The skeletal system is a complex network of bones, cartilage, and connective tissues that provides structure, support, and protection for the body. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the skeletal system is crucial for healthcare professionals, athletes, and individuals seeking to maintain overall health and well-being.
This article will delve into Chapter 5 of the skeletal system worksheet, which explores key concepts related to bone structure, joint types, and the skeletal system’s role in movement and protection. By providing detailed answers to the worksheet questions, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of these critical topics.
Some of the fundamental questions discussed in this chapter include: What are the different types of bones and their functions? How does bone growth and remodeling occur? What are the different types of joints and their movements? What are the main functions of the skeletal system?
By exploring these questions and providing thorough answers, this article aims to enhance readers’ knowledge and comprehension of the skeletal system. Whether you are a student, healthcare professional, or someone interested in learning more about their own body, this chapter will serve as a valuable resource in understanding the intricate workings of the skeletal system.
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Worksheet Answers
The skeletal system is an essential part of the human body, providing structure, support, and protection for our organs. Understanding the skeletal system is crucial for medical professionals and anyone interested in human anatomy. Chapter 5 of the textbook focuses specifically on the skeletal system and provides a worksheet with questions and answers to test your knowledge.
Worksheet Answers
1. The skeletal system is made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
2. The main functions of the skeletal system include providing support for the body, protecting internal organs, facilitating movement, producing blood cells, and storing minerals.
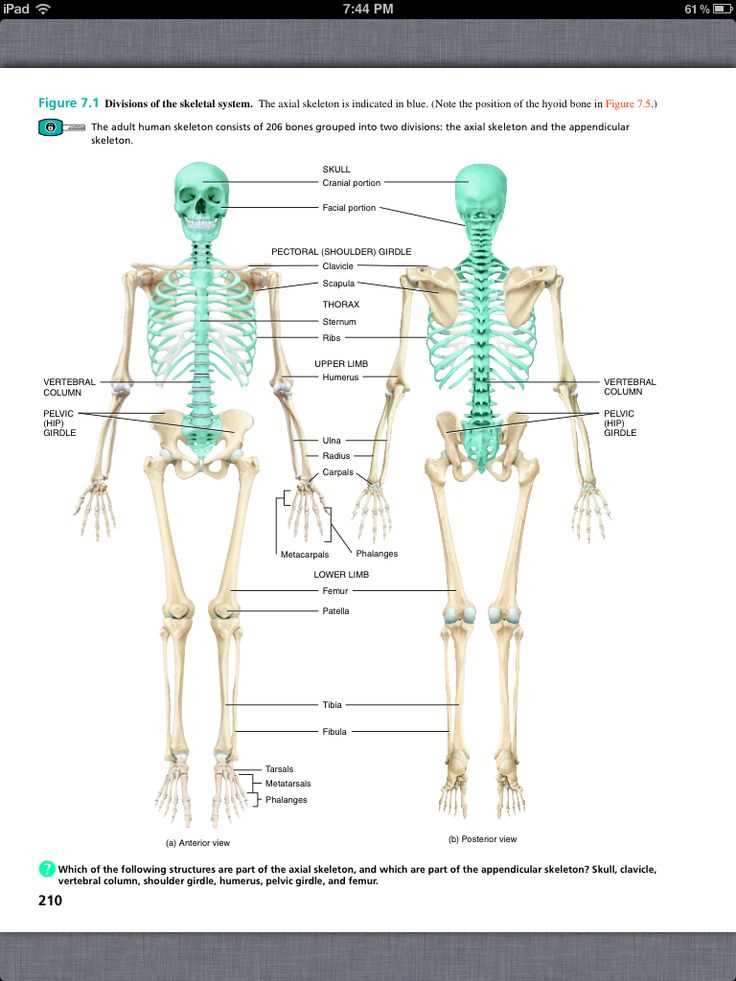
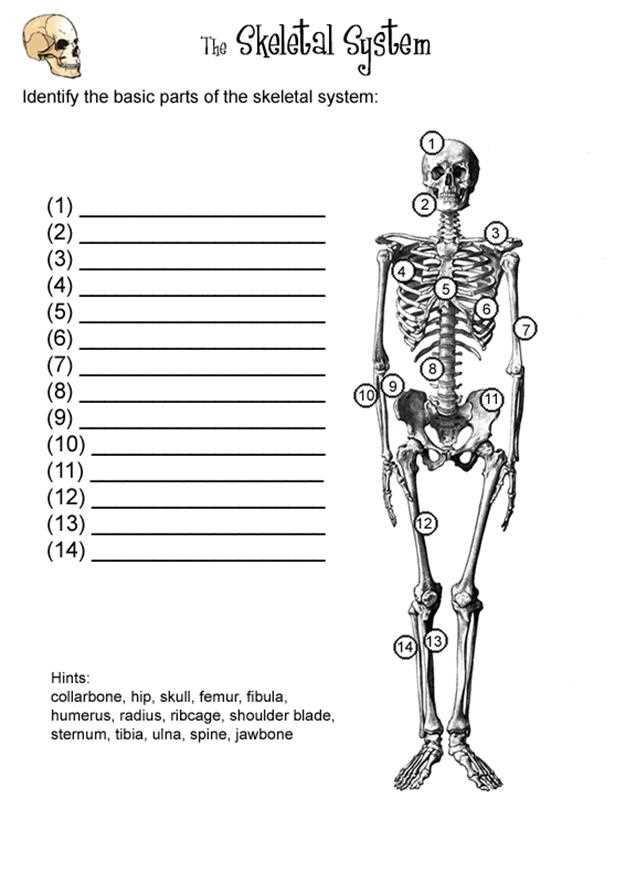
3. There are 206 bones in the human body, divided into two main categories: axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton.
