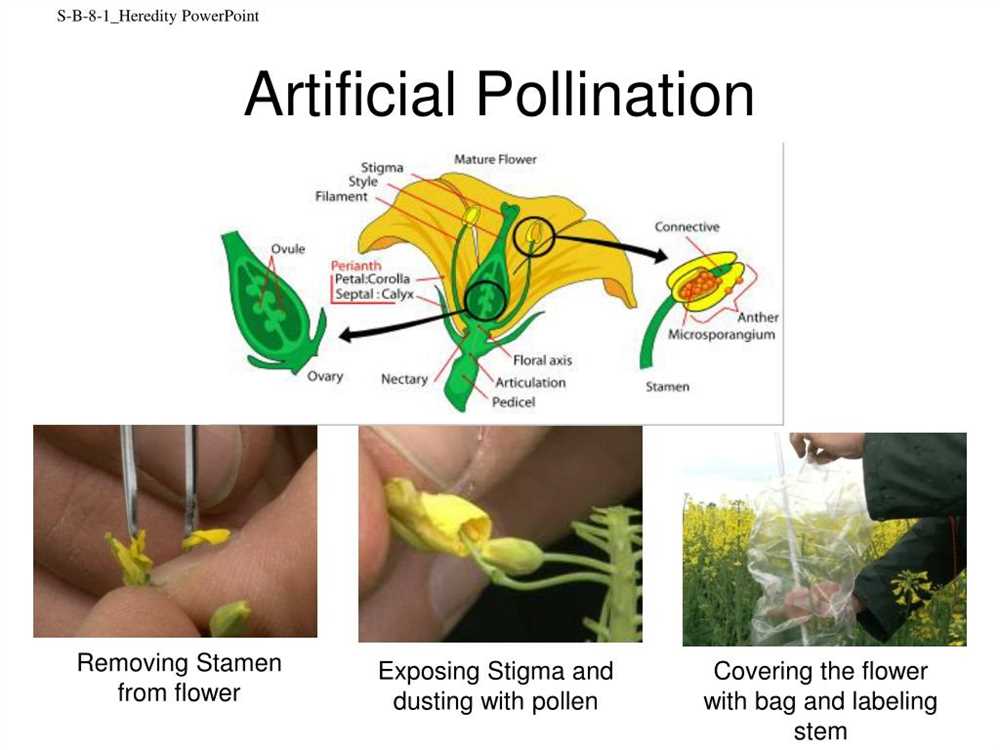
The process of flower pollination is a vital mechanism for the reproduction and survival of many plant species. It involves the transfer of pollen grains from the male parts of a flower to the female parts, leading to fertilization and the production of seeds. To better understand this intricate process, a flower pollination gizmo has been developed, providing educators and students with a hands-on learning experience.
The flower pollination gizmo answer key serves as a guide to help users navigate through the various components and activities of the gizmo. It provides detailed explanations and solutions to the questions and challenges presented in the gizmo, allowing users to deepen their understanding of the pollination process.
One key aspect covered in the flower pollination gizmo is the different methods of pollen transfer, including self-pollination and cross-pollination. By exploring these concepts, users can gain insights into the advantages and disadvantages of each method, as well as how they contribute to the genetic diversity and adaptation of plants.
Additionally, the flower pollination gizmo answer key delves into the role of pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds, in the pollination process. It highlights the importance of these organisms in the ecosystem and how their behaviors and characteristics enhance the efficiency of pollination.
