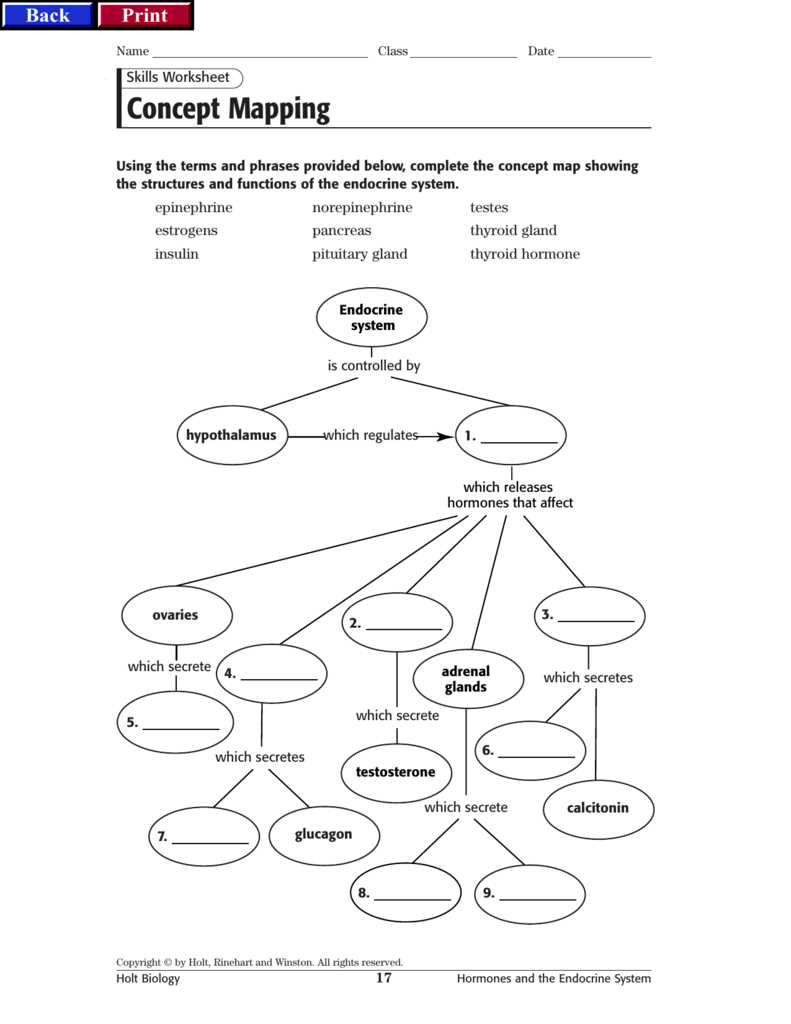
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, from growth and metabolism to reproduction and mood. Understanding the intricate workings of this system is essential for comprehending the complex interplay of hormones within our body. In Chapter 9 of our study, we delve deep into the fascinating world of the endocrine system, tackling various aspects of its anatomy and physiology.
One of the key highlights of this chapter is the endocrine system worksheet, which serves as a valuable tool for assessing your knowledge and understanding of the subject. The worksheet contains a series of thought-provoking questions that require you to demonstrate your grasp of key concepts and phenomena related to the endocrine system. With this answer key, you can now check your responses and evaluate your level of comprehension.
By exploring the answers provided in this key, you will not only gain insight into the correct responses but also develop a deeper understanding of the underlying principles. The key serves as a comprehensive guide, offering detailed explanations and insights into the functioning of various endocrine glands, such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and more.
Whether you are a student seeking to bolster your understanding of the endocrine system or a healthcare professional looking to refresh your knowledge, this Chapter 9 endocrine system worksheet answer key is an invaluable resource. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of the endocrine system together!
