
The osteopathic structural exam is a comprehensive assessment that evaluates the alignment, mobility, and functionality of the body’s musculoskeletal system. It is a fundamental part of osteopathic medicine, as it helps identify any structural imbalances or dysfunctions that may be contributing to a patient’s symptoms.
This exam goes beyond just examining joint range of motion; it involves a hands-on approach where the physician palpates, or feels, the body’s structures to assess their position, texture, and function. By doing so, they can identify any areas of tension, restrictions, or misalignments that may be causing pain, discomfort, or other symptoms.
During the osteopathic structural exam, the physician focuses not only on the area of complaint but also assesses the whole body. They understand that the body functions as an interconnected system, and imbalances in one area can affect the body as a whole. By evaluating the body from head to toe, the physician can identify any underlying structural issues that may be contributing to the patient’s condition.
Once the physician has completed the osteopathic structural exam, they can develop a personalized treatment plan based on their findings. This may involve a combination of hands-on techniques, such as soft tissue manipulation, joint mobilization, or muscle energy techniques, to restore proper alignment and function to the body. The goal is to promote the body’s natural ability to heal itself and alleviate the patient’s symptoms.
Osteopathic Structural Exam: An Essential Assessment Tool for Osteopaths
The osteopathic structural exam is a crucial assessment tool used by osteopaths to evaluate the musculoskeletal system and identify any structural imbalances or dysfunctions. It is a comprehensive examination that involves observing, palpating, and evaluating the patient’s body alignment, posture, range of motion, and tissue texture. This exam allows osteopaths to gather valuable information about the patient’s physical condition and guide their treatment approach.
During the osteopathic structural exam, the osteopath carefully assesses the patient’s standing, sitting, and lying positions to evaluate the alignment of the spine, pelvis, and other body structures. This assessment helps the osteopath identify any misalignments or asymmetries that may be contributing to the patient’s symptoms or impairing their overall function. By assessing the patient’s range of motion, the osteopath can also determine the mobility and flexibility of the joints, muscles, and ligaments, which can provide further insights into the patient’s condition.
The osteopathic structural exam involves palpation, which allows the osteopath to assess the tissue texture of various body structures. By using their hands, the osteopath can feel for areas of tension, tightness, or abnormalities in the muscles, fascia, and other soft tissues. Palpation provides valuable information about the health and condition of the tissues and helps the osteopath identify any areas of dysfunction that need to be addressed during treatment.
In addition to evaluating the musculoskeletal system, the osteopathic structural exam also includes assessing other body systems, such as the respiratory and circulatory systems. By observing the patient’s breathing patterns and listening to their heart and lung sounds, the osteopath can gather information about the patient’s overall health and any potential dysfunctions that may be affecting their well-being.
The osteopathic structural exam is an essential assessment tool for osteopaths as it allows them to gather comprehensive information about their patients’ physical condition and determine the most appropriate treatment approach. By evaluating the musculoskeletal system, palpating the tissues, and assessing other body systems, osteopaths can identify the root causes of their patients’ symptoms and provide targeted and effective treatment.
