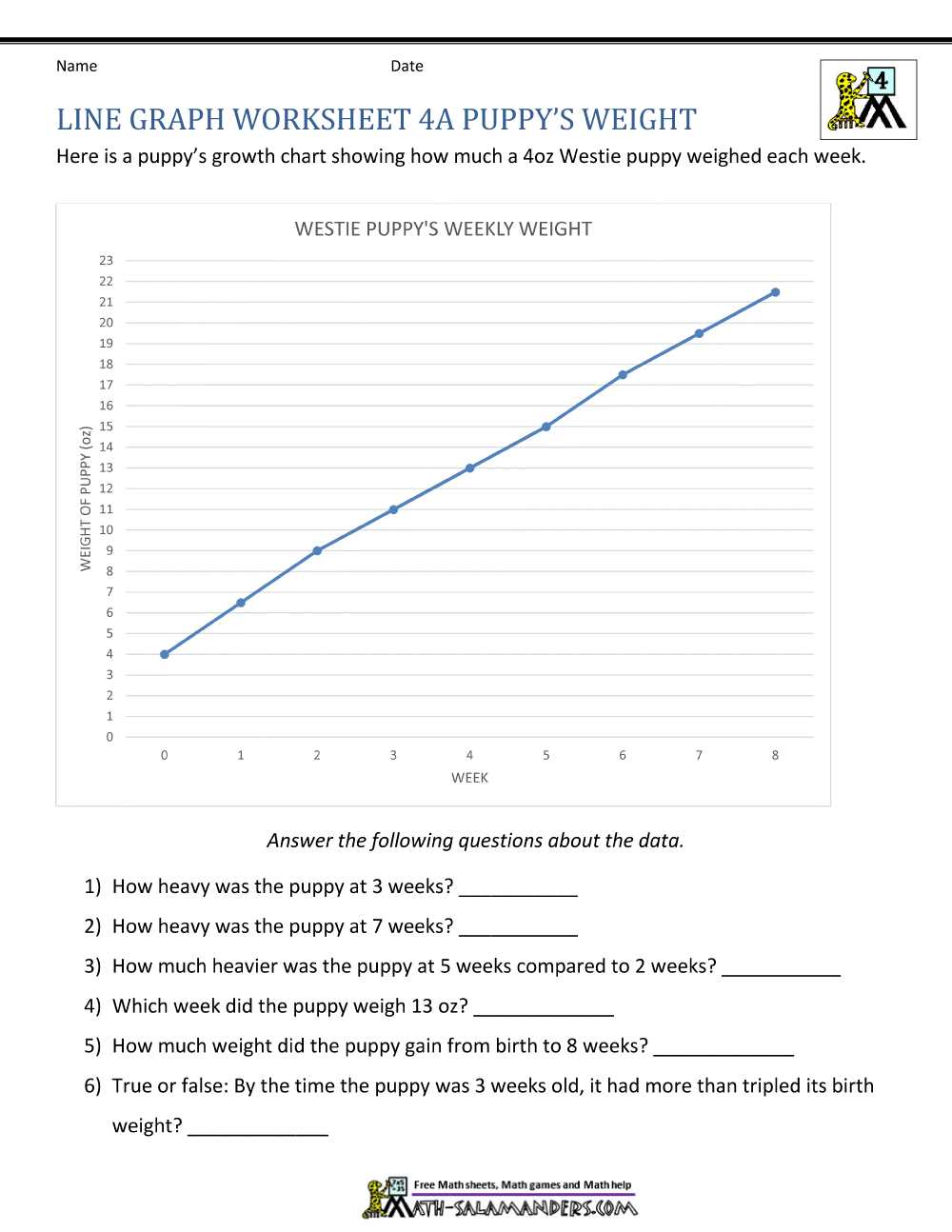
Understanding and interpreting graphics is a crucial skill that is used in various fields and industries. Whether it’s analyzing data, reading charts and graphs, or interpreting visual information, being able to effectively interpret graphics is essential for making informed decisions.
In Chapter 16 of our comprehensive guide, we will dive into the world of interpreting graphics. We will explore different types of graphics, such as line graphs, bar graphs, and pie charts, and discuss the different ways in which they can be used to represent data. We will also provide detailed answers to common questions and problems that arise when interpreting graphics.
Our expert team of data analysts and statisticians have compiled a comprehensive list of questions and solutions to help you enhance your skills in interpreting graphics. From understanding how to read and interpret axes, to identifying trends and patterns in data, our answers will provide you with the knowledge and confidence needed to excel in this area.
So, whether you’re a student working on a project, a professional analyzing market trends, or simply someone who wants to improve their ability to interpret graphics, Chapter 16 of our guide is a valuable resource that you don’t want to miss. Get ready to unlock the power of interpreting graphics and discover the insights they hold!