Chapter 9 Endocrine System Worksheet Answer Key
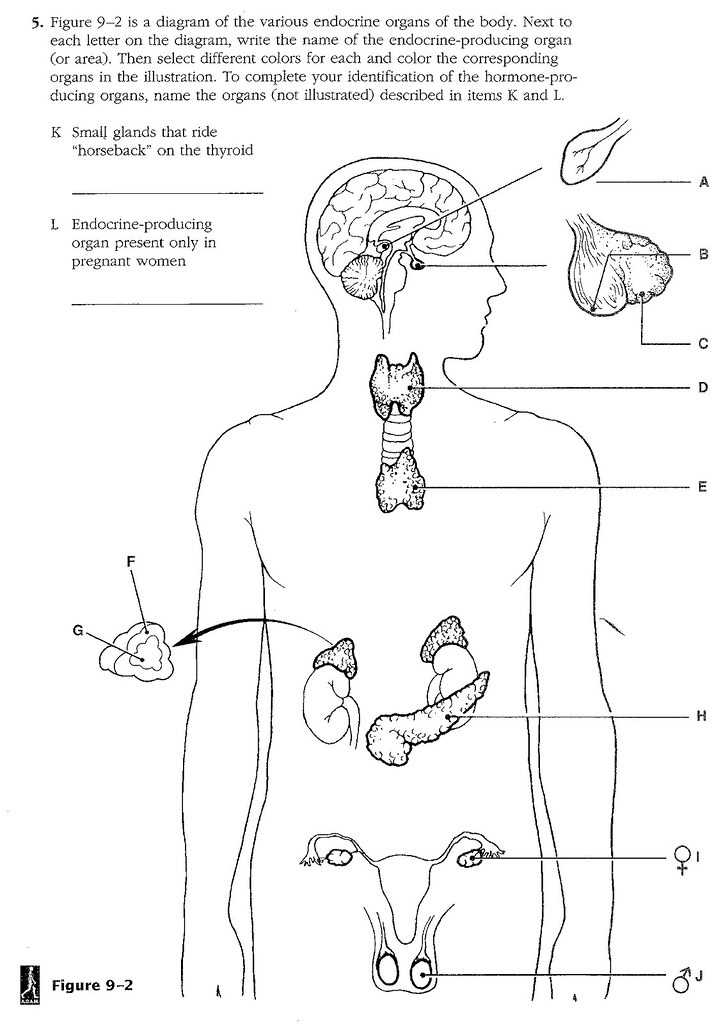
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that produce and secrete hormones, which regulate various functions in the body. Understanding the endocrine system and its role in maintaining homeostasis is key to understanding human physiology. In Chapter 9 of the anatomy and physiology course, students were introduced to the endocrine system and learned about its components and functions.
The Chapter 9 endocrine system worksheet provided students with a series of questions and scenarios to test their understanding of the material covered. The answer key to this worksheet is a valuable resource for students to check their answers and ensure they have a solid grasp of the concepts discussed in class.
One key concept covered in this chapter is the feedback mechanism that regulates hormone secretion. This mechanism involves a sequence of events in which a hormone is released in response to a certain stimulus, and then acts to inhibit or stimulate further hormone production. Understanding this feedback mechanism is crucial for understanding how hormonal imbalances occur and how they can be treated.
The answer key for the Chapter 9 endocrine system worksheet provides students with the correct answers to questions and scenarios related to this feedback mechanism, as well as other important topics such as hormone synthesis, target cells, and specific hormone functions. It serves as a useful tool for students to review their understanding of the material and identify areas where they may need further clarification or study.
Overall, the Chapter 9 endocrine system worksheet and its answer key are important resources for students studying anatomy and physiology. They provide an opportunity for students to test their knowledge and understanding of the endocrine system and ensure they are on track with their studies. By utilizing the answer key, students can identify areas of weakness and focus their efforts on improving their understanding of these concepts.
Understanding the Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and hormones that work together to regulate various bodily functions. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, which is the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment. Understanding how the endocrine system works is essential for understanding how our bodies function and how imbalances can lead to various health issues.
One key aspect of the endocrine system is its use of hormones to communicate messages throughout the body. Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted by specific glands and travel through the bloodstream to reach their target organs or tissues. These hormones bind to specific receptors on the cells and initiate various physiological responses.