Understanding the Osteopathic Structural Exam
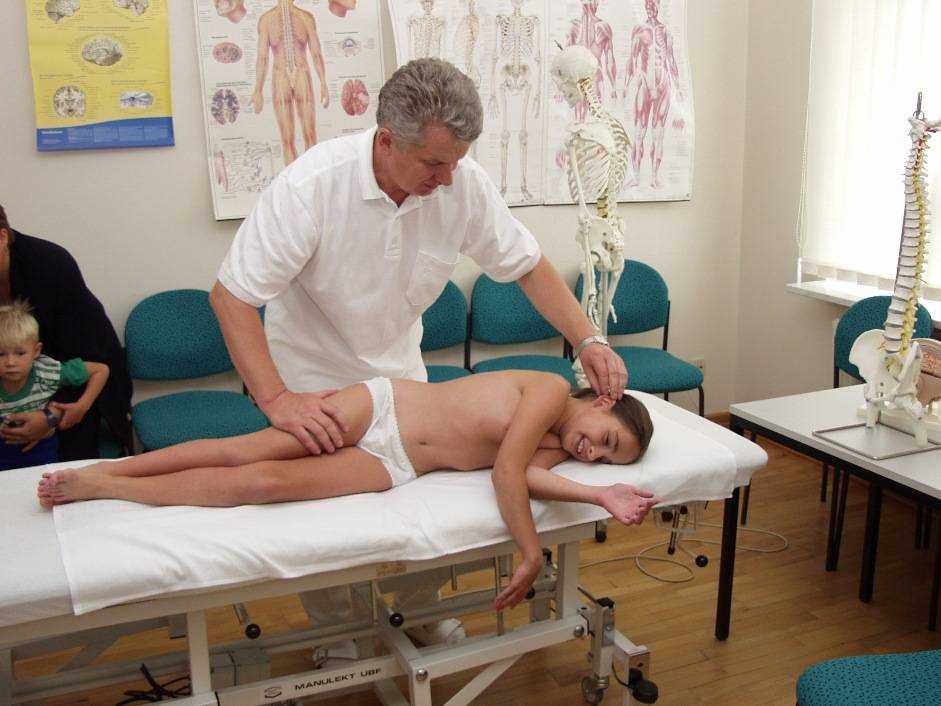
The Osteopathic Structural Exam is a comprehensive assessment technique used by osteopathic physicians to evaluate the musculoskeletal system. It involves a systematic evaluation of the patient’s posture, range of motion, and tissue texture abnormalities. The exam aims to identify any structural imbalances or dysfunctions that may be contributing to the patient’s overall health concerns. By assessing the body as a whole and identifying areas of restriction or asymmetry, the osteopathic physician can develop a targeted treatment plan to address the underlying issues and promote optimal health and well-being.
During the Osteopathic Structural Exam, the physician will carefully observe the patient’s posture both in motion and at rest. They will assess the alignment and symmetry of the spine, pelvis, and other major joints. Any deviations from the optimal alignment will be noted and further examined. The physician will also assess the patient’s range of motion, testing the flexibility and mobility of various joints and muscles. Restrictions or limitations in movement may indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Additionally, the osteopathic physician will utilize palpation to evaluate the tissue texture of muscles, fascia, and other soft tissues. They will look for areas of tenderness, tightness, or abnormal texture that may indicate muscle imbalances or dysfunction. By applying gentle pressure and moving their hands along the patient’s body, the physician can identify areas of tension or restriction and determine their significance in relation to the patient’s overall health. This hands-on approach allows for a detailed assessment of the musculoskeletal system and aids in treatment planning.
The information gathered during the Osteopathic Structural Exam is valuable in establishing a diagnosis and developing a treatment plan. It can help identify the root causes of a patient’s symptoms and guide the physician in selecting appropriate osteopathic techniques and interventions to address those issues. By addressing any structural imbalances or dysfunctions, the physician aims to improve overall function, restore mobility, and alleviate pain or discomfort. The Osteopathic Structural Exam is an essential component of osteopathic medicine, allowing for a holistic evaluation of the patient and the integration of osteopathic principles into their care.
- Comprehensive assessment technique to evaluate the musculoskeletal system.
- Systematic evaluation of posture, range of motion, and tissue texture abnormalities.
- Identify structural imbalances or dysfunctions contributing to health concerns.
- Assess alignment, symmetry, and range of motion of major joints.
- Utilize palpation to evaluate muscle/fascia texture and identify areas of tension or restriction.
- Valuable in establishing a diagnosis and developing a treatment plan.
- Addressing structural imbalances to improve overall function and alleviate pain or discomfort.
