When discussing the topic of the Cold War, it is crucial to understand its origins, key events, and notable figures. This webquest offers a comprehensive look into the Cold War, providing answers to important questions and shedding light on its impact on global politics. By exploring the webquest, readers will gain a deeper understanding of the geopolitical tensions between the United States and Soviet Union that defined this era.
One of the first questions that arise when studying the Cold War is: What were the main causes of the Cold War? The answer lies in the ideological differences between the two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union. The United States championed capitalism and democracy, while the Soviet Union promoted communism. This clash of ideologies, along with geopolitical competition and a deep mistrust between the two nations, fueled the tensions that led to the Cold War.
Another crucial aspect to examine is the key events that occurred during the Cold War. From the Berlin Airlift to the Cuban Missile Crisis, these events played a significant role in shaping the course of the conflict. The Berlin Airlift was a response to the Soviet blockade of West Berlin, showcasing the determination of the United States and its allies to support the democratic enclave. The Cuban Missile Crisis, on the other hand, brought the world to the brink of nuclear war, as the United States and Soviet Union engaged in a tense standoff over Soviet missiles in Cuba.
Naturally, when delving into the Cold War, it is important to explore the individuals who played prominent roles during this period. Figures such as Winston Churchill, Harry Truman, Joseph Stalin, and Nikita Khrushchev all had significant influence in shaping the outcome of the Cold War. Churchill’s famous “Iron Curtain” speech, Truman’s Truman Doctrine, Stalin’s leadership of the Soviet Union, and Khrushchev’s ousting of Stalin all had lasting impacts on the geopolitical landscape of the time.
In conclusion, the Cold War was a complex and multifaceted conflict that spanned over several decades. By embarking on this webquest and exploring the answers to key questions surrounding the Cold War, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of this pivotal era in global history.
Cold War Webquest Answers
The Cold War was a period of intense geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, spanning from the end of World War II to the early 1990s. It was characterized by ideological clashes, proxy wars, and a race for global influence between the two superpowers. This webquest provides answers to key questions about the Cold War, shedding light on its causes, major events, and consequences.
Causes of the Cold War:
- The ideological differences between capitalism and communism played a significant role in the emergence of the Cold War. The United States championed capitalism and democracy, while the Soviet Union promoted socialism and communism.
- The power vacuum left by the collapse of Nazi Germany and the subsequent division of Europe into Eastern and Western spheres of influence also fueled tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union.
- The development and stockpiling of nuclear weapons by both countries intensified the arms race and heightened fears of a potentially devastating nuclear conflict.
Major Events of the Cold War:
- The Berlin Blockade and Airlift: In response to the Western Allies’ decision to introduce a new currency in West Berlin, the Soviet Union blockaded the city. The United States and its allies responded with an airlift campaign to supply West Berlin with essential goods, marking a significant standoff between the two powers.
- The Cuban Missile Crisis: The closest the Cold War came to direct nuclear confrontation, the Cuban Missile Crisis occurred when the United States discovered Soviet nuclear missiles in Cuba. Tensions ran high, but ultimately a peaceful resolution was reached, with both sides withdrawing their missiles.
- The Korean War: Fought between North and South Korea, the Korean War was a proxy war between the United States and the Soviet Union. It ended in a stalemate, with the Korean peninsula divided at the 38th parallel.
Consequences of the Cold War:
- The division of Europe into Western and Eastern spheres of influence led to the formation of military alliances such as NATO and the Warsaw Pact, which further solidified the bipolar nature of the Cold War.
- The arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union resulted in the production of vast quantities of nuclear weapons, heightening fears of a global catastrophe.
- The Cold War also had significant impacts on proxy wars in other parts of the world, such as Vietnam, Afghanistan, and Angola, where the United States and the Soviet Union supported opposing factions.
In conclusion, the Cold War was a complex and multifaceted period of international tension. This webquest provides answers to important questions about its causes, major events, and consequences, highlighting the deep ideological divide and geopolitical rivalries between the United States and the Soviet Union.
The Origins of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension that lasted from the end of World War II in 1945 until the early 1990s. It was a conflict between the two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union, who were ideologically opposed to each other. The origins of the Cold War can be traced back to several key events and factors.
