamination and the spread of pathogens.
- Education and training: Proper training and education of food handlers and workers can help promote awareness and understanding of safe food handling practices.
By following these prevention and control measures, individuals can reduce the risk of contracting foodborne illnesses and contribute to safer food practices in their communities.
Symptoms and Effects of Foodborne Illnesses

Foodborne illnesses can have a variety of symptoms and effects on the human body. These illnesses are caused by consuming food or beverages that are contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins. It is important to be aware of the potential symptoms and effects of foodborne illnesses in order to quickly identify and address the issue.
Common symptoms of foodborne illnesses include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may last for a few hours to several days. In some cases, individuals may also experience dehydration, muscle aches, and fatigue. It is important to note that the severity and duration of symptoms can vary depending on the type and amount of contamination.
- Bacterial infections: Bacterial foodborne illnesses such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever. In some cases, these infections can lead to more serious complications, including kidney failure.
- Viral infections: Viral foodborne illnesses, such as norovirus and hepatitis A, can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. These infections can be highly contagious and can spread rapidly in settings such as restaurants, schools, and cruise ships.
- Parasitic infections: Parasitic foodborne illnesses, such as giardiasis and cryptosporidiosis, can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. These infections are usually caused by consuming contaminated water or food, such as undercooked meat or unwashed fruits and vegetables.
- Toxin-induced illness: Some foodborne illnesses are caused by consuming toxins produced by bacteria or other microorganisms. These toxins can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. One example is botulism, a rare but serious illness caused by the toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a foodborne illness, especially if you experience severe symptoms, persistent vomiting or diarrhea, or if you are pregnant, elderly, or have a weakened immune system. Prompt treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure a faster recovery.
Factors Contributing to Foodborne Illnesses
There are several factors that contribute to the occurrence of foodborne illnesses. Understanding these factors is crucial for preventing and mitigating the risks associated with foodborne illnesses.
One of the main factors is improper food handling and preparation. This includes inadequate hand hygiene, cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods, and improper cooking temperatures. Contaminated hands or utensils can introduce harmful bacteria or viruses to the food, while not cooking food to the proper internal temperature can leave pathogens alive and capable of causing illness.
Another factor is the consumption of raw or undercooked foods. Many foodborne illnesses are caused by consuming foods that are not properly cooked, such as undercooked meat, eggs, or seafood. These foods may contain harmful bacteria or parasites that can cause illness if not destroyed by proper cooking. It is therefore important to follow proper cooking temperatures and guidelines to ensure the safety of these foods.
Furthermore, poor personal hygiene practices can also contribute to the spread of foodborne illnesses. Food handlers who do not practice proper hygiene, such as not washing hands after using the restroom or handling raw meat, can transfer harmful bacteria or viruses to the food they prepare. This can result in the contamination of the food and subsequent illness in those who consume it.
Contaminated water or ingredients can also play a role in foodborne illnesses. If water used in food preparation or ingredients used in recipes are contaminated with bacteria or viruses, they can introduce these pathogens into the food and cause illness. It is important to ensure that water and ingredients are safe and properly handled before use in food preparation.
In conclusion, factors such as improper food handling and preparation, consumption of raw or undercooked foods, poor personal hygiene practices, and contaminated water or ingredients can all contribute to the occurrence of foodborne illnesses. By understanding these factors and implementing proper food safety practices, it is possible to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and protect the health of consumers.