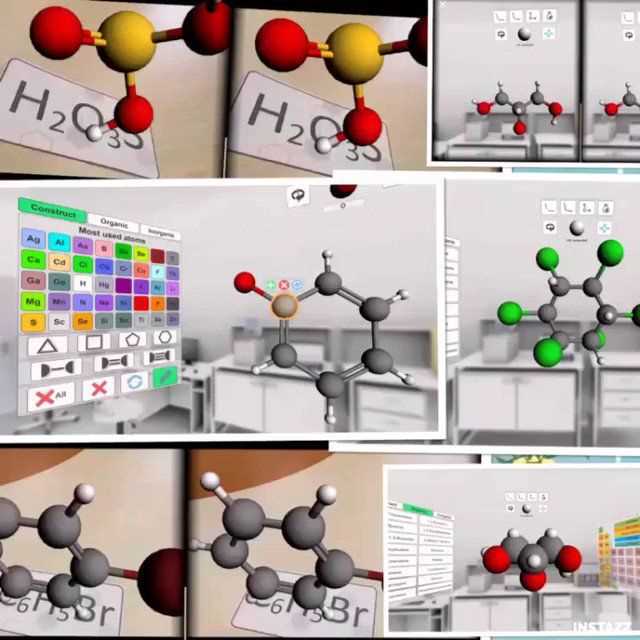
The 3D Molecular Designs Translation Activity Guide provides educators with a valuable resource to engage students in hands-on learning about molecular structures. This guide offers a comprehensive answer key to assist educators in assessing their students’ understanding and progress.
With the answer key, educators can easily evaluate the accuracy and completeness of their students’ translations. The key includes clear and concise explanations for each question, allowing educators to provide insightful feedback to their students. By using this guide, educators can ensure that their students are grasping key concepts and mastering important skills.
The answer key covers a wide range of topics, including amino acids, DNA, and protein synthesis. By utilizing the key, educators can guide their students through the translation activity and reinforce important concepts along the way. This resource is an invaluable tool for educators seeking to enhance their students’ understanding of molecular structures and their functions.
The Importance of Molecular Models
Molecular models play a crucial role in understanding the complex structures and interactions of molecules. These models are essential tools in chemistry and biology research, allowing scientists to visualize and manipulate molecules in three-dimensional space. By representing atoms and bonds in a physical form, molecular models provide a tangible representation of complex molecular structures and help researchers uncover valuable insights into their properties and behaviors.
One of the key advantages of molecular models is their ability to simplify complex concepts. Models allow scientists to visually grasp the spatial arrangement and connectivity of atoms in a molecule, making it easier to comprehend and analyze the molecule’s properties. By manipulating these models, researchers can explore different conformations and study how molecular structures affect their reactivity, stability, and interactions with other molecules. This hands-on approach enhances understanding and facilitates the discovery of new molecular structures with desired properties.
Furthermore, molecular models serve as powerful educational tools. They help students learn and visualize abstract concepts related to atomic and molecular structures, facilitating a deeper understanding of chemistry and biology. By physically building models, students engage in kinesthetic learning, which taps into their spatial intelligence and enhances long-term retention of information. Additionally, using molecular models in classroom settings encourages active participation and collaboration, fostering a deeper appreciation and interest in the sciences.
Molecular models also play a critical role in drug discovery and development. By constructing models of drug molecules and their target receptors, researchers can better understand how these molecules bind and interact, ultimately leading to the design of more effective and selective drugs. Molecular models are invaluable tools for guiding the rational design of therapeutics, allowing scientists to predict and optimize drug-receptor interactions and potentially reduce the time and cost involved in drug discovery processes.
In conclusion, molecular models are indispensable tools in scientific research, education, and drug development. They provide a visual representation of complex molecular structures, simplifying concepts and facilitating deeper understanding. Molecular models enhance learning, stimulate collaboration, and enable the design of more efficient drugs. With their versatility and practical applications, molecular models continue to contribute greatly to advancements in the fields of chemistry and biology.
Purpose of the Translation Activity Guide

The Translation Activity Guide serves as a comprehensive tool for educators and students alike to enhance their understanding and application of 3D molecular designs. Through a series of hands-on activities and exercises, this guide aims to facilitate the translation of molecular structures from 2D models to 3D models, providing a deeper comprehension of molecular interactions and functions.
The primary objective of the Translation Activity Guide is to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application in the field of molecular biology. By actively engaging in the translation process, students can develop critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities essential for a successful career in scientific research or related fields.