Understanding the Flower Pollination Gizmo
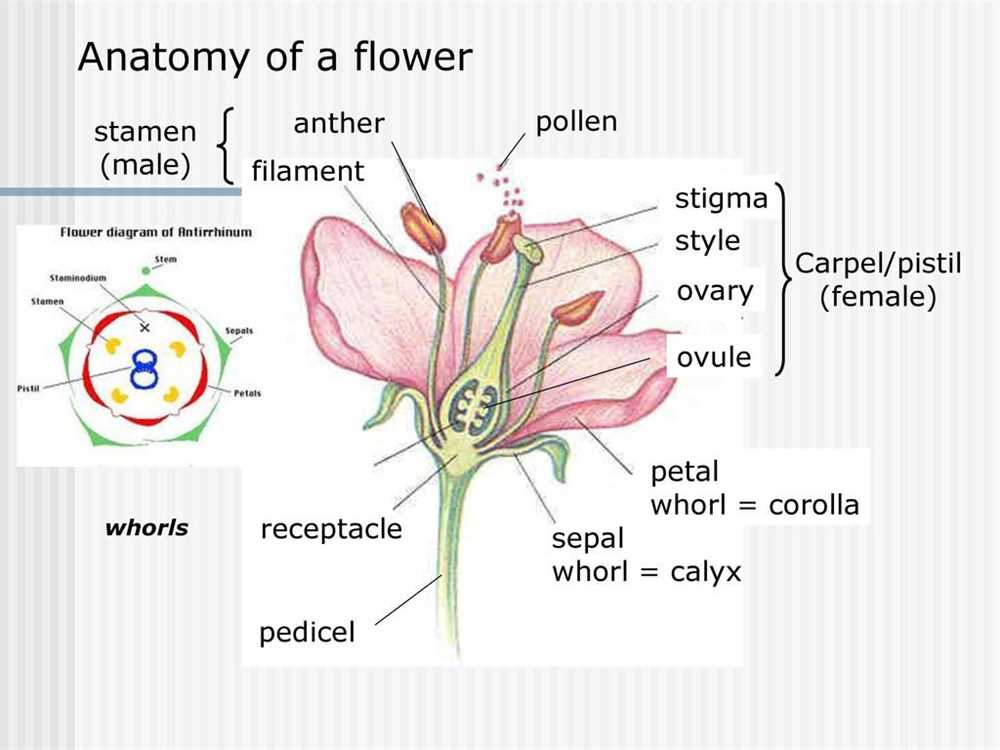
Flower pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the male reproductive organ (stamen) to the female reproductive organ (pistil) of a flower, resulting in the fertilization of the flower and the production of seeds. This process is essential for plant reproduction and the continuation of species. To understand this intricate process, a flower pollination gizmo has been developed, which allows for hands-on exploration and observation of pollination.
The flower pollination gizmo consists of several components that mimic the different parts of a flower and the agents involved in pollination. These components include a flower model with detachable parts such as the petals, stamens, and pistil, as well as various tools such as a paintbrush and tweezers. The gizmo also comes with a detailed guide that provides information on the different types of pollination and the role of specific agents such as insects, birds, and wind.
The use of the flower pollination gizmo
The flower pollination gizmo is designed to engage learners in hands-on activities that simulate the process of flower pollination. By manipulating the different parts of the flower model and using the tools provided, learners can observe how pollination occurs and understand the various mechanisms involved.
- Exploring different types of pollination: The gizmo enables learners to explore the different types of pollination, such as self-pollination and cross-pollination. By removing the anthers (male reproductive organs) from one flower and brushing the pollen onto the stigma (female reproductive organ) of another flower, learners can simulate cross-pollination and observe how the pollen is transferred.
- Examining the role of pollinators: The gizmo allows learners to understand the crucial role of pollinators in the pollination process. By using the tools provided, learners can mimic the actions of insects or birds in transferring pollen from one flower to another. They can also explore how wind pollination occurs by gently blowing on the flower model and observing how the pollen moves through the air.
- Observing the formation of seeds: After simulating pollination, learners can observe the formation of seeds by examining the pistil and looking for changes in the flowers’ reproductive structures. This helps reinforce the connection between pollination and seed production.
The flower pollination gizmo offers an engaging and interactive way for learners to understand the intricate process of flower pollination. Through hands-on exploration and observation, learners can develop a deeper appreciation for the role of pollination in plant reproduction and the importance of various agents in this process.
