
Pigments and paints are essential components in various industries and everyday life. Pigments are substances that give color to other materials, such as paints, inks, plastics, and textiles. They are responsible for the visual appeal and aesthetic quality of products and objects.
The answer key to understanding pigments and paints lies in their chemical and physical properties. Pigments can be natural or synthetic, organic or inorganic, and vary in their ability to reflect or absorb light. The color of a pigment is determined by the wavelengths of light it reflects, and this is based on the pigment’s molecular structure.
Paints, on the other hand, are the materials that contain pigments and are used to create a protective or decorative coating on surfaces. They consist of a binder, a solvent, and various additives. The binder acts as a glue that holds the pigment particles together and adheres them to the surface. The solvent provides the necessary consistency for application and evaporates as the paint dries, leaving a solid film.
Pigments and Paints Answer Key

When it comes to understanding pigments and paints, having an answer key can be incredibly helpful. Pigments are the colored substances that are used to create paint, and understanding their properties and characteristics is key to creating a successful painting. The answer key provides a comprehensive guide to pigments and paints, helping artists navigate the complex world of colors and materials.
Types of Pigments: The answer key outlines the different types of pigments used in paints. This includes organic pigments, which are derived from natural sources such as plants and animals, as well as inorganic pigments, which are made from minerals and synthetic compounds. The key also highlights the various categories of pigments, such as earth tones, transparent pigments, and metallic pigments, providing artists with a clear understanding of the diverse range of colors available to them.
Properties of Pigments: The answer key delves into the properties of pigments, helping artists understand how different pigments behave when mixed with binding agents and applied to different surfaces. This includes information on opacity and transparency, lightfastness, and pigments’ ability to withstand fading over time. By understanding these properties, artists can make informed choices when selecting pigments for their artwork, ensuring that their colors will remain vibrant and true for years to come.
Mixing and Application: The answer key also provides guidance on mixing pigments to achieve desired colors and shades. It explains how to create different hues and tints by adding white or black pigments, as well as the importance of understanding color theory in achieving harmonious color combinations. Additionally, the key offers tips and techniques for applying paint, including brushwork and layering, helping artists achieve the desired effects and textures in their artwork.
Paint Safety and Health: The answer key also addresses important considerations when working with paints, such as safety and health precautions. It provides information on proper ventilation, protective measures, and safe disposal of paint materials, ensuring that artists can work with pigments and paints without compromising their well-being. This knowledge is crucial for artists to create art in a safe and responsible manner.
Overall, the pigments and paints answer key serves as a valuable resource for artists, providing them with the knowledge and guidance they need to make informed choices about pigments, mix colors effectively, and create art that is both visually stunning and enduring.
Understanding Pigments

Pigments are colored substances that are used to give paints, inks, and other materials their vibrant and varied hues. They play a crucial role in the field of art, design, and manufacturing, as they allow artists and manufacturers to create an extensive palette of colors to work with.
There are various types of pigments available, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. Inorganic pigments, such as titanium dioxide and iron oxide, are derived from minerals and often offer excellent lightfastness and durability. Organic pigments, on the other hand, are synthetic compounds that can offer a wider range of color options but may be less stable over time.
Pigments can be classified based on their chemical composition or their application:
- Inorganic pigments: These include oxide pigments, sulfide pigments, and various mineral-based pigments.
- Organic pigments: These are carbon-based compounds synthesized from chemicals and can provide a broader range of colors.
- Special effect pigments: These include metallic pigments, fluorescent pigments, and pearlescent pigments, which add unique visual effects to coatings and artwork.
- Pigments for specific applications: There are pigments designed specifically for use in plastics, textiles, ceramics, and other materials, offering properties tailored to meet the specific requirements of each application.
Understanding pigments is essential for artists, designers, and manufacturers. It allows them to create visually appealing and durable products by making informed decisions about color selection, lightfastness, and compatibility with different mediums.
Types of Pigments
Pigments are substances that impart color to paints, inks, plastics, and other materials. They are classified into various types based on their chemical composition, origin, and properties. Understanding the different types of pigments is important for artists, manufacturers, and scientists to achieve desired color results and performance.
