
Have you ever wondered how your brain works? The brain is one of the most fascinating and complex organs in the human body. It controls everything we do, think, and feel, from our basic bodily functions to our thoughts and emotions. But what are the different parts of the brain and how do they work together to create our experiences?
Understanding the parts of the brain is like solving a puzzle. Each part has a specific function, and when they all work together, they create a cohesive system that allows us to perceive the world, make decisions, and interact with others. From the cerebrum, which is responsible for our conscious thoughts and voluntary actions, to the cerebellum, which coordinates movement and balance, each part plays a crucial role in our everyday lives.
One key part of the brain is the hippocampus. This small, seahorse-shaped structure is located in the temporal lobe and is involved in the formation of new memories. Without the hippocampus, we would struggle to remember new information and events. Another important part is the amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotions and memories related to emotional events. It helps us react to potential threats and regulate our emotional responses.
So, how do we know about the different parts of the brain and their functions? Scientists have used various techniques, such as neuroimaging and studies on patients with brain injuries, to map out the different regions and understand how they work. These discoveries have provided invaluable insights into how the brain operates, which could have implications for treating mental disorders and improving our understanding of human cognition.
The Parts of the Brain ReadWorks Answer Key
The brain is a complex organ with many different parts that work together to control various functions of the body. Understanding the different parts of the brain and their functions is essential for understanding how the brain works and how it can be affected by injury or disease.
The Parts of the Brain ReadWorks Answer Key provides detailed information about the different parts of the brain and their functions. This answer key can be used as a resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in learning more about the brain.
The Parts of the Brain:
- Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher functions such as thinking, memory, and voluntary movement.
- Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain and is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture.
- Brainstem: The brainstem is located at the base of the brain and is responsible for regulating basic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
- Hippocampus: The hippocampus is located in the temporal lobe of the brain and is involved in the formation and retrieval of memories.
- Amygdala: The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe of the brain and is involved in processing emotions, especially fear and aggression.
- Frontal Lobe: The frontal lobe is located at the front of the brain and is responsible for decision-making, problem-solving, and controlling emotions.
- Parietal Lobe: The parietal lobe is located at the top of the brain and is responsible for processing sensory information and spatial awareness.
- Occipital Lobe: The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain and is responsible for processing visual information.
- Temporal Lobe: The temporal lobe is located on the sides of the brain and is responsible for processing auditory information and language.
The Parts of the Brain ReadWorks Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of the different parts of the brain and their functions. It is a valuable resource for anyone wanting to learn more about this complex organ.
Understanding the Structure of the Brain
The human brain is an incredibly complex organ that controls all of our thoughts, emotions, and actions. It is made up of many different parts, each with its own specific function. By understanding the structure of the brain, we can gain insight into how it works and how different parts of it are responsible for different aspects of our behavior.
One of the key parts of the brain is the cerebrum, which is divided into two hemispheres– the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body and is responsible for different functions. The left hemisphere, for example, is often associated with language, logic, and analytical thinking, while the right hemisphere is more involved in creativity, spatial awareness, and emotional processing.
Another important part of the brain is the cerebellum, located at the back of the skull. The cerebellum is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture. It helps us walk, run, and perform complex motor tasks. Without the cerebellum, we would have difficulty with coordination and would struggle to perform even the simplest movements.
Additionally, the brain has a structure known as the brainstem, which connects the brain to the rest of the body. The brainstem controls vital functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. It is also involved in basic reflexes, such as blinking or swallowing. Without the brainstem, our bodies would not be able to carry out these essential functions.
In conclusion, the brain is a remarkable organ with a complex structure that allows us to think, feel, and move. Understanding the different parts of the brain and their functions is crucial in comprehending how our brain influences our behavior and overall well-being.