The Importance of Pollination
Pollination is a crucial process in the reproduction of flowering plants. It involves the transfer of pollen grains from the male part of the flower, called the stamen, to the female part, known as the pistil. This transfer can occur through various means, including wind, water, animals, and insects.
One of the primary reasons why pollination is essential is that it enables the fertilization of plants, resulting in the production of seeds. These seeds serve as the foundation for the growth and propagation of new plants. Additionally, successful pollination leads to the development of fruits, which are not only important for the plant’s reproduction but also serve as a valuable food source for animals, including humans.
Insects
Insects, such as bees, butterflies, and beetles, are one of the most common carriers of pollen. They are attracted to flowers by their vibrant colors, scents, and nectar, which serves as their source of food. As insects move from one flower to another, they unintentionally pick up and deposit pollen, facilitating the pollination process. This mutually beneficial relationship between plants and insects is known as mutualism.
Wind
Wind pollination, also known as anemophily, occurs in plants that produce large quantities of lightweight pollen grains. These plants do not rely on the direct involvement of animals or insects for pollination. Instead, they release their pollen into the air, where it can be carried over long distances by the wind. This method of pollination is common in various grasses, trees, and some agricultural crops.
Benefits for Biodiversity
The process of pollination plays a vital role in maintaining biodiversity. By allowing plants to reproduce and produce seeds, pollinators contribute to the growth and diversity of plant populations. Additionally, pollination helps in the dispersal of plant genes, which aids in the adaptation of plants to changing environmental conditions. Without pollinators, many plant species would struggle to survive, leading to a significant loss of biodiversity.
In conclusion, pollination is a critical process that ensures the reproductive success of flowering plants. It enables the production of seeds and fruits, facilitates the growth and propagation of new plants, and contributes to the overall biodiversity of our ecosystems. Understanding and preserving the mechanisms of pollination is essential for the sustainability of our natural environments and the well-being of both plants and animals.
Role of the flower gizmo in pollination
The flower gizmo plays a crucial role in the process of pollination. It is a tool designed to mimic the flower’s reproductive organs and attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds. With its vibrant colors, intricate shapes, and enticing scents, the flower gizmo effectively lures these pollinators, encouraging them to land and interact with it.
One of the key features of the flower gizmo is its ability to produce nectar, a sugary substance that serves as a reward for the pollinators. Nectar acts as a food source, providing the necessary energy for the pollinators to continue their flight and visit other flowers. As the pollinators feed on the nectar, they inadvertently come into contact with pollen grains, which are located on the stamen of the flower gizmo.
The pollen grains, which contain the male reproductive cells of the flower, attach themselves to the bodies of the pollinators. When the pollinators move on to another flower gizmo or a different flower altogether, they transfer the pollen grains to the stigma, the female reproductive organ. This process is known as pollination and is essential for the fertilization and reproduction of flowering plants.
The flower gizmo also plays a role in ensuring cross-pollination, which is the transfer of pollen between different plants of the same species. By attracting a variety of pollinators, the flower gizmo increases the chances of cross-pollination occurring. This genetic exchange increases the genetic diversity of the plant population, making it more resilient to changes in the environment and increasing the chances of successful reproduction.
In conclusion, the flower gizmo acts as a powerful tool in the process of pollination. By mimicking the flower’s reproductive organs and attracting pollinators, it facilitates the transfer of pollen and ensures the reproduction of flowering plants. Its role in promoting cross-pollination also contributes to the genetic diversity and adaptation of plant populations. Overall, the flower gizmo is an essential device in understanding and studying the complex process of pollination.
Components of the flower gizmo

The flower gizmo is a tool that is designed to simulate the process of flower pollination. It consists of several key components that work together to create a realistic and interactive simulation. These components include:
- Flower Parts: The gizmo allows users to manipulate and explore the different parts of a flower, including the petals, stamen, and pistil. The petals can be opened and closed, the stamen can be moved, and the pistil can be accessed and examined.