The Importance of the Osteopathic Structural Exam in Diagnosis
The osteopathic structural exam is a vital component of diagnosing and treating patients with musculoskeletal issues. This examination allows osteopathic physicians to assess the overall alignment and function of the patient’s body, providing valuable information that can aid in the diagnosis of various conditions. By evaluating the body as a whole and understanding how different parts are interconnected, osteopathic physicians can identify areas of dysfunction and develop targeted treatment plans.
During the osteopathic structural exam, the physician evaluates the patient’s posture, range of motion, and specific structural landmarks. They may also use palpation techniques to assess the mobility and tension of different tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, and joints. By observing and systematically examining the patient’s body, they can identify any asymmetries, imbalances, or restrictions that may be contributing to the patient’s symptoms. This comprehensive approach allows for a more accurate diagnosis by taking into account not only the presenting complaint but also any underlying structural issues that may be present.
The osteopathic structural exam is particularly important in the diagnosis of conditions such as musculoskeletal pain, back pain, and sports injuries. It can help distinguish between the various causes of pain, whether it be related to muscle strains, joint dysfunction, or spinal misalignments. By identifying the root cause of the pain, osteopathic physicians can develop a treatment plan that addresses the underlying issue rather than just providing symptomatic relief. This can lead to more effective and long-lasting results for the patient.
In addition to its diagnostic value, the osteopathic structural exam also plays a crucial role in monitoring the progress of the patient’s treatment. By regularly assessing the patient’s structural alignment and function, the physician can track changes over time and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. This ensures that the patient is receiving the most appropriate and individualized care for their specific condition.
In conclusion, the osteopathic structural exam is an essential tool for diagnosing and treating patients with musculoskeletal issues. By evaluating the body as a whole and identifying areas of dysfunction, osteopathic physicians can develop targeted treatment plans that address the root cause of the problem. This comprehensive approach not only leads to more accurate diagnoses but also allows for more effective and individualized care, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Components of the Osteopathic Structural Exam
The osteopathic structural exam is a comprehensive assessment conducted by osteopathic physicians to evaluate a patient’s musculoskeletal system. It involves a series of observations, palpations, and movements to identify any structural dysfunctions or imbalances. The exam is an important part of osteopathic diagnosis and treatment, as it provides valuable information about the patient’s overall health and helps guide the osteopath in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Observation: The first component of the osteopathic structural exam involves observing the patient’s posture and overall body alignment. The osteopath carefully evaluates the patient’s standing and sitting posture, looking for any deviations, asymmetries, or abnormal movements. They also assess the patient’s gait and how they walk to determine if there are any issues with coordination or balance.
Palpation: Palpation is a key component of the osteopathic structural exam, as it allows the osteopath to feel and assess the patient’s muscles, bones, and other tissues. By using their hands, the osteopath can identify areas of tenderness, muscle tightness, joint restrictions, or other abnormalities. They may also perform specific palpation techniques to evaluate the condition of the patient’s organs and other internal structures.
Motion testing: Another important component of the osteopathic structural exam is motion testing. The osteopath guides the patient through a series of movements to assess the range of motion, flexibility, and strength of various body parts. This helps the osteopath determine if there are any restrictions or dysfunctions in the patient’s joints, muscles, or other soft tissues. The osteopath may also perform specific tests to evaluate the patient’s neurological function and assess any potential nerve impingements or abnormalities.
Functional assessment: In addition to the physical examination, the osteopathic structural exam also includes a functional assessment. This involves evaluating how the patient’s structural dysfunctions or imbalances may be affecting their overall functional abilities and daily activities. The osteopath may ask the patient to perform certain functional tasks or movements to assess their ability to perform everyday activities without difficulty or pain.
Summary and treatment plan: After completing the osteopathic structural exam, the osteopath summarizes their findings and develops a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs. This may involve various osteopathic manipulative techniques, exercises, lifestyle modifications, or referrals to other healthcare providers if necessary. The osteopath will also provide the patient with education and guidance on how they can actively participate in their own healing process.