The major glands of the endocrine system include:
- The hypothalamus: located in the brain, it controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
- The pituitary gland: often referred to as the “master gland,” it secretes hormones that regulate other endocrine glands.
- The thyroid gland: located in the neck, it produces hormones that regulate metabolism.
- The adrenal glands: located on top of the kidneys, they produce hormones that regulate stress response, metabolism, and electrolyte balance.
- The pancreas: it produces insulin and glucagon, hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
- The ovaries (in females) and testes (in males): these glands produce sex hormones.
Imbalances in the endocrine system can have significant effects on overall health. For example, an overproduction or underproduction of certain hormones can lead to conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances. It is crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced diet, and stress management, to support the proper functioning of the endocrine system.
Functions of the Endocrine System
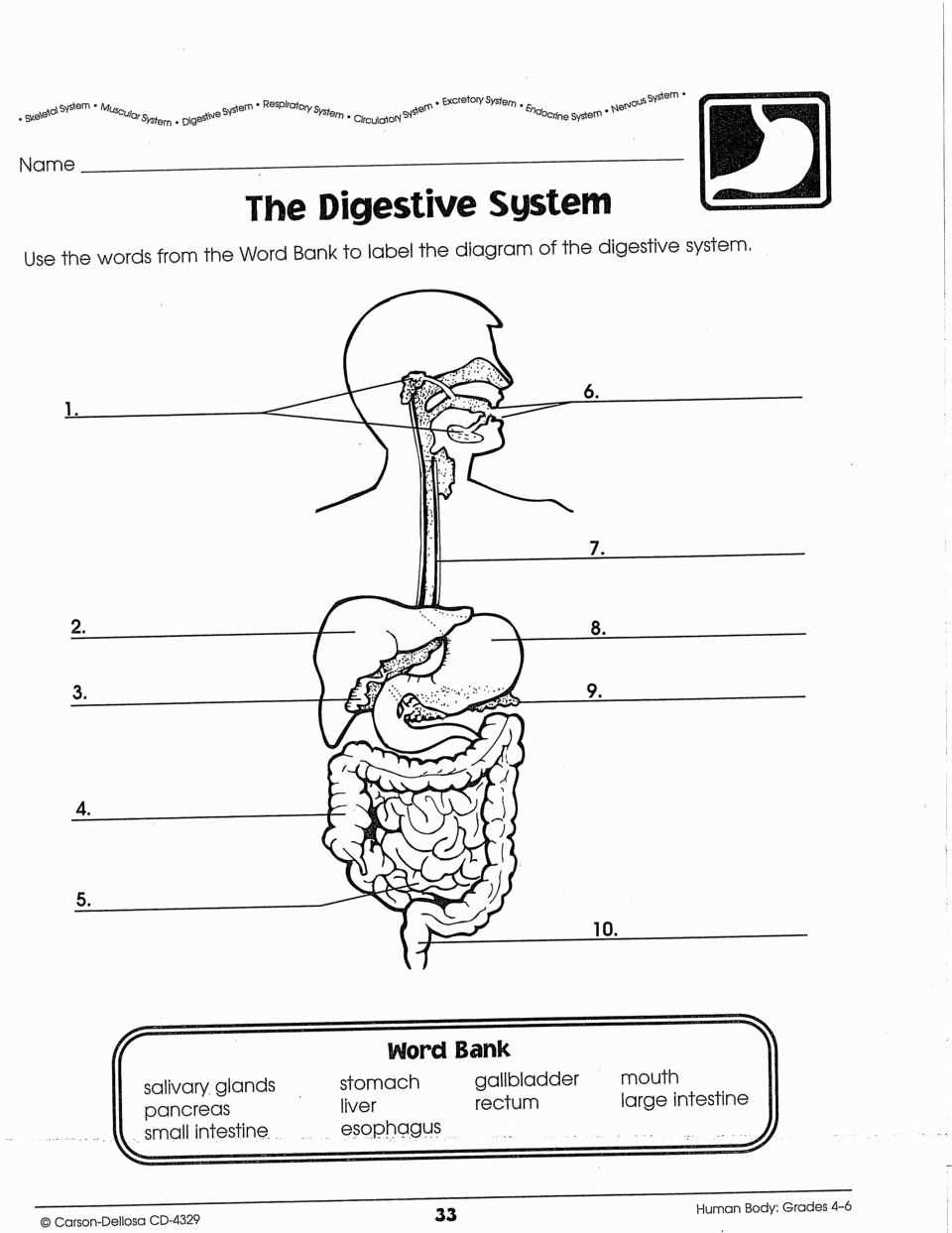
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, or the balance of the body’s internal environment. It is a complex network of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, where they travel to target tissues and organs. These hormones act as chemical messengers, controlling a wide range of bodily functions.
