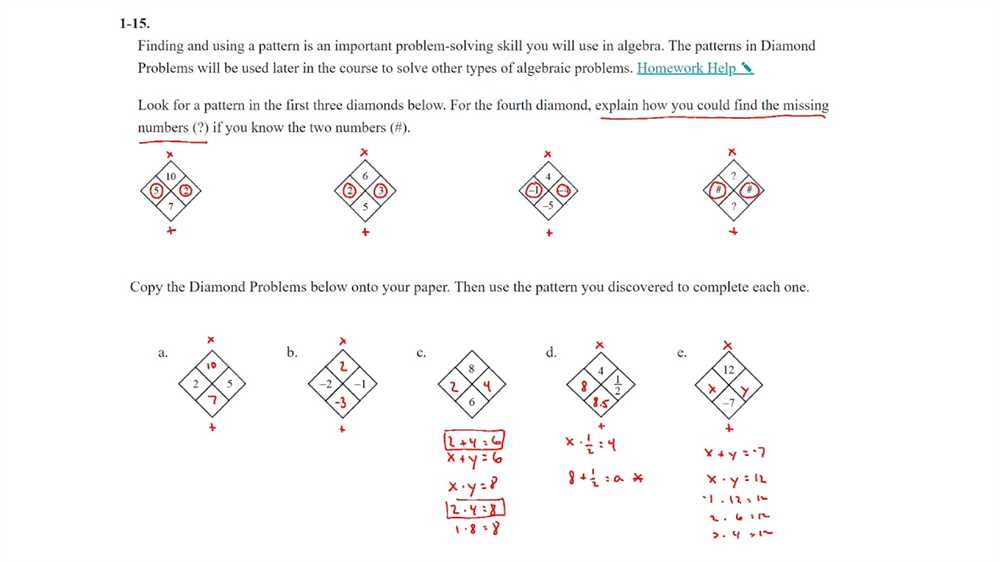
CPM, which stands for College Preparatory Mathematics, is an educational program that focuses on teaching students problem-solving strategies and critical thinking skills. The program aims to help students develop a deep understanding of mathematical concepts and their real-life applications.
CPM 2-1-1 refers to a specific lesson or section within the CPM curriculum. This section is designed to reinforce and expand upon the concepts learned in previous lessons. It covers various topics, including algebraic expressions, solving equations, and understanding patterns and relationships.
Having a comprehensive answer key for CPM 2-1-1 can be extremely helpful for both teachers and students. It allows teachers to assess student understanding and identify areas that may require additional instruction. For students, the answer key serves as a valuable resource for self-assessment and practice, helping them reinforce their knowledge and improve their problem-solving skills.
In this article, we will provide a detailed answer key for CPM 2-1-1, including step-by-step solutions and explanations for each problem. Whether you’re a teacher looking for additional resources or a student in need of extra practice, this answer key will be an invaluable tool to enhance your understanding of CPM 2-1-1.
CPM 2-1-1 Answer Key: Everything You Need to Know

CPM 2-1-1 is a comprehensive resource that provides individuals with valuable information, referrals, and assistance for various community services. Whether you are in need of emergency housing, healthcare services, or financial assistance, CPM 2-1-1 aims to connect you with the right resources to meet your needs. This answer key is a helpful tool that provides answers to commonly asked questions and helps users navigate through the CPM 2-1-1 system.
One of the key features of the CPM 2-1-1 answer key is its comprehensive list of frequently asked questions. This section provides answers to common inquiries regarding eligibility criteria, program availability, and how to access specific services. Whether you are looking for information on food assistance programs or housing resources, the answer key can provide you with the essential details you need.
The answer key also includes a detailed directory that lists the various community resources available through the CPM 2-1-1 system. This directory is organized by different categories, making it easier for users to find the specific services they are looking for. From healthcare and mental health resources to employment and education programs, the directory is a valuable tool for individuals seeking assistance.
In addition, the CPM 2-1-1 answer key provides step-by-step instructions on how to access the services listed in the directory. It outlines the process of contacting the appropriate agencies, understanding the eligibility requirements, and completing any necessary applications or paperwork. This guidance ensures that individuals can navigate the system effectively and access the help they need.