The Cerebral Cortex: The Thinking Cap of the Brain
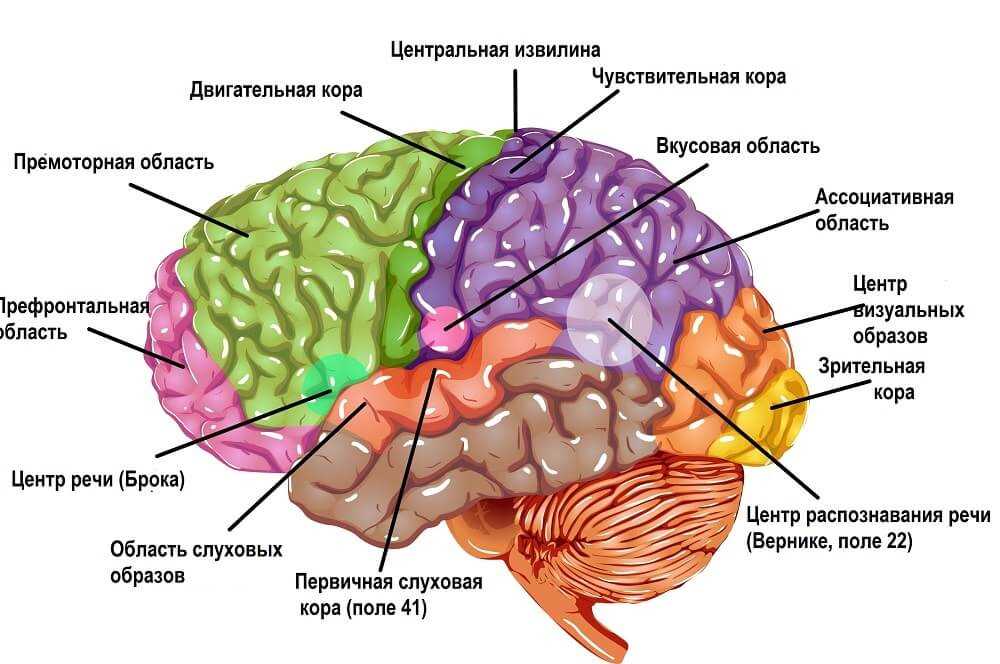
The cerebral cortex, also known as the thinking cap of the brain, is the outer layer of the brain that plays a crucial role in many complex cognitive functions. Located in the topmost part of the brain, it is responsible for processing sensory information, generating thoughts and ideas, and controlling voluntary movements.
One of the key functions of the cerebral cortex is sensory processing. It receives and interprets information from the five senses–sight, hearing, taste, touch, and smell–and transforms it into meaningful perceptions. For example, when you see a bright red apple, your cerebral cortex processes the visual information and recognizes it as an apple. Similarly, when you hear a bird chirping, your cerebral cortex processes the auditory information and identifies it as the sound of a bird.
The cerebral cortex also plays a crucial role in higher-level cognitive functions, such as memory, attention, language, and problem-solving. It is divided into different regions, each specializing in particular functions. For instance, the frontal lobe, located in the front of the cerebral cortex, is responsible for planning, decision-making, and controlling impulses, while the temporal lobe, located on the sides of the cerebral cortex, is involved in processing auditory information and language comprehension.
In conclusion, the cerebral cortex is truly the thinking cap of the brain. It is responsible for processing sensory information, generating thoughts and ideas, and controlling various cognitive functions. Its intricate structure and specific regions allow us to perceive the world around us, understand language, and think critically. Without the cerebral cortex, our brains would not be able to perform the complex tasks that make us human.
The Limbic System: Emotions and Memory
The limbic system is a complex network of structures located deep within the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating emotions and forming memories. One key structure in the limbic system is the amygdala, which is responsible for processing and interpreting emotions. The amygdala helps us recognize and respond to threats, fear, and other intense emotions. It also plays a role in the formation of emotional memories.
Another important component of the limbic system is the hippocampus. The hippocampus is involved in the formation of new memories, particularly declarative memories which involve facts and events. It helps us store and retrieve information from our long-term memory. Damage to the hippocampus can result in memory disorders, such as amnesia, where individuals may struggle to form new memories.
Additionally, the limbic system includes the hypothalamus, which is responsible for regulating basic functions and behaviors such as hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sleep. The hypothalamus also plays a role in the release of hormones, which are chemical messengers that influence our physical and emotional state.
In summary, the limbic system is a complex network of structures that regulates emotions and memory. The amygdala helps process emotions, the hippocampus is involved in memory formation, and the hypothalamus regulates basic functions and behaviors. Understanding the role of the limbic system can provide insights into how emotions and memories are processed and experienced.
The Brain Stem: Control Center of Vital Functions
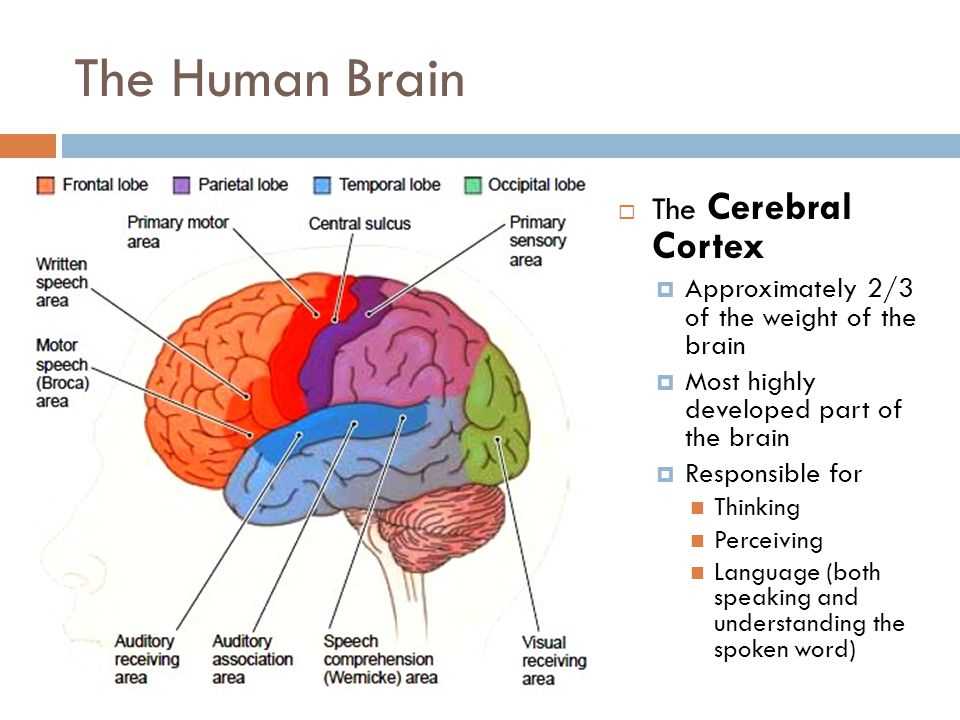
The brain stem is a crucial part of the brain that plays a vital role in controlling essential functions necessary for our survival. It is located at the base of the brain and connects the spinal cord to the rest of the brain. The brain stem consists of three main parts: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain.