4. The axial skeleton consists of the skull, vertebral column, and ribcage. It provides support and protection for the central axis of the body.
5. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs, as well as the pectoral and pelvic girdles. It allows for movement and mobility.
6. Bones are classified into four main types: long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones.
7. Long bones, such as the femur and humerus, are longer than they are wide and have a shaft (diaphysis) with two ends (epiphysis).
8. Short bones, like those found in the wrist and ankle, are roughly equal in length and width and provide stability and support.
9. Flat bones, such as the skull and scapula, are thin, flat, and often curved. They provide protection for underlying organs.
10. Irregular bones, like the vertebrae and facial bones, have complex shapes and do not fit into the other categories. They provide support and protection in specific areas.
These are just a few of the answers to the worksheet questions on the skeletal system. By studying and understanding these answers, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of the skeletal system and its role in the human body.
What is the Skeletal System?
The skeletal system is the framework of bones that provides support and protection for the body. It is made up of bones, ligaments, and cartilage, and plays a vital role in the overall structure and movement of the body. The skeletal system also works with the muscular system to enable movement and provides a site for the production of blood cells.
The main functions of the skeletal system include providing structure and support, protecting vital organs, enabling movement, producing blood cells, storing minerals, and regulating mineral balance. Without the skeletal system, our bodies would not be able to maintain their shape and perform essential functions.
The skeletal system is composed of over 200 bones of various shapes and sizes. These bones are connected by joints, which allow for movement and flexibility. The bones themselves are made up of living tissues that are constantly undergoing a process of remodeling and repair. This helps to maintain the strength and integrity of the skeletal system.
In addition to bones, the skeletal system also includes ligaments and cartilage. Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect bones to other bones, providing stability and preventing excessive movement. Cartilage is a smooth, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of bones and helps to cushion and protect them during movement.
The skeletal system is essential for overall health and well-being. It not only provides structural support for the body, but also helps to protect vital organs and allows for movement and flexibility. Maintaining a healthy skeletal system through proper nutrition and exercise is important for preventing bone diseases and injuries, and ensuring optimal physical function.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system performs several vital functions in the human body. First and foremost, it provides structural support and shape to the body. The bones of the skeletal system serve as the framework that holds everything together, giving the body its form and allowing it to stand upright. Without the skeletal system, our bodies would be shapeless and unable to maintain their structure.
An important function of the skeletal system is to protect our vital organs. Many of our organs, such as the brain, heart, and lungs, are located within the skeletal system, specifically within the cranial and thoracic cavities. The bones of the skull and ribcage provide a protective barrier around these organs, helping to shield them from injury and damage.
The skeletal system also plays a crucial role in movement. Our muscles are attached to bones through tendons, and when muscles contract or relax, they pull on the bones, causing movement. Without the skeletal system to provide a stable foundation, our muscles would be unable to effectively generate movement, and simple tasks such as walking, running, and lifting would be impossible.
In addition to these functions, the skeletal system is responsible for the production of blood cells. The marrow inside our bones is involved in the production of red and white blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body, while white blood cells help to fight off infection. Without a healthy skeletal system, our bodies would struggle to produce an adequate supply of these essential blood cells.
Overall, the skeletal system is not just a framework of bones; it is a complex system that performs multiple crucial functions for our bodies. From providing structure and protection to enabling movement and blood cell production, the skeletal system is essential for our overall health and well-being.
Structure of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. It provides support, protection, and movement for the body. The skeletal system is divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum, while the appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs, as well as the pelvic girdle.
Bones are the main component of the skeletal system and are made up of hard, mineralized tissue. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from long bones like the femur in the leg, to flat bones like the scapula in the shoulder. Each bone has several parts, including the compact bone, which provides strength and support, and the spongy bone, which contains red bone marrow responsible for the production of blood cells.
The skeletal system also includes cartilage, which is a flexible connective tissue that covers the surface of bones and helps to reduce friction and absorb shock during movement. Ligaments are fibrous tissues that connect bones to other bones, while tendons connect muscles to bones, allowing for movement. Together, these components work together to provide stability, flexibility, and protection to the body.
- The skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
- The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum.
- The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs, as well as the pelvic girdle.
- Bones are made up of hard, mineralized tissue, and have several parts including compact bone and spongy bone.
- Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that covers the surface of bones.
- Ligaments connect bones to other bones, while tendons connect muscles to bones.