Chapter 16 Interpreting Graphics Answers
In Chapter 16 of the textbook, we learned about the importance of interpreting graphics in scientific research. Graphics, such as graphs, charts, and diagrams, allow us to visually represent data and information, making it easier to understand and analyze complex concepts.
One type of graphic that we encountered in this chapter is the line graph. Line graphs are commonly used to show how a variable changes over time. By plotting data points on a grid and connecting them with lines, we can easily see trends and patterns. In order to interpret a line graph, we need to look at the slope of the line, the shape of the curve, and any intersections or points of interest.
Another important type of graphic is the bar graph. Bar graphs are used to compare categories or groups by displaying data using bars of different heights or lengths. By looking at the height or length of each bar, we can determine which category or group has the highest or lowest value. Bar graphs can also be used to show percentages or proportions by using stacked bars or segmented bars.
Additionally, Chapter 16 introduced us to scatter plots, which are used to examine relationships between two variables. Scatter plots are created by plotting individual data points on a graph, with one variable represented on the x-axis and the other variable represented on the y-axis. By looking at the distribution of the data points and the general trend of the scatter plot, we can determine if there is a positive, negative, or no correlation between the variables.
In conclusion, Chapter 16 provided us with the necessary tools and knowledge to interpret various types of graphics commonly used in scientific research. By understanding how to analyze line graphs, bar graphs, and scatter plots, we can effectively interpret and draw conclusions from visual representations of data and information.
Understanding Graphical Representations
Graphical representations are visual tools used to present data and information in a clear and concise manner. They are effective in conveying complex ideas, patterns, and relationships, allowing the viewers to quickly grasp the main message. Through the use of various types of graphs and charts, graphical representations provide a visual context that enhances the understanding and interpretation of data.
One commonly used graphical representation is the line graph, which is useful for showcasing trends over time. It uses a series of data points connected by lines to illustrate the change in values over a specific period. By analyzing the slope and direction of the lines, viewers can determine whether values are increasing, decreasing, or remaining constant. Line graphs are particularly valuable in analyzing stock market trends, weather patterns, and population growth.
Another type of graphical representation is the bar graph, which is effective in comparing different sets of data. Vertical or horizontal bars are used to represent each category, with the length or height of the bars indicating the magnitude of the data. Bar graphs are often used in business presentations to illustrate market share, sales figures, and survey results. By comparing the heights or lengths of the bars, viewers can easily identify the largest or smallest values and make informed decisions based on the data presented.
When interpreting graphical representations, it is important to pay attention to the scales, legends, and labels provided. These elements provide crucial information about the values being represented and the context in which they should be analyzed. It is also essential to consider the data source, sample size, and potential biases that may affect the accuracy of the graphical representation. By critically evaluating these factors, viewers can make informed conclusions and avoid misinterpretations.
In summary, graphical representations are powerful tools for presenting data in a visual and accessible format. They allow viewers to quickly understand trends, make comparisons, and draw meaningful insights. However, it is important to approach graphical representations with a critical eye and consider the contextual factors that may influence their interpretation.
Importance of Interpreting Graphics
Interpreting graphics is a crucial skill that is essential in many fields. Graphics, such as charts, graphs, and diagrams, are used to present data and information in a visual format, making it easier to understand and analyze complex concepts. Being able to interpret these graphics accurately allows individuals to make informed decisions, communicate effectively, and draw meaningful conclusions.
One of the main reasons why interpreting graphics is important is because it enables effective communication. Graphics often convey information in a concise and visually appealing manner, making it easier for the audience to grasp the main points quickly. Whether it’s a business presentation, an academic report, or a scientific publication, using graphics can enhance the clarity and impact of the message being conveyed.
Moreover, interpreting graphics is essential for data analysis. Charts and graphs can provide a visual representation of patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. By understanding and interpreting these graphics correctly, researchers, analysts, and decision-makers can gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. For example, a sales chart can help identify the best-selling products or the most profitable markets, while a line graph can show the progression of a variable over time.
Interpreting graphics also allows individuals to evaluate the reliability and credibility of information. With the abundance of information available today, it is crucial to be able to determine whether a graphic accurately represents the data or if it has been manipulated or biased. By examining the source, labels, scales, and other elements of the graphic, individuals can assess its accuracy and make informed judgments.
In conclusion, interpreting graphics is a vital skill that has multiple applications in various fields. It enhances communication, facilitates data analysis, and aids in evaluating the reliability of information. By honing this skill, individuals can become more effective decision-makers, researchers, and communicators.
Analyzing Bar and Line Graphs
Bar and line graphs are common types of graphical representation used to visualize data. These graphs can help us analyze and understand the relationship between different variables or the trend of a particular data set.