One of the main causes of the Cold War was the ideological differences between the United States and the Soviet Union. The United States was a capitalist democracy, while the Soviet Union was a communist state. These opposing ideologies clashed and created tensions between the two countries. The United States viewed communism as a threat to its democratic values and sought to contain its spread.
- Yalta Conference: Another key event that contributed to the origins of the Cold War was the Yalta Conference in 1945. This conference was held between the leaders of the United States, the Soviet Union, and Great Britain to discuss the post-war reorganization of Europe. However, the conference revealed the differences in their objectives and led to mistrust and suspicion between the two superpowers.
- Soviet Expansion: The Soviet Union’s expansionist policies also played a significant role in the origins of the Cold War. The Soviet Union aimed to spread communism and exert dominance over Eastern Europe. This expansionist agenda threatened the United States and its allies, leading to a heightened sense of tension and rivalry.
- Nuclear Arms Race: The development and proliferation of nuclear weapons also fueled the Cold War. Both the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in an arms race, each trying to outdo the other in terms of military power. This arms race heightened the fear of a global nuclear conflict and further intensified the Cold War tensions.
- Proxy Wars: The Cold War also saw the emergence of proxy wars, where the United States and the Soviet Union supported opposing factions in other countries. These conflicts, such as the Korean War and the Vietnam War, further deepened the divide between the two superpowers and their respective allies.
In conclusion, the origins of the Cold War can be attributed to the ideological differences, key events like the Yalta Conference, Soviet expansionism, the nuclear arms race, and proxy wars. These factors created a climate of mistrust and rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, which defined the Cold War era.
Key Players of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of intense political and military rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union that lasted from the end of World War II until the early 1990s. During this time, several key players emerged who played crucial roles in shaping the course of the conflict.
1. United States
The United States, led by President Harry S. Truman, was one of the main players in the Cold War. The country advocated for the spread of democracy and capitalism, while opposing the expansion of communism. The United States implemented several containment strategies, such as the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan, to prevent the spread of communism in Europe.
2. Soviet Union
The Soviet Union, under the leadership of Joseph Stalin and later Nikita Khrushchev, was the other major player in the Cold War. The country promoted the ideology of communism and sought to spread it globally. The Soviet Union established the Eastern Bloc, a group of communist states in Eastern Europe, and supported various revolutions and movements that aligned with their interests.
3. Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, played a significant role in shaping the early years of the Cold War. In his famous “Iron Curtain” speech in 1946, Churchill warned about the Soviet Union’s expansionist policies and called for a united front against communism. His strong stance against the Soviet Union helped rally Western countries in their opposition to communism.
4. Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong, the leader of the Chinese Communist Party and later the Chairman of the Communist Party of China, was a key player in the Cold War. Mao led the communist revolution in China and established the People’s Republic of China in 1949. The Soviet Union and China formed an alliance during the early years of the Cold War, but their relationship deteriorated in the 1960s.
5. Fidel Castro
Fidel Castro, the leader of the Cuban Revolution, played a significant role in the Cold War as the leader of a communist state situated just 90 miles off the coast of Florida. Castro’s Cuba became a close ally of the Soviet Union, and the presence of Soviet nuclear missiles in Cuba led to the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962, one of the most dangerous moments of the Cold War.
- Other key players in the Cold War include leaders like John F. Kennedy, Ronald Reagan, Mikhail Gorbachev, and Ho Chi Minh who played important roles in shaping the conflict and its eventual resolution.
Overall, the Cold War was characterized by intense rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, with several key players shaping the political, military, and ideological aspects of the conflict.
Events that Escalated Tensions
The Cold War was characterized by a series of events that escalated tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union. These events, often referred to as “flashpoints,” brought the two superpowers to the brink of war and contributed to the overall atmosphere of hostility and mistrust that defined the Cold War.
One such event was the Berlin Blockade and Airlift. In 1948, the Soviet Union blockaded the city of Berlin, cutting off all road, rail, and water access to the Western-occupied sectors. In response, the United States and its allies launched the Berlin Airlift, a massive effort to supply the city with food, fuel, and other essentials by air. This standoff lasted for almost a year and showcased the determination of the Western powers to preserve their presence in Berlin. It also highlighted the East-West divide and the potential for direct military conflict.