Overall, the CPM 2-1-1 answer key serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding and utilizing the resources available through the CPM 2-1-1 system. Whether you are in a crisis situation or simply need assistance with everyday life challenges, this answer key is an invaluable resource that can help connect you with the services you need to thrive.
Understanding Cpm 2 1 1: Definition and Overview
The Cpm 2 1 1 model is a project management technique used to plan and monitor projects. Cpm stands for Critical Path Method, while the numbers 2 1 1 refer to the sequence of steps involved in the process. This model is widely used in various industries and sectors to ensure efficient project execution.
The Cpm 2 1 1 technique involves several key steps, starting with the identification and sequencing of project activities. Each activity is assigned a duration and dependencies are established to determine the critical path, which represents the longest sequence of dependent activities that determines the overall project duration. By understanding the critical path, project managers can focus their efforts on optimizing these activities to ensure timely project completion.
The Cpm 2 1 1 process typically includes the following steps:
- Step 1: Define project scope and objectives – Clearly define the goals and deliverables of the project.
- Step 2: Identify project activities – Break down the project into smaller activities that need to be completed.
- Step 3: Determine activity dependencies – Identify the relationships between different activities and establish their dependencies.
- Step 4: Estimate activity durations – Assign realistic timeframes for each activity.
- Step 5: Develop the project schedule – Use the Cpm method to sequence the activities and determine the critical path.
- Step 6: Monitor and control the project – Regularly track the progress of the project and make necessary adjustments to ensure on-time completion.
The Cpm 2 1 1 model provides project managers with a structured approach to planning and executing projects. By identifying the critical path and monitoring project progress, managers can effectively manage resources, allocate tasks, and make informed decisions to keep projects on track. This technique helps minimize risks and delays, resulting in successful project outcomes.
Importance of Cpm 2 1 1 in Performance Measurement
CPM 2 1 1 is a powerful tool in performance measurement that allows organizations to analyze and improve their effectiveness and efficiency. It provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating key performance indicators (KPIs) and identifying areas for improvement. By using CPM 2 1 1, organizations can easily track their performance over time, identify trends, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
One of the key benefits of CPM 2 1 1 is its ability to align organizational objectives with individual goals and activities. It helps create a clear line of sight between strategy and execution by defining clear targets, establishing performance measures, and monitoring progress. This ensures that everyone in the organization is working towards the same goals and priorities, leading to increased alignment and improved performance.
CPM 2 1 1 also promotes accountability and transparency within an organization. By regularly collecting and reporting performance data, organizations can hold themselves accountable for their results and demonstrate their commitment to continuous improvement. This helps build trust with stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and investors, and enhances the organization’s reputation.
The use of CPM 2 1 1 also enables organizations to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. By analyzing performance data, organizations can identify potential problems and implement necessary changes to optimize processes and increase productivity. This can lead to reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, and increased competitive advantage.
In conclusion, CPM 2 1 1 plays a crucial role in performance measurement by providing organizations with a structured approach to evaluating and improving their performance. By using this framework, organizations can align their objectives, promote accountability, and identify areas for improvement, leading to increased effectiveness and success.
How to Calculate Cpm 2 1 1: Step-by-Step Guide

In the advertising world, CPM (Cost per Thousand Impressions) is a widely-used metric to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of an advertising campaign. CPM is calculated by dividing the total cost of an ad campaign by the number of impressions (or views) it generates, and then multiplying that result by 1,000. Cpm 2 1 1 is a specific formula used to calculate the CPM for a 2-week advertising campaign with 1 ad played 1 time per hour.
To calculate Cpm 2 1 1, you will need to gather the following information:
- Total cost of the advertising campaign
- Number of hours in the campaign
- Number of times the ad is played per hour
Once you have all the necessary information, follow these steps:
- Divide the total cost of the campaign by the number of hours in the campaign. This will give you the cost per hour.
- Multiply the cost per hour by the number of times the ad is played per hour. This will give you the cost per hour per ad.
- Multiply the cost per hour per ad by 2 (for the 2-week duration of the campaign). This will give you the total cost for the 2-week campaign.
- Divide the total cost for the 2-week campaign by the number of impressions generated during that time period.
- Multiply the result by 1,000 to convert to CPM.
