Estimating large numbers plays an essential role in various fields, including finance, statistics, and economics. Accurately calculating these figures is crucial for making informed decisions and identifying trends. This article will delve into the practice of analyzing numerical data and provide an answer key for estimating large numbers. It will outline key principles and methodologies for estimating figures and highlight the importance of precision and accuracy.
One commonly used technique for estimating large numbers is rounding. Rounding involves approximating a number to the nearest whole or specified decimal place. This method is especially useful when dealing with extensive datasets or figures that are difficult to calculate precisely. By rounding large numbers, analysts can simplify calculations and provide a general approximation of the figure under consideration.
Another approach to estimating large numbers is using scientific notation. Scientific notation represents numbers in a condensed format by expressing them as a product of a coefficient and a power of 10. This method is particularly helpful when dealing with extremely large or small values. By converting large numbers to scientific notation, analysts can better grasp the magnitude of the figure and make comparisons more manageable.
Additionally, regression analysis is a powerful tool for estimating large numbers. Regression analysis allows analysts to identify relationships and trends in datasets and use them to predict future values. This method involves fitting a regression line to the data points and extrapolating it to estimate values beyond the observed range. Regression analysis takes into account various factors and variables, providing a comprehensive estimation of large numbers.
Accurate estimation of large numbers is vital for decision-making, trend analysis, and strategic planning. By using techniques such as rounding, scientific notation, and regression analysis, analysts can obtain reliable approximations and make informed conclusions. Precision and accuracy are key when dealing with large numbers, as even a small deviation can have significant consequences. This answer key provides a foundation for effectively analyzing numerical data and estimating large numbers to support critical decision-making processes.
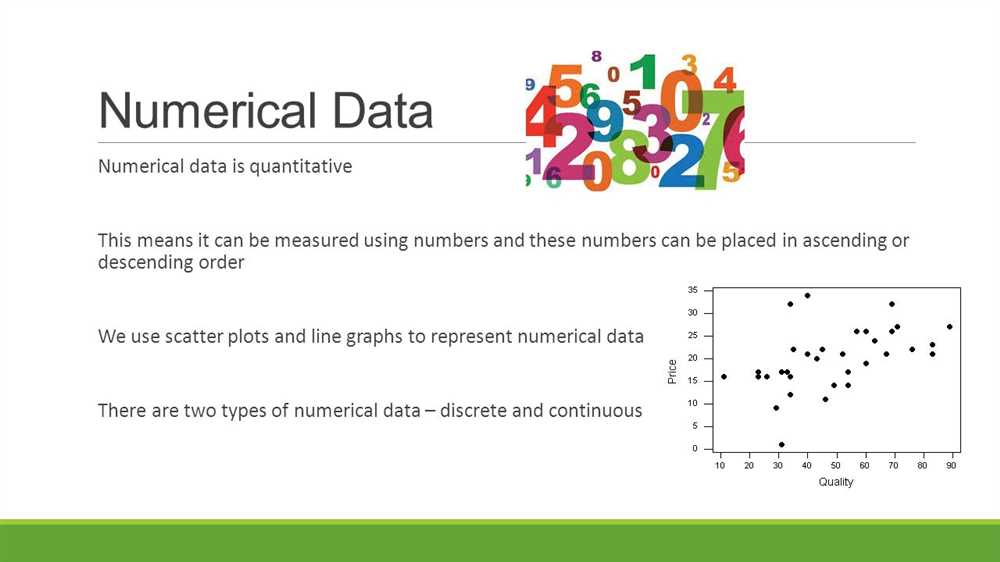
Understanding numerical data analysis
Numerical data analysis plays a crucial role in various fields, including finance, economics, and scientific research. It involves the use of mathematical and statistical techniques to interpret and make sense of large sets of numerical data. By analyzing numerical data, valuable insights and patterns can be discovered, which can be used for decision-making, problem-solving, and prediction.
In order to understand numerical data analysis, it is important to have a basic understanding of key concepts and techniques. One such concept is descriptive statistics, which involves summarizing and presenting data in a meaningful way. This includes measures such as mean, median, and standard deviation, which can provide information about the central tendency and variability of the data.