Proper Execution of the Osteopathic Structural Exam
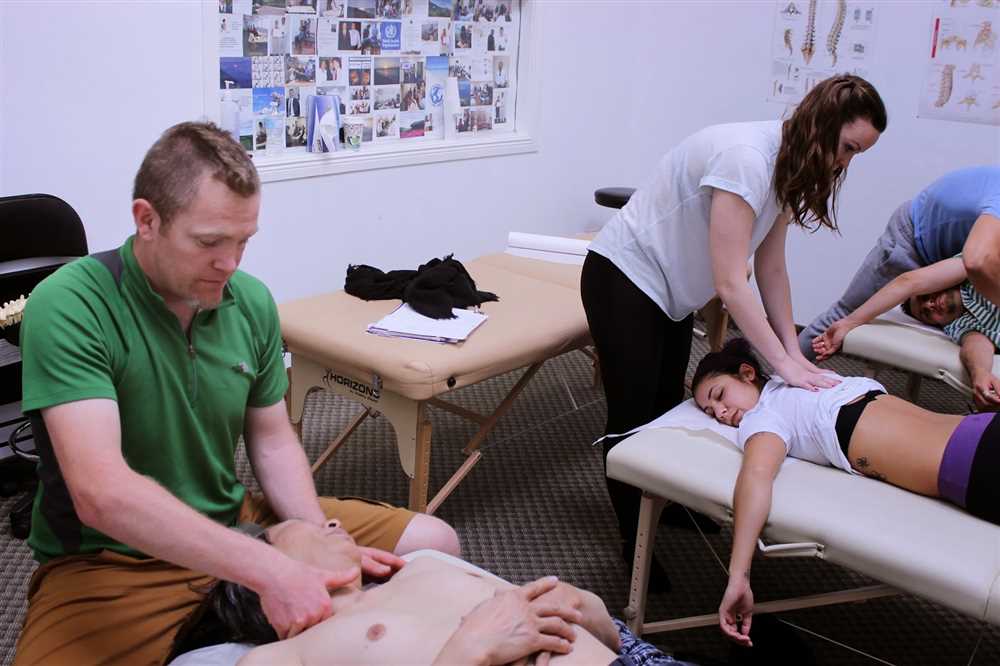
The osteopathic structural exam, also known as structural diagnosis, is a crucial step in osteopathic medicine that enables practitioners to assess and evaluate the musculoskeletal system of their patients. This exam involves a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of the patient’s posture, alignment, and movement patterns in order to identify any structural abnormalities or dysfunctions that may be contributing to their health concerns.
To properly execute the osteopathic structural exam, the practitioner must first establish a comfortable and trusting environment for the patient. This can be achieved by explaining the purpose and process of the exam, addressing any concerns or questions the patient may have, and obtaining their informed consent. The next step is to conduct a thorough medical history and physical examination, paying close attention to the patient’s complaints, symptoms, and previous medical conditions.
During the exam, the practitioner carefully observes the patient’s posture and gait, looking for any asymmetries, imbalances, or abnormal movements. They may also use their hands and fingers to palpate various areas of the body to identify specific points of tenderness, muscle tightness, or joint restrictions. This hands-on approach allows the practitioner to assess the mobility, flexibility, and function of different regions of the body.
Furthermore, the practitioner may utilize specific tests and maneuvers to further evaluate the patient’s musculoskeletal system. These tests can include range of motion assessments, muscle strength testing, and joint stability assessments. By conducting these tests, the practitioner can gather more objective data about the patient’s structural integrity and identify any potential areas of concern.
Once the osteopathic structural exam is completed, the practitioner utilizes the gathered information to develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs. This plan may involve various osteopathic techniques, such as soft tissue manipulation, joint mobilization, and therapeutic exercise, aimed at restoring structural balance, improving mobility, and alleviating pain or discomfort.
In conclusion, the proper execution of the osteopathic structural exam is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning in osteopathic medicine. Through careful observation, palpation, and assessment, the practitioner can identify any structural dysfunctions and develop an individualized approach to optimize the patient’s health and well-being.