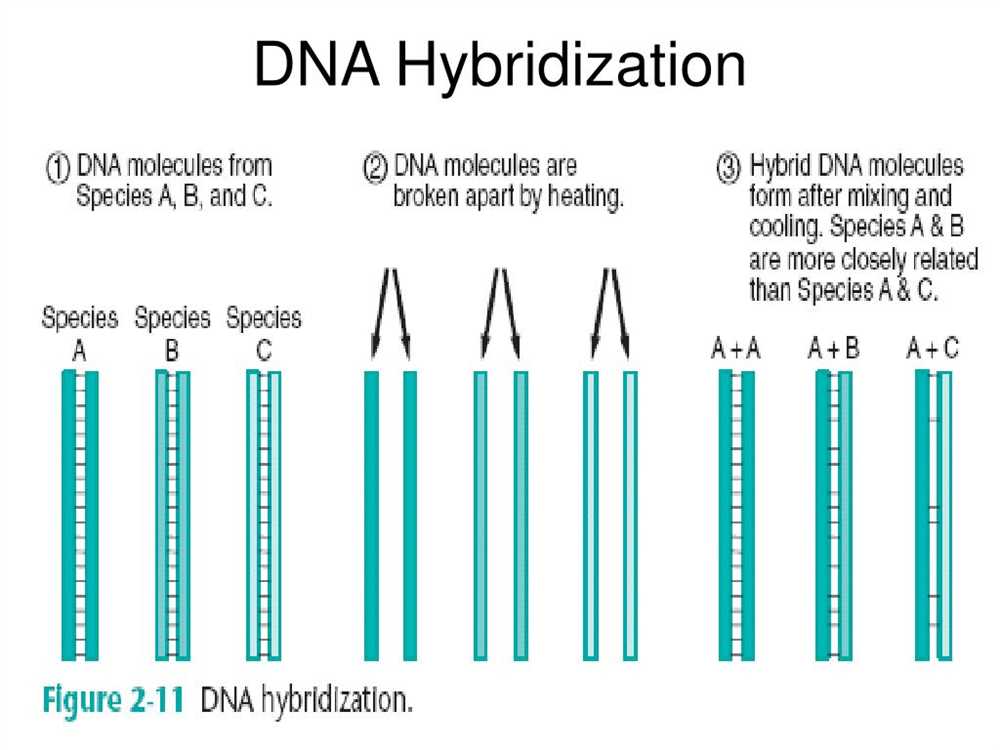
In the field of biology, relationships between organisms and the state of biodiversity are important factors to consider when studying ecosystems. Understanding the interconnections between species and the overall health of an ecosystem can provide valuable insights into the impacts of human activities and efforts to conserve biodiversity.
The Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab is a practical activity that allows students to investigate and analyze the relationships between different species in a simulated ecosystem. By examining data and making connections, students can develop a deeper understanding of how the presence or absence of certain species can affect the overall biodiversity and stability of an ecosystem.
The lab also provides opportunities for students to explore the concept of keystone species, which are species that have a disproportionately large impact on an ecosystem relative to their abundance. By identifying and studying keystone species, students can gain a greater appreciation for the delicate balance of nature and the importance of conserving biodiversity.
Understanding Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab PDF Answers
The Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab is designed to help students understand the concept of biodiversity and its importance in maintaining healthy ecosystems. By conducting field surveys and analyzing data, students are able to explore the relationships between different species in a specific area.
The lab provides students with a PDF file containing data tables and questions to guide their analysis. The answers to these questions can help students draw conclusions about the biodiversity of the area and the interdependencies of species within it.
One of the key aspects of the lab is the use of Shannon diversity indices to measure the biodiversity of different sites. These indices take into account both the number of species present and their relative abundance. By calculating these indices for different sites, students can compare the biodiversity levels and determine which sites have higher or lower diversity.