By following these steps, you can calculate the Cpm 2 1 1 for your advertising campaign and determine its cost-effectiveness.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Calculating Cpm 2 1 1
Calculating Cpm 2 1 1, which stands for Cost Per Thousand, is an important metric in digital advertising. However, there are several common mistakes that advertisers often make when calculating Cpm 2 1 1, which can lead to inaccurate results and wasteful spending. To ensure accurate calculations and avoid these mistakes, it is important to pay attention to the following key points:
1. Incorrect Conversion of Units
One of the most common mistakes when calculating Cpm 2 1 1 is the incorrect conversion of units. Cpm 2 1 1 is calculated as the cost per 1,000 impressions, so it is important to make sure that all units are consistent. For example, if the cost is given in dollars and the impressions are given in thousands, make sure to convert the cost to a per thousand basis. Failing to convert the units correctly can result in inaccurate Cpm 2 1 1 calculations.
2. Not Considering Additional Costs
Another common mistake is not considering additional costs when calculating Cpm 2 1 1. Cpm 2 1 1 is typically used to evaluate the cost efficiency of advertising campaigns, and it is important to take into account all relevant costs. This includes not only the cost of media placement, but also any production costs, agency fees, and other expenses. Failing to include all costs can lead to an artificially low Cpm 2 1 1 and an inaccurate assessment of campaign performance.
3. Inaccurate Impression Count
A third common mistake when calculating Cpm 2 1 1 is an inaccurate impression count. Impressions are the number of times an ad is displayed to users, and it is crucial to have an accurate count to calculate Cpm 2 1 1 correctly. Incorrectly counting impressions can lead to overestimating or underestimating the reach of an ad campaign and can skew the Cpm 2 1 1 calculation. It is important to use reliable tracking tools and data sources to ensure an accurate impression count.
By avoiding these common mistakes, advertisers can ensure accurate Cpm 2 1 1 calculations and make informed decisions about their digital advertising campaigns. Paying attention to unit conversions, considering all costs, and using accurate impression counts will lead to a more accurate assessment of campaign performance and ultimately better return on investment.
Interpreting Cpm 2 1 1 Results: What Do They Mean?
When analyzing the results of a Cpm 2 1 1 experiment, it is important to understand what the numbers and data mean. The Cpm 2 1 1 design is a powerful tool for evaluating the impact of a treatment or intervention, but interpreting the results can be complex. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind when interpreting Cpm 2 1 1 results:
1. Baseline data: Before the intervention, it is important to examine the baseline data to understand the starting point of the experiment. This helps to establish a comparison for evaluating the effects of the treatment. By comparing the baseline data to the post-intervention data, researchers can determine if there has been a significant change due to the intervention or if the observed effects are within the natural variation.
2. Treatment effects: The Cpm 2 1 1 design allows for the evaluation of both the immediate and cumulative effects of the treatment. The immediate effect is measured by comparing the post-intervention data of the treatment group to the control group. The cumulative effect is evaluated by comparing the post-intervention data of the treatment group to the pre-intervention data. By examining these effects, researchers can determine if the treatment has had a significant impact.
Example:
- The immediate treatment effect may indicate whether the intervention had an immediate impact on the outcome measure, such as changes in behavior or performance.
- The cumulative treatment effect may show the long-term effects of the intervention, such as sustained improvements over time.
3. Statistical significance: When interpreting Cpm 2 1 1 results, it is important to consider the statistical significance of the findings. Statistical significance indicates whether the observed differences can be attributed to the treatment or if they are due to chance. Statistical tests such as t-tests or ANOVA can be used to determine the significance of the results. A p-value of less than 0.05 is often considered statistically significant.
4. Practical significance: In addition to statistical significance, the practical significance of the findings should also be considered. Practical significance refers to the real-world implications and importance of the observed effects. Even if a result is statistically significant, it may not have a meaningful impact in practice. Researchers should carefully evaluate the practical significance of their findings to determine the relevance and applicability of the intervention.
5. Limitations: Lastly, it is important to acknowledge and consider the limitations of the Cpm 2 1 1 design and the interpretation of its results. This includes factors such as sample size, external validity, and potential confounding variables. By recognizing these limitations, researchers can provide a more balanced and nuanced interpretation of the results.
In conclusion, interpreting Cpm 2 1 1 results requires a careful consideration of baseline data, treatment effects, statistical and practical significance, and limitations. By taking these factors into account, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the impact of their interventions and make informed decisions for future research or implementation.