Key components of the Translation Activity Guide include:
- Step-by-step instructions: The guide provides clear and concise instructions for each activity, ensuring that both educators and students can easily follow along and achieve the desired learning outcomes.
- Visual aids: Visual representations, such as diagrams and illustrations, are included to enhance understanding and aid in the visualization of molecular structures.
- Real-world applications: The guide incorporates real-world examples and case studies to demonstrate the relevance and practicality of 3D molecular designs in various scientific and medical contexts.
- Assessment tools: Assessment tools, including quizzes and self-evaluation exercises, are included to gauge the students’ understanding and knowledge retention.
In summary, the Translation Activity Guide serves as a valuable resource for educators and students seeking to deepen their understanding of 3D molecular designs. By providing a structured approach to translating molecular structures, this guide empowers learners to apply their knowledge in practical scenarios, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for success in the field of molecular biology.
Understanding the Basics of Molecular Translation
In the field of chemistry, molecular translation plays a crucial role in helping scientists understand and manipulate the structure of molecules. By translating molecular structures into visual representations, scientists can gain valuable insights into the properties and behavior of these complex substances.
Molecular translation refers to the process of converting the abstract language of chemistry into a tangible and visual form. This allows scientists to communicate and analyze molecular structures more effectively, fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing within the scientific community.
One common method of molecular translation is the use of 3D models. By creating physical representations of molecules, scientists can gain a better understanding of their three-dimensional shape and the interactions between atoms. These models can be made from a variety of materials, such as plastic or metal, and can be manipulated to explore different aspects of the molecule.
- Molecular visualization software is another powerful tool for molecular translation. This software allows scientists to generate realistic 3D representations of molecules on a computer screen. It provides a dynamic and interactive way to explore and analyze molecular structures, enabling researchers to study their properties and predict their behavior.
- Translation guides are often used in educational settings to help students understand the complex concepts of molecular chemistry. These guides provide step-by-step instructions on how to translate abstract chemical structures into visual representations, helping students develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Collaboration and sharing of molecular designs is another important aspect of molecular translation. Through online platforms and databases, scientists can share their molecular designs with other researchers around the world. This allows for greater collaboration and innovation in the field of chemistry, ultimately leading to advancements in various scientific disciplines.
In conclusion, molecular translation is a fundamental concept in the field of chemistry that allows scientists to understand, communicate, and manipulate the structures of molecules. By utilizing 3D models, molecular visualization software, translation guides, and collaborative platforms, researchers can gain valuable insights into the properties and behavior of complex substances, leading to advancements in various scientific disciplines.
What is Molecular Translation?
Molecular translation is the process of converting information about a molecule from one representation to another. It involves translating the structure and properties of a molecule between different 2D or 3D models, such as translating a chemical diagram into a physical 3D model or vice versa. Molecular translation is an important tool in the field of chemistry, as it allows scientists to visualize and understand the structure and behavior of molecules in different forms.
In molecular translation, various software tools and algorithms are used to convert molecular data from one format to another. This can include translating between different file types, such as converting a 2D chemical structure file into a 3D molecular model file. Additionally, molecular translation can involve converting between different representations, such as translating a line bond formula into a ball-and-stick model.
Molecular translation is essential in many areas of molecular research and analysis. It allows scientists to communicate and share information about molecules in a standardized and easily understandable format. It also enables the generation of accurate physical models for further experimentation and analysis. By translating molecular data between different representations, scientists can gain a deeper insight into the structure, properties, and interactions of molecules, leading to a greater understanding of chemical processes and the development of new drugs, materials, and technologies.
Key Concepts in Molecular Translation

The process of molecular translation involves the conversion of a two-dimensional molecular structure into a three-dimensional model. This is achieved by considering the spatial arrangement of atoms and bonds within the molecule and representing them in a physical form. By creating a 3D model, scientists can better understand the structure and properties of a molecule, which can be further utilized in various applications such as drug design, materials science, and chemical synthesis.
Spatial arrangement: The spatial arrangement of atoms and bonds within a molecule is a key concept in molecular translation. It involves understanding the three-dimensional positions of each atom and the connections between them. By accurately representing the spatial arrangement, scientists can visualize the molecule’s structure and its interactions with other molecules.
Physical representation: In molecular translation, the two-dimensional molecular structure is transformed into a physical model. This can be achieved using various techniques, including computer-aided design software, physical modeling kits, or even 3D printing. The physical representation allows scientists to manipulate and analyze the molecule in a tactile way, enabling a deeper understanding of its properties.
Molecule properties: The translation of a molecular structure into a 3D model provides insight into the properties of the molecule. This includes characteristics such as shape, size, polarity, and electronic configuration. By visualizing these properties, scientists can make predictions about the molecule’s behavior and interactions with other molecules, which is crucial in fields like drug discovery and materials science.