Bar graphs are often used to compare different categories or groups. They consist of rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values they represent. By examining the heights of the bars, we can easily compare the values and draw conclusions. For example, a bar graph showing the sales of different products can help identify which product is the most popular or has the highest revenue.
Line graphs, on the other hand, are used to show the changes or trends over time. They represent data points connected by lines, which allows us to observe the progression of a variable. By analyzing the trend of a line graph, we can make predictions, identify patterns, or detect anomalies in the data. For instance, a line graph showing the temperature fluctuations throughout the year can help us understand the seasonal patterns and make predictions about future weather conditions.
Interpreting Pie Charts and Histograms

A pie chart is a circular graph divided into sectors that represent different categories or proportions of a whole. It is commonly used to show percentages or proportions of a certain variable. The size of each sector is determined by the corresponding numerical value it represents. By analyzing a pie chart, we can easily compare the contribution of each category and identify the dominant or smallest ones.
For example, suppose we have a pie chart illustrating the distribution of expenses in a household budget. The chart may show that 40% of the budget is spent on housing, 30% on food, 20% on transportation, and 10% on other miscellaneous expenses. By examining this chart, we can quickly understand the relative importance of each category in terms of budget allocation.
A histogram, on the other hand, is a graphical representation of a frequency distribution. It consists of a series of vertical bars where the width of each bar represents a range of values and the height represents the frequency or count of data falling within that range. Histograms are commonly used to understand the distribution and spread of data.
For instance, let’s say we have a histogram representing the heights of students in a classroom. The x-axis of the histogram would represent the height ranges (e.g., 150-160 cm, 160-170 cm, etc.), while the y-axis would represent the frequency or count of students falling within each height range. By analyzing this histogram, we can get an idea of the range of heights present in the classroom and identify any patterns or outliers.
Examining Scatter Plots and Box Plots
Scatter plots and box plots are powerful visual tools used to examine and analyze data. These plots provide a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables and allow us to identify patterns, trends, and outliers.
Scatter plots display data points as individual dots on a two-dimensional graph, with one variable plotted on the x-axis and the other variable plotted on the y-axis. By examining the dispersion and direction of the dots, we can determine if there is a positive, negative, or no relationship between the variables. Scatter plots are especially useful for identifying clusters, outliers, and any patterns or trends in the data.
Box plots, also known as box-and-whisker plots, provide a visual summary of the distribution of a dataset. They display several key statistics, such as the minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum values. The box in the plot represents the interquartile range (IQR), which is the range between the first and third quartiles. The whiskers extend from the box to the minimum and maximum values, excluding any outliers. Box plots are helpful in comparing the distribution of different variables or groups and identifying any significant differences.
Both scatter plots and box plots are essential tools in data analysis and can provide valuable insights into the relationship and distribution of variables. By interpreting these graphical representations, we can make informed decisions, identify potential outliers, understand patterns and trends, and communicate our findings effectively.
Tips for Interpreting Graphics
When it comes to interpreting graphics, whether they are charts, graphs, or diagrams, it is important to follow certain guidelines in order to extract accurate information and draw meaningful conclusions. Here are some tips to help you effectively interpret graphics:
1. Understand the Visual Representation
Before jumping into analyzing the data, take a moment to understand the type of graphic you are looking at. Is it a bar graph, a pie chart, or a line graph? Each type of graphic presents data in a different way, so understanding the visual representation will give you a better grasp of the information being conveyed.
2. Examine the Axes and Labels
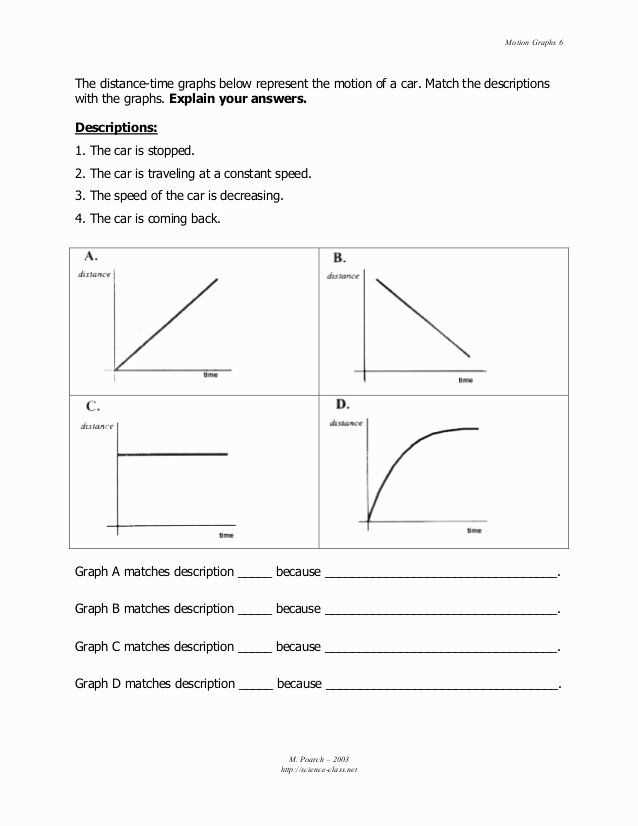
The axes and labels play a crucial role in interpreting graphics. Look for the X-axis and the Y-axis, and make note of what they represent. Additionally, pay attention to the labels of the data points or categories. These labels provide important context and help in understanding the information being presented.