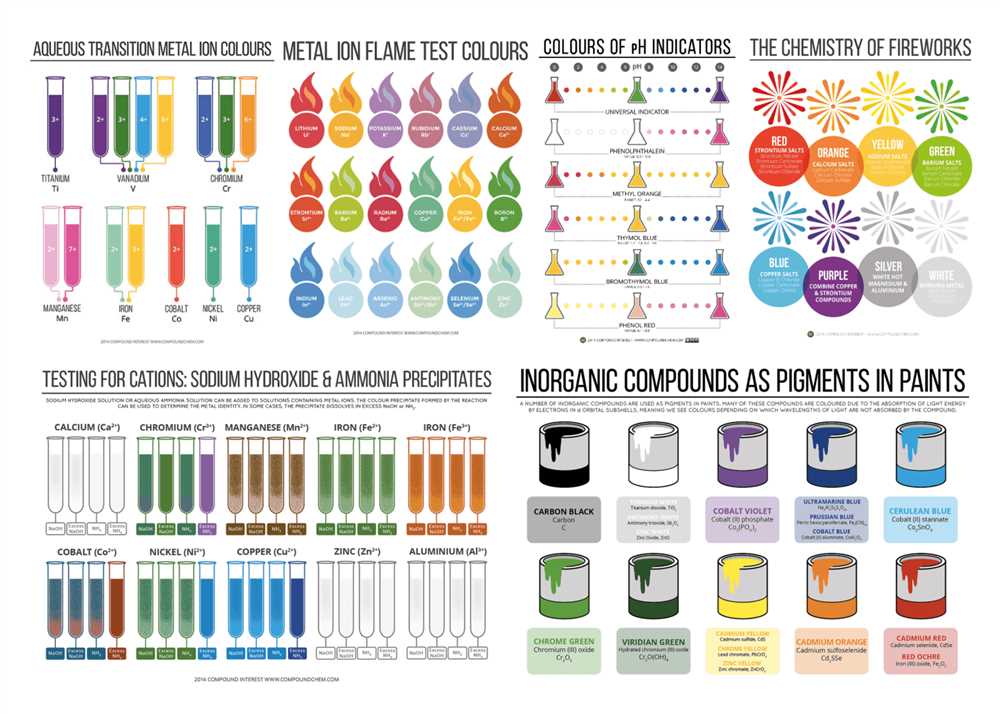
1. Inorganic Pigments: Inorganic pigments are derived from minerals and have excellent lightfastness and heat stability. These pigments are known for their durability and resistance to fading. Examples of inorganic pigments include titanium dioxide (white), iron oxide (red, yellow, and brown), and chromium oxide (green).
2. Organic Pigments: Organic pigments are carbon-based compounds that are synthesized through chemical processes. They offer a wide range of colors and are often used in the production of paints, inks, and dyes. Organic pigments have good color strength but may not be as lightfast as inorganic pigments. Examples of organic pigments include phthalocyanine blue, quinacridone red, and azo yellow.
3. Natural Pigments: Natural pigments are derived from plants, animals, or minerals found in nature. These pigments have been used for centuries by artists and have unique and vibrant colors. Natural pigments include indigo (blue), cochineal (red), and ocher (yellow).
4. Metallic Pigments: Metallic pigments are made from metals or alloys and are used to create metallic or reflective effects in paints and coatings. They provide a lustrous finish and are commonly used in automotive coatings, cosmetics, and packaging materials. Examples of metallic pigments include aluminum, bronze, and mica.
5. Fluorescent Pigments: Fluorescent pigments are specially designed to emit bright, vibrant colors under UV light. They are often used in safety signs, textiles, and printing inks. Fluorescent pigments provide high visibility and can create eye-catching effects.
Overall, the choice of pigment depends on the desired color, stability, and application requirements. Different pigments have different properties and characteristics, and understanding these distinctions is crucial for achieving the desired visual appearance and functionality of the final product.
The Role of Pigments in Paints
Pigments play a crucial role in the world of paints, serving as the main component responsible for the color and appearance of the finished product. They are finely ground powders that are insoluble in the paint medium, making them suitable for creating vibrant and long-lasting colors.
Color Determination: Pigments determine the color of the paint through their ability to selectively absorb and reflect certain wavelengths of light. Each pigment has its own unique chemical composition, which determines its specific color. For example, titanium dioxide is a commonly used white pigment that reflects all wavelengths of light, while cadmium red is a red pigment that absorbs all wavelengths except for red, giving it its distinct hue.
Inorganic vs. Organic Pigments: Pigments can be classified into two main categories: inorganic and organic. Inorganic pigments, such as titanium dioxide and iron oxide, are derived from minerals and typically offer excellent lightfastness and weather resistance. Organic pigments, on the other hand, are carbon-based compounds and often provide a wider range of colors, but may be more prone to fading over time.
Opacity and Transparency: The choice of pigment also affects the opacity and transparency of the paint. Opacity refers to the ability of the paint to completely block out underlying layers, while transparency allows some light to pass through, creating a more translucent effect. Pigments with higher levels of titanium dioxide tend to be more opaque, while those with lower levels create more transparent layers.
Other Functional Properties: Pigments not only contribute to the visual appearance of paint, but they also offer other functional properties. Some pigments, like zinc oxide, have antimicrobial properties, making them suitable for use in paints for hospitals and healthcare facilities. Others, like iron oxide, provide corrosion protection when used in metal coatings.
Safety Considerations: When working with pigments, it is important to consider their safety. Certain pigments, such as lead-based pigments, can be toxic and pose health hazards if ingested or inhaled. It is essential to handle and store pigments properly, following recommended safety guidelines and using appropriate protective equipment.