The lab also explores the concept of indicator species, which are species that can provide information about the overall health of an ecosystem. By identifying and studying the presence or absence of indicator species in different sites, students can gain insights into the environmental conditions and the impacts of human activity on the biodiversity of the area.
Overall, the Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab PDF answers provide students with the tools and knowledge to understand and analyze the relationships between species and their impact on biodiversity. Through this lab, students can develop a deeper understanding of the importance of biodiversity conservation and the need for sustainable practices to protect ecosystems.
What is the Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab PDF?
The Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab PDF is a document that provides instructions and information for conducting a laboratory investigation on the relationships between organisms and their environments. This lab explores the concept of biodiversity and its importance in maintaining healthy ecosystems. The PDF contains step-by-step procedures, data tables, and analysis questions to guide students through the experiment.
In this lab, students will observe and analyze different ecosystems to determine the biodiversity within each. They will collect data on the number and types of organisms present in each ecosystem, as well as the environmental factors that may affect biodiversity, such as temperature, pH, and sunlight. By comparing and analyzing the data, students will be able to draw conclusions about the relationships between biodiversity and environmental factors.
The Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab PDF is an essential resource for teachers and students studying ecology and environmental science. It provides a structured and hands-on approach to understanding the interconnectedness of organisms and their environments. Through this lab, students will develop critical thinking and data analysis skills while gaining a deeper appreciation for the importance of biodiversity in maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems.
Key Concepts and Objectives of the Lab
In the “Relationships and Biodiversity” lab, the main objective is to explore the relationship between biodiversity and the health of an ecosystem. Biodiversity refers to the variety of different species and the abundance of each species within a given area. This lab aims to understand how changes in biodiversity can impact the overall functioning and stability of an ecosystem.
One key concept addressed in this lab is the idea of an ecosystem’s resilience. Resilience refers to the ability of an ecosystem to withstand disturbances and maintain its structure and function. By studying the relationship between biodiversity and resilience, we can gain insight into the mechanisms that allow ecosystems to recover from disturbances and prevent the loss of species.
Another important concept explored in this lab is the concept of species interdependence. Different species within an ecosystem often have interconnected relationships, such as predator-prey interactions or mutualistic partnerships. Changes in biodiversity can disrupt these relationships, potentially leading to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
The lab also focuses on the concept of ecological niches. A niche refers to the specific role or function that a species plays within its ecosystem. Each species has unique adaptations and requirements, and these ecological niches contribute to the overall diversity and stability of an ecosystem. By understanding the relationships between species and their niches, we can better appreciate the intricate web of interactions that support biodiversity.
The lab provides an opportunity to analyze real-world data and observe patterns in species abundance and diversity. Through hands-on activities and data analysis, students will develop their skills in scientific inquiry, data interpretation, and critical thinking. Ultimately, the lab aims to deepen our understanding of the importance of biodiversity in maintaining healthy and resilient ecosystems.