One of the main functions of the endocrine system is to regulate metabolism. The thyroid gland, for example, produces hormones that control the rate at which the body uses energy. If the thyroid gland is overactive, the body’s metabolism speeds up, leading to weight loss and increased heart rate. On the other hand, if the thyroid gland is underactive, the body’s metabolism slows down, resulting in weight gain and fatigue.
The endocrine system also plays a key role in growth and development. The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” releases growth hormones that stimulate cell division and growth in various tissues and organs. These hormones are especially important during childhood and adolescence, when growth spurts occur. In addition to growth, the endocrine system is involved in regulating sexual development and reproduction.
In addition to metabolism and growth, the endocrine system helps regulate blood sugar levels. The pancreas, for example, produces insulin, a hormone that allows cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream. Insulin helps lower blood sugar levels by facilitating the storage of glucose in the liver and muscles. In diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels.
The endocrine system also influences mood, emotions, and behavior. The adrenal glands, located on top of the kidneys, release hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol in response to stress. These hormones help the body react to challenging situations, providing a surge of energy and increasing alertness. However, chronic stress can disrupt the balance of hormones in the body, leading to anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders.
In summary, the endocrine system is responsible for regulating metabolism, growth and development, blood sugar levels, and emotional responses. Without the proper functioning of this system, various imbalances and disorders can occur. Understanding the functions of the endocrine system is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Key Hormones and their Functions
The endocrine system is composed of various glands that produce and release hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating and controlling various bodily functions. Understanding the functions of key hormones can provide insight into how the body maintains homeostasis and promotes overall health.
1. Insulin: Insulin is produced by the pancreas and regulates blood sugar levels. It allows cells to take up glucose and stores excess glucose as glycogen for later use. Insufficient insulin production or impaired insulin function can lead to diabetes mellitus.
2. Thyroxine: Thyroxine, also known as T4, is produced by the thyroid gland and regulates metabolism. It controls the rate at which cells convert nutrients into energy, therefore affecting growth, development, and body temperature.
3. Adrenaline: Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is produced by the adrenal glands and is responsible for the body’s response to stress or danger. It increases heart rate, blood pressure, and energy availability, preparing the body for the fight-or-flight response.
4. Progesterone: Progesterone is produced by the ovaries and plays a vital role in regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting pregnancy. It prepares the uterus for implantation and maintains the uterine lining during early pregnancy.
5. Growth Hormone: Growth hormone, produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates growth and development in children and adolescents. It also plays a role in regulating metabolism, muscle strength, and bone density in adults.
6. Oxytocin: Oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone,” is produced by the hypothalamus and released by the pituitary gland. It is involved in social bonding, sexual reproduction, and the initiation of labor during childbirth.
These are just a few examples of key hormones and their functions within the endocrine system. Each hormone has specific targets and effects on the body, contributing to the intricate balance that allows our bodies to function properly.
How the Endocrine System Works
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that work together to regulate and maintain various bodily functions. Its main function is to secrete hormones, which are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to target cells or organs. These hormones help to control growth, metabolism, reproduction, and many other processes in the body.