Another important aspect of numerical data analysis is inferential statistics, which involves making inferences or predictions about a population based on a sample. This is done through hypothesis testing and confidence intervals. Hypothesis testing allows researchers to determine whether a hypothesis or statement about a population is likely to be true or not. Confidence intervals provide a range of values within which a population parameter is likely to lie.
Furthermore, data visualization is a powerful tool in numerical data analysis. It involves creating visual representations, such as graphs and charts, to present data in a clear and concise manner. This can help identify trends, patterns, and outliers, making it easier to interpret and understand the data.
In conclusion, understanding numerical data analysis is essential for making informed decisions and drawing meaningful conclusions from large sets of numerical data. It involves the use of descriptive and inferential statistics, as well as data visualization techniques. By applying these techniques, valuable insights can be obtained, leading to better understanding and interpretation of numerical data.
The Importance of Estimating Large Numbers Accurately
Estimating large numbers accurately is crucial in various fields and industries, as it enables informed decision-making and planning. Whether in finance, economics, population studies, or scientific research, accurate estimations of large numbers provide valuable insights and help organizations and individuals make informed choices.
Effective resource management: In business and finance, estimating large numbers accurately is essential for efficient resource allocation. For example, accurately estimating the demand for a product or service can help businesses determine their production levels, inventory needs, and pricing strategies. Without accurate estimations, organizations may face the risk of overproduction or shortages, resulting in financial losses or missed opportunities.
Strategic planning: Accurate estimations of large numbers also play a vital role in strategic planning. In government and public policy, estimating the population size and growth rate of a region helps allocate resources for infrastructure development, healthcare, and education. In the field of environmental science, estimations of large numbers like greenhouse gas emissions or species populations guide conservation efforts and inform policies aimed at mitigating climate change and protecting biodiversity.
Data analysis and research: Estimating large numbers accurately is crucial in research and data analysis. Whether it’s analyzing survey results, conducting experiments, or studying large datasets, accurate estimations provide a solid foundation for drawing meaningful conclusions and making insightful observations. In fields such as market research or epidemiology, reliable estimations are essential for understanding trends, patterns, and potential risks.
Risk assessment and decision-making: Accurate estimations of large numbers are crucial in assessing and managing risks. Whether it’s financial institutions evaluating the creditworthiness of borrowers or insurance companies assessing probabilities of accidents or claims, accurate estimations help organizations make sound risk assessments and informed decisions. In cases where the magnitude of potential losses or impacts is significant, the importance of accurate estimations becomes even more evident.
In conclusion, accurate estimations of large numbers are of utmost importance across various sectors. They enable effective resource management, strategic planning, data analysis, and risk assessment. By estimating large numbers accurately, organizations and individuals can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and maximize their chances of success.
Common methods used for estimating large numbers
Estimating large numbers can be a challenging task, but there are several common methods that can be used to provide an approximate estimation. These methods rely on various techniques and assumptions to arrive at a reasonable estimate without the need for precise calculations or extensive data collection.
One commonly used method is the sampling technique, where a small portion of the population is studied and the data collected is used to make inferences about the larger population. This method assumes that the small sample is representative of the entire population, allowing for extrapolation of the findings to estimate the larger numbers. Sampling can be done through random selection or systematic sampling, depending on the specific research objectives.
Another method is the use of historical or existing data. This approach involves analyzing previous data or trends to make predictions about future numbers. For example, if there is historical data on population growth rates, it can be used to estimate the population size in the coming years. This method assumes that the past patterns will continue to hold true in the future and can be a useful tool in estimating large numbers.
Estimation techniques also include the use of mathematical models or formulas that are based on certain assumptions. These models can be applied to specific scenarios and can provide approximate estimations with a certain level of accuracy. The accuracy of the estimate will depend on the assumptions made in the model and the underlying data used.
In conclusion, estimating large numbers requires the use of various methods, including sampling techniques, historical data analysis, and mathematical models. These methods provide approximate estimations without the need for precise calculations, allowing for a reasonable estimation of large numbers in various contexts.