Pigment Selection and Color Matching
When it comes to selecting pigments for paint formulation, there are several factors to consider. One of the most important factors is the desired color. Each pigment has its own unique color properties, and it is important to choose a pigment that will achieve the desired hue. This can be done by comparing the color of the pigment to a standardized color chart or by visually matching it to a reference sample.
Another important factor in pigment selection is the transparency or opacity of the pigment. Transparent pigments allow light to pass through, creating a more vibrant and luminous effect. On the other hand, opaque pigments block light, creating a more solid and opaque appearance. The choice between transparent and opaque pigments depends on the desired effect and the specific application of the paint.
To ensure accurate color matching, it is essential to use standardized color matching systems, such as the Pantone Matching System (PMS) or the Munsell Color System. These systems provide a set of color standards and formulas that can be used to match colors precisely. By following these systems, paint manufacturers can ensure consistency in color across different batches of paint.
In addition to color matching, it is also important to consider the chemical and physical properties of the pigments. Some pigments may have certain limitations or requirements when it comes to compatibility with other materials, stability, or lightfastness. These factors should be taken into account to ensure that the final paint formulation meets the desired quality and performance standards.
In conclusion, pigment selection and color matching play a crucial role in the formulation of paints. By considering factors such as desired color, transparency or opacity, and using standardized color matching systems, paint manufacturers can achieve accurate and consistent color results. Additionally, taking into account the chemical and physical properties of the pigments ensures that the final paint formulation meets the necessary quality and performance requirements.
Pigment Properties and Performance
Pigments are an essential component of paints, as they provide color and opacity. The properties of pigments play a crucial role in determining the performance and quality of paints. One important property of pigments is their particle size. Pigments with smaller particle sizes generally have better color development and opacity, as they can disperse more evenly in the paint matrix. On the other hand, larger particle sizes can result in a rougher appearance and reduced color intensity.
Another important property of pigments is their chemical composition. Pigments can be organic or inorganic, and they can have different chemical structures and properties. Inorganic pigments, such as titanium dioxide and iron oxides, are known for their excellent lightfastness and weather resistance. Organic pigments, on the other hand, are often used for their vibrant color and high tinting strength. However, organic pigments may be less lightfast and less stable than inorganic pigments, making them suitable for indoor applications or shorter-term outdoor use.
Moreover, the morphology of pigments can also influence their performance. Pigments can have different shapes, such as spherical, plate-like, or irregular. Spherical pigments can provide better hiding power and easier dispersion, while plate-like pigments can enhance light reflection and create special effects. The choice of pigment morphology can depend on the desired application and the specific requirements of the paint formulation.
In summary, the properties of pigments, including particle size, chemical composition, and morphology, greatly impact the performance and quality of paints. Paint manufacturers carefully select and evaluate pigments to ensure that they meet the desired color, opacity, lightfastness, and weather resistance requirements. By understanding the properties of pigments, paint formulators can create paints that not only provide beautiful colors but also deliver long-lasting and durable finishes.
Pigments in Different Paint Applications
Pigments play a crucial role in various paint applications, providing color, opacity, and durability to the final product. Each type of paint application requires specific pigments to achieve the desired results.
In architectural paints, pigments are used to create aesthetically pleasing colors that enhance the appearance of buildings. Titanium dioxide is one of the most commonly used pigments in architectural paints due to its excellent opacity and whiteness. Iron oxides are also extensively used to produce earthy tones such as red, yellow, and brown. These pigments not only add color but also protect the building’s surface from UV radiation and environmental damage.
Industrial paints
In industrial paint applications, pigments must withstand harsh environments, including exposure to chemicals, abrasion, and high temperatures. In this context, inorganic pigments such as chromates and lead compounds are often utilized for their exceptional durability. Zinc phosphate is another commonly used pigment as it provides excellent corrosion resistance for metal surfaces.
Automotive paints require pigments that offer high color intensity, good lightfastness, and resistance to weathering. Metallic pigments, such as aluminum flakes, are widely used to create metallic or pearlescent effects. These pigments reflect light and provide a unique appearance to the painted surface. Organic pigments, on the other hand, are commonly used for their vibrant and intense colors.
Specialty coatings
In specialty coatings, pigments are utilized for specific purposes, such as anti-corrosion coatings or heat-resistant paints. Zinc-rich primers containing zinc dust as a pigment are often used for their corrosion protection properties. Heat-resistant coatings, used for applications like the automotive and aerospace industries, are typically made with ceramic pigments that can withstand high temperatures without color degradation.
In conclusion, pigments are an essential component of various paint applications, serving different purposes according to the specific requirements of each industry. Whether it is providing vivid colors, durability, or functionality, pigments play a vital role in the overall performance and appearance of painted surfaces.