Bones of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is composed of over 200 bones that provide support, protection, and movement for the body. These bones are essential for maintaining the shape and structure of the body, as well as allowing for the attachment of muscles and ligaments. The human skeletal system can be divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
The axial skeleton consists of the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The skull is made up of 22 bones, including the cranial bones that protect the brain and the facial bones that give the face its shape. The vertebral column is composed of 33 individual vertebrae, which protect the spinal cord and provide support for the body. The thoracic cage includes the ribs and sternum, which protect the organs in the chest and help with breathing.
- The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs, as well as the bones that attach them to the axial skeleton. The upper limb consists of the humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges. These bones allow for movement and dexterity of the hand and arm.
- The lower limb includes the femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges. These bones provide support and allow for movement of the leg and foot.
Together, the bones of the skeletal system work in harmony to provide the body with stability, protection, and movement. They also play a role in the production of blood cells and the storage of minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus. Maintaining a healthy skeletal system is crucial for overall well-being and functionality.
Joints and Movement

In the human body, joints play a crucial role in allowing movement. Joints are the locations where two or more bones come together and allow the body to bend, rotate, and move in various ways. They provide stability and flexibility to the skeletal system, enabling us to perform different activities and tasks.
There are several types of joints in the human body, each with its own structure and function. One type is the hinge joint, which allows movement in one plane, like the elbow or knee. Another type is the ball and socket joint, which allows movement in multiple directions, like the shoulder or hip. There are also pivot joints, which enable rotation, such as in the neck.
When we move our bodies, muscles contract and pull on the bones, causing movement at the joints. The muscles and tendons surrounding the joints work together to create coordinated movements, allowing us to perform activities ranging from simple tasks like walking and writing to complex movements like dancing and playing sports.
It is important to take care of our joints to ensure their optimal function throughout our lives. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding excessive strain or repetitive movements can help keep our joints strong and flexible. If joint pain or injury occurs, it is important to seek medical attention and possibly undergo physical therapy to promote healing and restore proper joint function.
The skeletal system is vital for providing structure and support to the body. However, there are several disorders that can affect the health and functionality of the skeletal system. These disorders can vary in severity and can affect different parts of the skeleton.
Common Skeletal Disorders
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes the bones to become weak and brittle. It is commonly associated with aging, but can also be caused by hormonal changes, certain medications, and lifestyle factors such as lack of exercise and poor nutrition. This disorder increases the risk of fractures and can lead to chronic pain and loss of mobility.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a group of disorders that cause inflammation and stiffness in the joints. There are several types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. Arthritis not only affects the joints, but can also impact the surrounding tissues, such as tendons and ligaments. This can result in pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition that causes an abnormal curvature of the spine. This disorder typically develops during adolescence, and its cause is often unknown. Scoliosis can range from mild to severe, and in severe cases, it can affect lung function and heart health. Treatment options for scoliosis include bracing and surgery.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, and it occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time. This can result in pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joints. Osteoarthritis is often associated with aging, overuse of joints, and obesity.
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Skeletal injuries (fractures, dislocations)
- Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
- Bone cancer
In addition to these disorders, there are also various skeletal injuries and conditions such as fractures, dislocations, osteomyelitis (bone infection), and bone cancer that can affect the skeletal system. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and management of these disorders are important in order to maintain the health and functionality of the skeletal system.
How to Maintain a Healthy Skeletal System
Having a healthy skeletal system is essential for overall health and well-being. Your skeletal system provides the structure and support for your body, protects your internal organs, and allows for movement. To maintain a healthy skeletal system, it is important to follow a few key practices.
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of your skeletal system. It is important to consume foods that are rich in calcium and vitamin D, as these nutrients are essential for bone health. Calcium can be found in dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods, while vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight, fatty fish, and fortified dairy products. Including these foods in your diet can help ensure that your bones stay strong and healthy.
2. Engage in Regular Weight-Bearing Exercise
Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing exercises, is important for maintaining a healthy skeletal system. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, dancing, or weightlifting, help stimulate the production of new bone tissue and strengthen existing bones. By incorporating these types of exercises into your routine, you can help reduce the risk of bone loss and maintain bone density.
3. Avoid Sedentary Lifestyle
Avoiding a sedentary lifestyle is crucial for maintaining a healthy skeletal system. Prolonged periods of inactivity can lead to a loss of bone density and muscle mass, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. It is important to engage in regular physical activity and avoid sitting or lying down for extended periods. Incorporating regular movement and exercise into your daily routine can help keep your skeletal system strong and healthy.
4. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can have negative effects on your skeletal system. Smoking decreases blood flow to the bones, making them more prone to fractures and slowing down the healing process. Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with the formation and absorption of calcium, leading to brittle bones and an increased risk of fractures. It is important to avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake to maintain a healthy skeletal system.
5. Get Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help ensure that any potential issues with your skeletal system are detected and addressed early on. Your healthcare provider may recommend bone density tests, blood tests, or other diagnostic procedures to assess your skeletal health. By staying proactive and seeking regular medical attention, you can take necessary measures to maintain a healthy skeletal system.
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy skeletal system requires a combination of proper nutrition, regular exercise, and eliminating harmful habits. By following these guidelines, you can support the health and strength of your skeletal system, leading to improved overall well-being.