Key techniques for analyzing numerical data
In order to effectively analyze numerical data and estimate large numbers, there are several key techniques that can be employed. These techniques involve the use of statistical methods, data visualization, and mathematical calculations to gain insights and make accurate estimations.
One key technique is the use of descriptive statistics, which involves summarizing and presenting the data in a meaningful way. Measures such as the mean, median, and standard deviation can provide valuable information about the central tendency and variability of the numerical data. This allows analysts to understand the distribution and patterns present in the data, aiding in making accurate estimations.
The use of data visualization techniques is another important approach when analyzing numerical data. Visual representations such as histograms, scatter plots, and boxplots can provide a clear and concise overview of the data. These visualizations help identify outliers, trends, and patterns, allowing analysts to make informed estimations about large numbers based on the observed data.
In addition to descriptive statistics and data visualization, mathematical calculations play a crucial role in analyzing numerical data and estimating large numbers. Techniques such as regression analysis, correlation analysis, and hypothesis testing can be used to uncover relationships between variables and make predictions based on the observed data.
Overall, by employing these key techniques of descriptive statistics, data visualization, and mathematical calculations, analysts can effectively analyze numerical data and make accurate estimations of large numbers. These techniques provide valuable insights and help in decision-making processes across various fields and industries.
Challenges in estimating large numbers
Estimating large numbers can pose several challenges, particularly when trying to analyze numerical data. The sheer magnitude of large numbers can make it difficult to accurately estimate and comprehend the scale of the data. Additionally, the complexity of the data can also make it challenging to analyze and interpret the information.
One challenge in estimating large numbers is the potential for errors or inaccuracies. When dealing with vast amounts of data, even a small margin of error can have significant implications. Estimations may be affected by sampling errors, measurement errors, or biases in data collection methods. These errors can lead to incorrect conclusions and impact the accuracy of any analysis.
Another challenge is the difficulty in visualizing and grasping the magnitude of large numbers. Human cognition is not naturally inclined to comprehend large numbers, and our intuition can be misleading when dealing with extremely large quantities. It can be challenging to put into context the significance of numbers in the millions, billions, or trillions, making it essential to employ visualization techniques and proper scaling to aid in understanding the data.
To overcome these challenges, various analytical techniques can be utilized. Breakdowns and comparisons can help to put large numbers into perspective. Breaking down a large number into smaller components or comparing it to known benchmarks can make it more manageable to understand. Additionally, using visual representations, such as graphs or charts, can aid in comprehending the scale and patterns within large datasets. Furthermore, employing statistical methods, such as sampling and hypothesis testing, can help mitigate errors and improve the accuracy of estimations.
Ultimately, accurately estimating and analyzing large numbers requires careful consideration of the challenges involved and implementing appropriate strategies to overcome them. By understanding the limitations and complexities of working with large numerical data, researchers and analysts can make more informed decisions and draw accurate conclusions.
Examples of numerical data estimation
When analyzing numerical data, it is often necessary to estimate large numbers in order to make accurate predictions or draw meaningful conclusions. Estimation is a valuable tool in many fields, including finance, economics, and statistics. Here are a few examples of situations where numerical data estimation is commonly used:
1. Population estimation: Estimating the population size of a city, country, or even the world is a common application of numerical data estimation. This is typically done by sampling a smaller population and extrapolating the results to the larger population. For example, conducting a survey of a few thousand people in a city and using the results to estimate the opinions or behaviors of the entire population.
2. Market research: Estimation is also commonly used in market research to gauge consumer preferences and behavior. For example, a company may estimate the demand for a new product by surveying a sample of their target market and extrapolating the results to the entire market. This estimation can help inform business decisions such as pricing, marketing strategies, and production levels.
- 3. Financial forecasting: Estimation plays a crucial role in financial forecasting, where analysts use historical data and other relevant information to estimate future trends and outcomes. This can include estimating sales figures, revenue projections, or even stock market trends. These estimates are used by businesses and investors to make informed decisions about investments, budgeting, and strategic planning.