The medulla oblongata, the lowest part of the brain stem, is responsible for controlling automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It also helps regulate reflexes and involuntary actions like swallowing and coughing. The medulla oblongata serves as a bridge between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain, allowing for the transmission of sensory and motor information.
The pons, located above the medulla, acts as a relay station between different parts of the brain and helps coordinate movements. It also plays a role in regulating sleep and dreaming. Additionally, the pons contains nuclei that are involved in controlling facial expressions and certain sensory functions, such as hearing.
The midbrain, the uppermost part of the brain stem, is responsible for relaying visual and auditory information to the appropriate areas of the brain. It also plays a crucial role in controlling eye movement, maintaining posture, and coordinating certain reflexes.
Overall, the brain stem is instrumental in ensuring the proper functioning of vital bodily functions. Without this control center, our bodies would not be able to perform essential tasks like breathing or regulating heart rate. Understanding the importance of the brain stem helps us appreciate the complexity and interconnectedness of the human brain.
The Cerebellum: Coordination and Balance
The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, plays a crucial role in the coordination and balance of our movements. It is often referred to as the “little brain” because of its size and appearance. Despite its small size, the cerebellum contains a vast number of neurons and is responsible for processing information from various parts of the brain and body to fine-tune our motor skills and movements.
One of the main functions of the cerebellum is to ensure smooth and coordinated movements. It receives information about the position and movement of different body parts from sensory receptors located throughout the body, as well as from other parts of the brain. It then compares this information with the intended movement and makes precise adjustments to ensure accurate execution. This allows us to perform complex activities such as walking, writing, and playing musical instruments with ease and precision.
The cerebellum also plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. It receives information from the inner ear, which helps us sense our body’s position in relation to gravity and make necessary adjustments to stay balanced. Additionally, it receives input from the visual system to further enhance our perception of balance. When the cerebellum is impaired due to injury or disease, it can result in issues with coordination and balance, leading to problems with motor control and movement.
In conclusion, the cerebellum is a vital brain structure that is responsible for coordination and balance. It receives and processes information from various sources to ensure smooth and precise movements. Without the cerebellum, our ability to perform everyday tasks that require coordination and balance would be significantly affected.
The Brain’s Left and Right Hemispheres: Specialization and Integration
The human brain is an incredibly complex organ, consisting of billions of neurons that work together to carry out various functions. One of the key features of the brain is its division into two hemispheres, known as the left and right hemispheres. Each hemisphere has its own specialized functions, but they also work together in a process called integration.
The left hemisphere of the brain is often referred to as the “logical” or “analytical” side. It is responsible for language processing, mathematical reasoning, and logical thinking. It controls the right side of the body and receives information from the right visual field. The left hemisphere is also involved in sequential processing, which means it is better at processing information that is presented in a linear, step-by-step manner.
On the other hand, the right hemisphere is often referred to as the “creative” or “intuitive” side. It is responsible for spatial awareness, visualization, and artistic abilities. It controls the left side of the body and receives information from the left visual field. The right hemisphere is also involved in holistic processing, which means it is better at processing information as a whole, rather than focusing on individual parts.
While each hemisphere has its own specialized functions, they work together in a coordinated and integrated manner. This integration allows for the harmonious functioning of different brain processes. For example, when you read a book, the left hemisphere processes the language and the right hemisphere helps you visualize the scenes described in the story.
The left and right hemispheres of the brain are not completely independent, and there is constant communication and interaction between them. This communication occurs through a thick, bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum allows for the exchange of information and enables the integration of different cognitive processes.
In conclusion, the brain’s left and right hemispheres have specialized functions, but they also work together in a process called integration. This integration allows for the seamless functioning of various cognitive processes, from logical reasoning to artistic creativity.