Importance of Relationships in Biodiversity
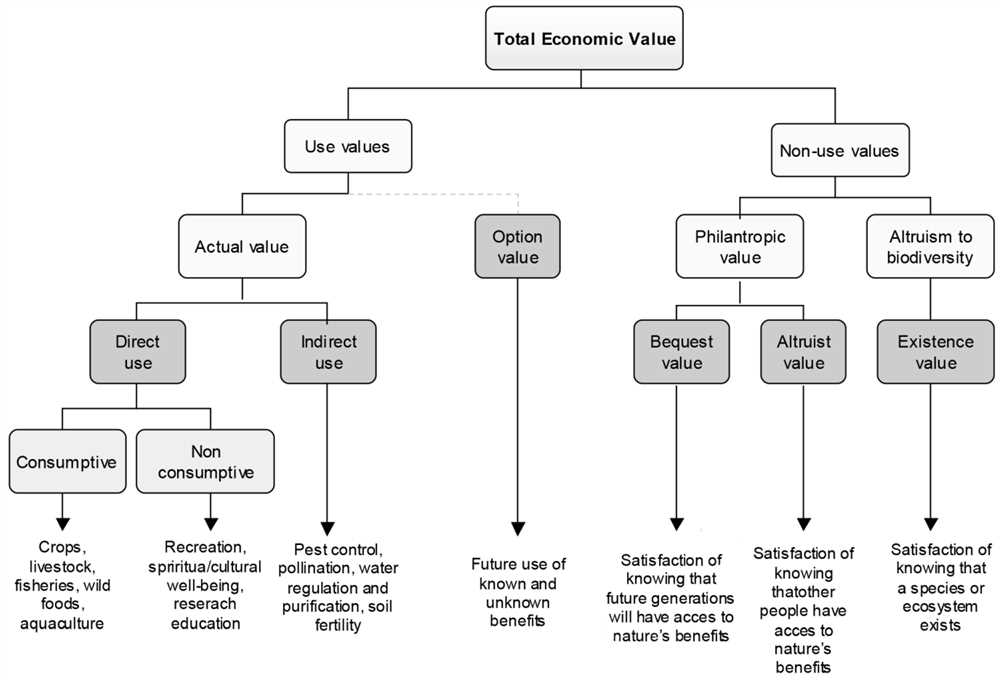
The diversity of life on Earth is maintained through complex and interconnected relationships between different organisms and their environments. These relationships play a crucial role in sustaining biodiversity, which is essential for the health and stability of ecosystems. Understanding the importance of relationships in biodiversity is key to conserving and protecting the natural world.
1. Interdependence: One of the key reasons why relationships are important in biodiversity is because of interdependence. Organisms rely on each other for resources, such as food, shelter, and reproduction. These relationships form intricate food webs and ecological networks, where the well-being of one species is closely linked to the well-being of others. The loss of one species can have cascading effects on an entire ecosystem, leading to imbalances and potential collapse.
2. Ecosystem Services: Relationships in biodiversity are also crucial for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystems, such as clean air and water, pollination, and regulation of climate. These services are often provided by a diverse array of organisms working together in complex relationships. For example, bees and other pollinators play a vital role in the reproduction of flowering plants, which in turn support the growth of other organisms and provide food for humans and wildlife.
3. Adaptation and Evolution: Relationships in biodiversity drive adaptation and evolution. Organisms continually interact with each other and their environment, leading to the development of specific traits and behaviors that increase their chances of survival and reproduction. These adaptations are often shaped by the relationships they have with other species, as well as the availability of resources. The diversity of relationships enhances the evolutionary potential of species and allows for the resilience and adaptability of ecosystems in the face of changing environmental conditions.
Overall, relationships in biodiversity form the fundamental building blocks of ecosystems and are essential for the maintenance of life on Earth. Understanding and appreciating these relationships is crucial for ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of our planet.
Exploring the Interconnectedness of Organisms
The intricate web of life on Earth is characterized by the interconnectedness of organisms and the relationships they form within ecosystems. From microscopic bacteria to large mammals, every organism plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of nature. Understanding these relationships is crucial for studying and conserving biodiversity.
One way scientists explore the interconnectedness of organisms is through the study of food webs. These webs depict the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another within an ecosystem. Each organism occupies a specific trophic level, indicating its position in the food chain. Producers, such as plants, convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, while consumers, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores, obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
Another aspect of interconnectedness is the mutualistic relationships that exist between different species. Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from each other’s presence. For example, bees and flowers have a mutualistic relationship, as bees collect nectar from flowers for food, while inadvertently pollinating them in the process. These relationships are vital for the reproduction and survival of many organisms.
The interconnectedness of organisms extends beyond individual species. Ecosystems are complex networks in which various organisms interact with one another and their environment. Changes in one part of an ecosystem can have far-reaching consequences for other organisms within the system. For example, the decline of a top predator can result in an increase in the population of its prey, leading to changes in plant communities and other ecological processes.