- Pollen: The gizmo features virtual pollen that can be collected and transferred between flowers. Users can see how pollen is transferred during pollination and how it fertilizes the ovules within the pistil.
- Bees: The gizmo also includes virtual bees that interact with the flowers. Users can observe how bees collect pollen from one flower and transfer it to another, mimicking the natural pollination process that occurs in the real world.
- Observations: Users can make observations and record data within the gizmo. They can note the number of pollen grains collected, track the movement of the bees, and record any changes they observe in the flowers as a result of pollination.
The flower gizmo provides a hands-on learning experience that allows users to explore the intricate process of flower pollination. It enables students to manipulate and interact with the different components of a flower, making it an effective tool for teaching and learning about plant reproduction.
How to use the flower pollination gizmo
The flower pollination gizmo is a useful tool that can help you understand the process of pollination in plants. By simulating the interaction between flowers and pollinators, you can observe and learn about the different strategies plants use to attract pollinators and ensure the successful transfer of pollen.
To use the flower pollination gizmo, start by selecting a flower from the available options. Each flower has unique characteristics such as color, shape, and scent, which can attract specific types of pollinators. Choose a flower that you want to examine and learn more about.
- Step 1: Select a flower
| Flower Type | Color | Shape | Scent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rose | Red | Round | Strong |
| Sunflower | Yellow | Disc | Mild |
| Tulip | Pink | Cup | None |
- Step 2: Observe the flower’s characteristics
Once you have selected a flower, take note of its color, shape, and scent. These characteristics play a crucial role in attracting specific pollinators. For example, brightly colored flowers like the rose may attract bees, while flowers with a strong scent like certain orchids may attract butterflies.
Remember to observe the flower’s characteristics closely and make note of any patterns or relationships between the flower and its potential pollinators.
- Step 3: Simulate pollination
Using the gizmo, simulate the process of pollination by selecting a pollinator and allowing it to interact with the flower. Pay attention to the behavior of the pollinator and how it interacts with the flower. Does it land on the flower? Does it attempt to collect pollen? Observe and take note of any changes in the flower’s structure and the behavior of the pollinator.
By simulating the process of pollination, you can gain insights into the relationship between flowers and pollinators and how different factors influence successful pollination.
Using the flower pollination gizmo provides a hands-on and interactive way to learn about the fascinating process of pollination in plants. By understanding the strategies plants use to attract pollinators, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships that exist in the natural world.
Troubleshooting common issues with the gizmo
Flower pollination gizmo is a valuable tool for understanding the process of pollination in flowers. However, like any technological device, it can sometimes encounter common issues that may cause difficulties in its functioning. Here are some common problems that users may experience while using the gizmo, along with possible solutions:
1. Gizmo not turning on:
If the gizmo is not turning on, the first thing to check is the battery. Make sure that the battery is properly inserted and has enough charge. If the battery is low, replace it with a new one. Another possible cause could be a faulty power button. Try pressing the power button firmly and make sure it is not stuck.
2. Plant not responding to pollination:
If the plant in the gizmo is not responding to pollination, there are a few things you can check. First, make sure that the gizmo is set to “Pollination Mode” and that the pollination tools are properly positioned near the flower’s stigma. Also, check if the flower is mature enough for pollination. If the flower is too young or too old, it may not respond to pollination.
3. Inaccurate pollination results:
If you are getting inaccurate pollination results, there could be a few reasons for this. Firstly, double-check that the pollination tools are in the correct position and that they are making contact with the flower’s stigma. Also, ensure that the flower is fully open and that there are no obstructions preventing proper pollination. Lastly, make sure that the gizmo is properly calibrated and that the measurements are accurate.
By troubleshooting these common issues, users can ensure a smooth functioning of the flower pollination gizmo. If the problem persists, it is recommended to refer to the user manual or seek assistance from the manufacturer for further troubleshooting steps.