The key players in the endocrine system are the glands, which include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and reproductive glands. Each gland produces and releases specific hormones that have unique functions and effects on the body. The hypothalamus, located in the brain, acts as the control center of the endocrine system and regulates the secretion of many hormones.
Hormones can have either a stimulating or inhibiting effect on their target cells or organs. They bind to specific receptors on these cells, triggering a cascade of events that result in a specific response. For example, the thyroid hormone stimulates metabolism in cells, while insulin promotes the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells.
The endocrine system works in close coordination with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis in the body. The nervous system provides rapid, short-term control over bodily functions through electrical signals, while the endocrine system provides slower, long-term regulation through hormone release. Together, these two systems ensure that the body functions properly and adapts to changes in the environment.
In summary, the endocrine system plays a vital role in regulating and maintaining various bodily functions. By producing and releasing hormones, the glands of the endocrine system help to control growth, metabolism, reproduction, and other processes in the body. Through their effects on target cells and organs, hormones ensure that the body functions properly and stays in balance.
Disorders of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that produce and release hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones regulate various bodily functions and maintain overall homeostasis. However, when there is a dysfunction or imbalance in the endocrine system, it can lead to a variety of disorders.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common disorders of the endocrine system. It occurs when the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin or when the body’s cells become resistant to insulin. This results in elevated blood glucose levels, which can lead to various complications if not properly managed. Diabetes mellitus is classified into two main types: type 1, which is an autoimmune disease, and type 2, which is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and poor diet.
Hyperthyroidism is another endocrine disorder that occurs when the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. This can lead to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and excessive sweating. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism and is characterized by the immune system attacking the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism is the opposite of hyperthyroidism and occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism and is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
Other disorders of the endocrine system include Cushing’s syndrome, which is characterized by excessive production of cortisol due to a tumor or long-term use of corticosteroid medications, and acromegaly, which occurs when the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone in adulthood, leading to enlarged hands, feet, and facial features.
In conclusion, disorders of the endocrine system can have significant impacts on an individual’s overall health and well-being. Proper diagnosis and management are essential in order to minimize the complications and improve quality of life for individuals with endocrine disorders.
Common Questions about the Endocrine System
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall balance and regulating various bodily functions. However, it can often be complex and confusing, leading to numerous questions. Here are some common questions about the endocrine system and their answers:
1. What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is a collection of glands that produces and secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones act as chemical messengers and regulate various bodily processes such as metabolism, growth, development, and reproduction. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads.
2. What are the common disorders of the endocrine system?
There are several disorders that can affect the endocrine system. Some common disorders include diabetes, thyroid disorders (such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism), adrenal disorders (such as Cushing’s syndrome and Addison’s disease), and reproductive disorders (such as polycystic ovary syndrome). These disorders can lead to various symptoms and complications and often require medical management.
3. How can I maintain a healthy endocrine system?
To maintain a healthy endocrine system, it is important to adopt a balanced and healthy lifestyle. This includes consuming a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, managing stress levels, getting enough sleep, and avoiding exposure to harmful substances. It is also crucial to undergo regular check-ups and screenings to detect any potential disorders early on and seek prompt medical intervention if needed.
4. How does aging affect the endocrine system?

Aging can have an impact on the endocrine system. As we age, the production and regulation of hormones may decrease, leading to hormonal imbalances and an increased risk of developing endocrine disorders. Additionally, certain age-related conditions, such as osteoporosis and menopause, can be influenced by hormonal changes. Regular monitoring and hormone replacement therapy may be necessary in some cases to manage these changes effectively.
5. Can lifestyle choices affect the endocrine system?
Yes, lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on the endocrine system. Factors such as diet, exercise, stress levels, and exposure to environmental toxins can affect hormone production and regulation. A healthy lifestyle that includes a nutritious diet, regular physical activity, stress management techniques, and avoidance of harmful substances can help maintain the optimal functioning of the endocrine system.
In conclusion, the endocrine system is a complex network of glands and hormones that regulate various bodily functions. Understanding common questions about the endocrine system can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and well-being.