By studying the interconnectedness of organisms, scientists gain a deeper understanding of the intricate relationships that shape the world around us. This knowledge is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and managing biodiversity. It also highlights the importance of preserving ecosystems in their entirety, as the loss of one species can have a cascading effect on others. To protect the delicate balance of nature, it is essential to recognize and appreciate the interconnectedness of all organisms.
The Role of Relationships in Maintaining Ecosystem Balance
Relationships between different species are crucial for maintaining the balance and stability of ecosystems. These relationships, known as ecological interactions, include predator-prey relationships, mutualistic relationships, and competitive relationships. Each of these interactions plays a unique role in regulating population sizes and ensuring the overall health of the ecosystem.
Predator-prey relationships are essential for controlling population sizes within an ecosystem. Predators help regulate the populations of their prey by consuming them, preventing their numbers from becoming too large. This not only helps to maintain a balance between predator and prey species but also prevents overgrazing or overconsumption of resources. For example, in an ecosystem where there is an abundance of herbivores, the presence of predators, such as lions or wolves, keeps the herbivore populations in check, preventing them from depleting the vegetation and disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
Mutualistic relationships, on the other hand, involve interactions where both species benefit. These relationships can be seen in instances of pollination, where plants provide nectar and pollen to attract pollinators, such as bees or butterflies, which, in turn, help in the reproduction and gene flow of plants. The mutualistic relationship between bees and flowers is an excellent example of how these interactions contribute to the maintenance of biodiversity. By facilitating the transfer of pollen, bees ensure the reproduction and survival of different plant species, which is crucial for maintaining the overall balance of the ecosystem.
Competitive relationships also play a significant role in ecosystem balance. In these interactions, species compete for limited resources such as food, water, or territory. This competition helps to ensure that no species dominates or monopolizes resources, allowing for niche differentiation and species coexistence. For instance, different bird species may compete for nesting sites, forcing them to occupy different habitats or use different nesting strategies. This competition helps to prevent any one species from becoming too dominant and disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, the relationships between different species are essential for maintaining ecosystem balance. Predator-prey relationships regulate population sizes, mutualistic relationships facilitate reproduction and gene flow, and competitive relationships prevent one species from dominating the ecosystem. Understanding and conserving these relationships is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the long-term survival of ecosystems.
Conducting the Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab
If you are completing the Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab, it is important to understand the steps involved and how to conduct the lab properly. This lab is designed to investigate the relationships between organisms and the impact of human activities on biodiversity.
To begin the lab, gather the necessary materials, including the field guide and dichotomous key provided. These tools will help you identify the different species of birds, insects, and plants that you will encounter during the lab. It is essential to familiarize yourself with these tools and how to use them effectively before starting your observations.
Step 1: Select a location in your local area where you can observe a variety of organisms. This could be a park, forest, or any other natural area. Make sure to choose a location that will allow you to encounter different species of birds, insects, and plants to ensure accurate data collection.
Step 2: Once you have chosen your location, begin your observations. Use the field guide and dichotomous key to identify the organisms that you encounter. Make notes of their common and scientific names, as well as any other relevant information about their behavior or habitat.
Step 3: As you observe the organisms, also pay attention to the impact of human activities on their habitats. Look for signs of pollution, deforestation, or other human-induced changes that may affect biodiversity. Take notes on these observations as well, as they will be important for analyzing the data later.
Step 4: After completing your observations, organize your data and analyze the results. Look for patterns in the species you encountered, as well as any correlations between human activities and changes in biodiversity. This analysis will help you draw conclusions about the relationships between organisms and the impact of human activities on biodiversity.
In conclusion, conducting the Relationships and Biodiversity State Lab requires careful observation, accurate data collection, and thorough analysis. By following the steps outlined in the lab procedure, you will be able to investigate the relationships between organisms and gain a better understanding of the impact of human activities on biodiversity.