- The Cuban Missile Crisis was another key event that escalated tensions in the Cold War. In 1962, the United States discovered that the Soviet Union had installed nuclear missiles in Cuba, just 90 miles off the coast of Florida. This discovery sparked a 13-day standoff, during which the world was on the brink of nuclear war. Ultimately, the crisis was resolved diplomatically, with the United States agreeing not to invade Cuba and the Soviet Union removing its missiles. However, the Cuban Missile Crisis revealed the immense dangers of the Cold War and marked a turning point in U.S.-Soviet relations.
- The Korean War, which took place from 1950 to 1953, was another event that heightened tensions between the two superpowers. The war began when North Korea, supported by the Soviet Union and China, invaded South Korea. The United States, with the backing of the United Nations, intervened to support South Korea. The conflict escalated into a brutal and bloody war, which ultimately ended in a stalemate with the establishment of a demilitarized zone along the 38th parallel. The Korean War served as a proxy conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union, highlighting their differing ideologies and strategies.
These are just a few examples of the events that escalated tensions during the Cold War. Each one contributed to the overall climate of hostility and suspicion between the United States and the Soviet Union, and reinforced the divisions between the two superpowers and their respective allies.
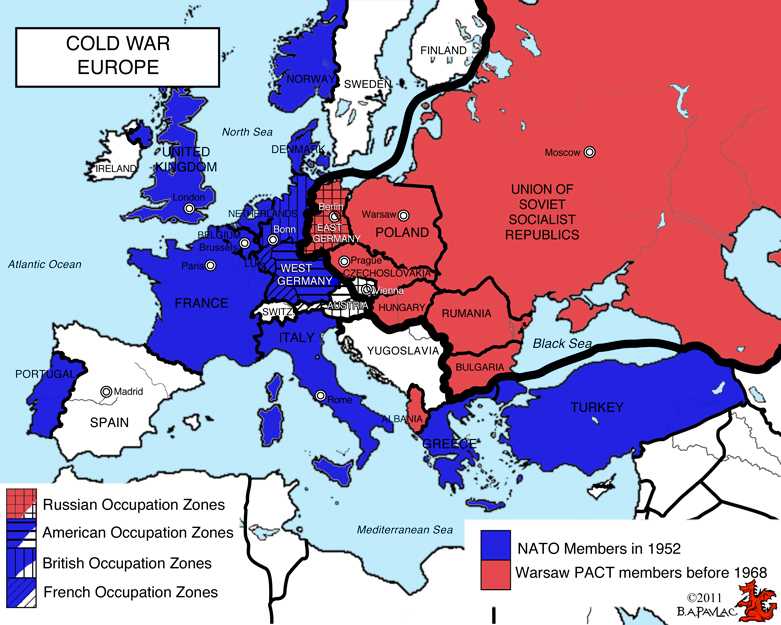
The Iron Curtain and Division of Europe
One of the most significant events during the Cold War was the establishment of the Iron Curtain, a term coined by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill in 1946. The Iron Curtain was a metaphorical and physical division that separated the Western democracies and the Soviet-controlled Eastern European countries. This division marked a clear boundary between the democratic Western world and the communist Eastern bloc.
Following World War II, the Soviet Union sought to expand its influence in Eastern Europe, establishing communist governments in countries such as Poland, Hungary, and Czechoslovakia. The Iron Curtain became a symbol of this division, as it represented not only a physical barrier, but also the ideological divide between communism and capitalism.
The Iron Curtain had significant political, economic, and social consequences for Europe.
- Politically, it solidified the bipolarity of the Cold War, with the United States and its Western allies forming NATO, and the Soviet Union and its Eastern bloc allies forming the Warsaw Pact. This division led to heightened tensions and the arms race between the two superpowers.
- Economically, the Iron Curtain inhibited trade and cooperation between the Western and Eastern European countries. As a result, the Eastern bloc states, under Soviet control, experienced economic stagnation and limited development.
- Socially, the Iron Curtain created a sense of isolation and limited freedom for the citizens of Eastern European countries. The communist governments tightly controlled information and stifled dissent, leading to a lack of political and cultural diversity.
In conclusion, the Iron Curtain was a symbol of the division between East and West during the Cold War. It had significant political, economic, and social consequences for Europe, reinforcing the ideological and military standoff between the United States and the Soviet Union.