3. Analyze the Trend
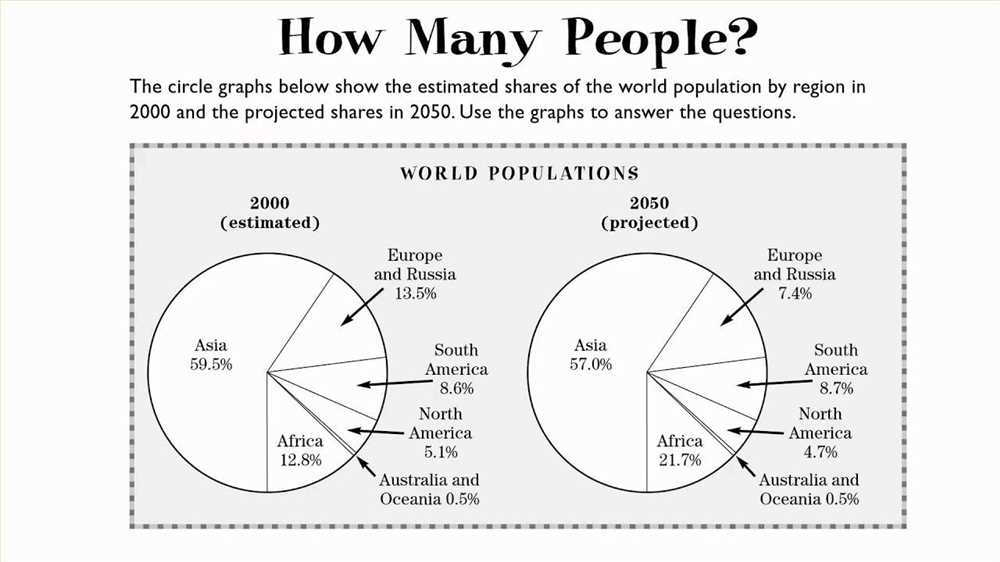
One of the main objectives of interpreting graphics is to identify trends or patterns within the data. Look for any noticeable increase or decrease over time, and try to identify any recurring patterns. This will allow you to make observations and draw conclusions based on the data.
4. Compare and Contrast
Graphics often allow for easy comparison and contrast between different categories or data points. Look for variations in the heights of bars, the sizes of pie slices, or the slopes of lines. By comparing and contrasting different elements within the graphic, you can gain a deeper understanding of the data and its implications.
5. Consider the Source and Context
When interpreting graphics, it is important to consider the source and the context in which the information is presented. Is the graphic from a reputable source? What is the purpose of the graphic? Understanding these factors can help you assess the credibility and reliability of the information being presented.
By following these tips, you can enhance your ability to interpret graphics effectively and make informed conclusions based on the data. Remember to approach each graphic with a critical mindset and be open to different insights and interpretations.
Common Mistakes in Interpreting Graphics
When it comes to interpreting graphics, there are several common mistakes that people often make. One of the biggest mistakes is assuming that the information presented in the graphic is accurate and unbiased. It is important to remember that graphics can be manipulated and skewed to present a certain point of view or to support a specific argument. Therefore, it is important to critically analyze the graphic and consider the source of the information before drawing any conclusions.
Another common mistake is failing to properly read and understand the labels and captions on the graphic. These labels and captions provide important context and help to explain what the graphic is representing. Ignoring or misunderstanding this information can lead to misinterpretation of the graphic’s message. It is essential to take the time to read and understand all the accompanying text when interpreting a graphic.
Additionally, many people make the mistake of assuming that the graphic tells the whole story. Graphics are often simplified representations of complex data sets and may not capture all the nuances and intricacies of the subject matter. It is important to remember that a graphic is only one piece of the puzzle and should be viewed in conjunction with other relevant information to get a complete understanding of the topic.
In conclusion, interpreting graphics requires careful analysis and critical thinking. Avoiding common mistakes such as blindly accepting the accuracy of the graphic, misreading labels and captions, and relying solely on the graphic for information will help improve the accuracy and reliability of your interpretations.