Applications: The knowledge gained from molecular translation has numerous practical applications. For example, in drug design, understanding the 3D structure of a target molecule can help scientists develop more effective and specific drugs. In materials science, the translation of molecular structures can aid in designing materials with desired properties. This process also plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis, as it allows scientists to plan and visualize the formation of new compounds.
In conclusion, molecular translation involves the conversion of a two-dimensional molecular structure into a three-dimensional model. Key concepts in this process include understanding the spatial arrangement of atoms and bonds, representing the structure physically, analyzing molecule properties, and utilizing the knowledge gained in various practical applications.
Exploring the 3D Molecular Designs Translation Activity Guide
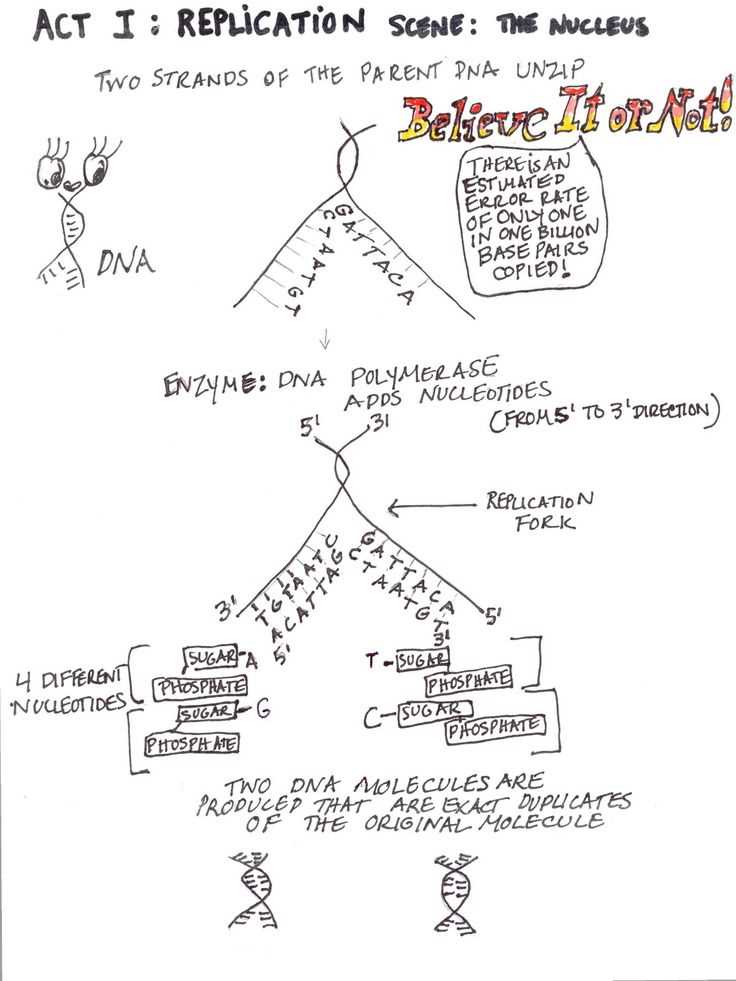
The 3D Molecular Designs Translation Activity Guide is a valuable resource for educators and students alike. It provides step-by-step instructions and materials for conducting hands-on activities that explore the world of molecular structures in a 3D format. This guide is an excellent tool for engaging students and helping them understand complex concepts in chemistry and biology.
One of the highlights of the Translation Activity Guide is the interactive nature of the activities. Students are encouraged to manipulate physical models of molecules and explore their structures and functions. This hands-on approach not only helps students visualize abstract concepts but also encourages active learning and critical thinking. By engaging in these activities, students gain a deeper understanding of molecular structures and how they relate to the world around them.
The guide includes a variety of activities that cater to different learning styles and educational needs. From building models of DNA and proteins to exploring the structure of organic compounds, there is something for everyone. Each activity is accompanied by clear instructions and explanations, making it easy for educators to incorporate them into their lesson plans. Additionally, the guide provides background information on each molecule and its significance in biological and chemical processes, further enhancing the educational value of the activities.
Overall, the 3D Molecular Designs Translation Activity Guide is a comprehensive and user-friendly resource for educators who want to introduce their students to the world of molecular structures. By incorporating these activities into their teaching, educators can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation for chemistry and biology in their students. Whether used in a classroom setting or for independent study, this guide is a valuable tool for enhancing scientific literacy and promoting hands-on learning.