A market economy is an economic system where the production and distribution of goods and services are determined primarily by demand and supply within the market. It is characterized by private ownership of resources and businesses, competition, and the pursuit of profit. In a market economy, individuals and businesses act in their own self-interest, which ultimately leads to the efficient allocation of resources.
Icivics, an educational organization, offers resources and teaching materials to help students understand the principles and workings of a market economy. The Icivics Market Economy Answer Key provides educators with the answers to the questions posed in the market economy lessons. It serves as a helpful guide for teachers to assess students’ understanding and comprehension of the concepts taught.
The Icivics Market Economy Answer Key covers topics such as supply and demand, competition, market equilibrium, and the role of government in a market economy. By referencing the answer key, educators can ensure that students are grasping the essential concepts and principles of a market economy.
Overall, the Icivics Market Economy Answer Key is a valuable resource for both students and educators. It helps students gain a deeper understanding of how a market economy functions, while providing teachers with an effective tool for assessing their students’ progress and knowledge in this important area of study.
Icivics Market Economy Answer Key: Unlocking the Answers to Your Questions
Understanding how a market economy works can be challenging, but with the help of Icivics Market Economy Answer Key, you can unlock the answers to your questions. This answer key serves as a valuable resource that provides clarity and insight into the various aspects of a market economy.
The Icivics Market Economy Answer Key is an essential tool for educators and students alike. It offers a comprehensive breakdown of key concepts and principles related to market economies, such as supply and demand, competition, and entrepreneurship. By using this answer key, students can gain a deeper understanding of economic concepts and develop critical thinking skills.
Key Features
- Comprehensive Coverage: The Icivics Market Economy Answer Key covers a wide range of topics, including the basics of market economies, the role of government, and the impact of competition. It provides detailed explanations and examples to ensure a thorough understanding of each concept.
- Clear and Concise: The answer key presents information in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to follow along and grasp complex economic concepts. It uses simple language and provides real-world examples to illustrate the principles being discussed.
- Interactive Learning: The Icivics Market Economy Answer Key encourages interactive learning through various activities and exercises. It includes thought-provoking questions, case studies, and discussion prompts that prompt students to apply their knowledge and think critically about economic issues.
- Complementary Resources: In addition to the answer key, Icivics provides supplementary resources, such as lesson plans, worksheets, and simulations, to further enhance understanding and engagement. These resources offer additional practice and reinforce the concepts covered in the answer key.
Whether you’re a student looking to deepen your knowledge of market economies or an educator seeking a comprehensive and interactive teaching tool, the Icivics Market Economy Answer Key is an invaluable resource. It unlocks the answers to your questions and empowers you to navigate the complexities of a market economy with confidence.
Understanding the Basics of Icivics Market Economy
In the study of civic education, it is crucial to have a strong foundation of knowledge regarding the various economic systems that exist in the world. One of the most prominent and widely used economic systems is the market economy, which is also a key concept in Icivics. A market economy is characterized by the interaction of buyers and sellers in the marketplace, where the forces of supply and demand determine the prices and allocation of goods and services.
Supply and demand are two essential elements of a market economy. Supply refers to the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to provide at a given price. It is influenced by factors such as production costs, technology, and availability of resources. Demand, on the other hand, represents the desire and ability of buyers to purchase a specific good or service at a given price. It is influenced by factors such as consumer preferences, income levels, and the availability of substitutes.
In a market economy, the interaction of supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity of a product. When the demand for a product exceeds its supply, the price tends to increase. On the other hand, when the supply of a product exceeds its demand, the price tends to decrease. This dynamic process helps allocate resources efficiently and promotes competition among producers to satisfy consumer needs and wants.
The concept of competition is central to the functioning of a market economy. In a competitive market, multiple sellers offer similar products, and buyers have the freedom to choose among them based on factors such as price and quality. This competition encourages producers to innovate, improve their products, and offer competitive prices to attract customers. It also provides consumers with a wide range of choices and the power to influence market outcomes through their purchasing decisions.
Overall, understanding the basics of a market economy is essential in the study of Icivics and civic education in general. It helps individuals grasp the fundamental principles that govern the allocation of resources, the determination of prices, and the interaction between buyers and sellers in the marketplace. Additionally, it empowers individuals to make informed economic decisions and participate actively in the economic affairs of their society.
Exploring the Key Components of a Market Economy
In order to understand how a market economy works, it is important to grasp its key components. These components serve as the building blocks that make the economy function and allow for the exchange of goods and services in a free and competitive market.
Supply and Demand: One of the fundamental concepts in a market economy is the interplay between supply and demand. Supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that producers are willing and able to offer for sale, while demand represents the quantity of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to purchase. The interaction between supply and demand determines the price and quantity of goods and services in the market.
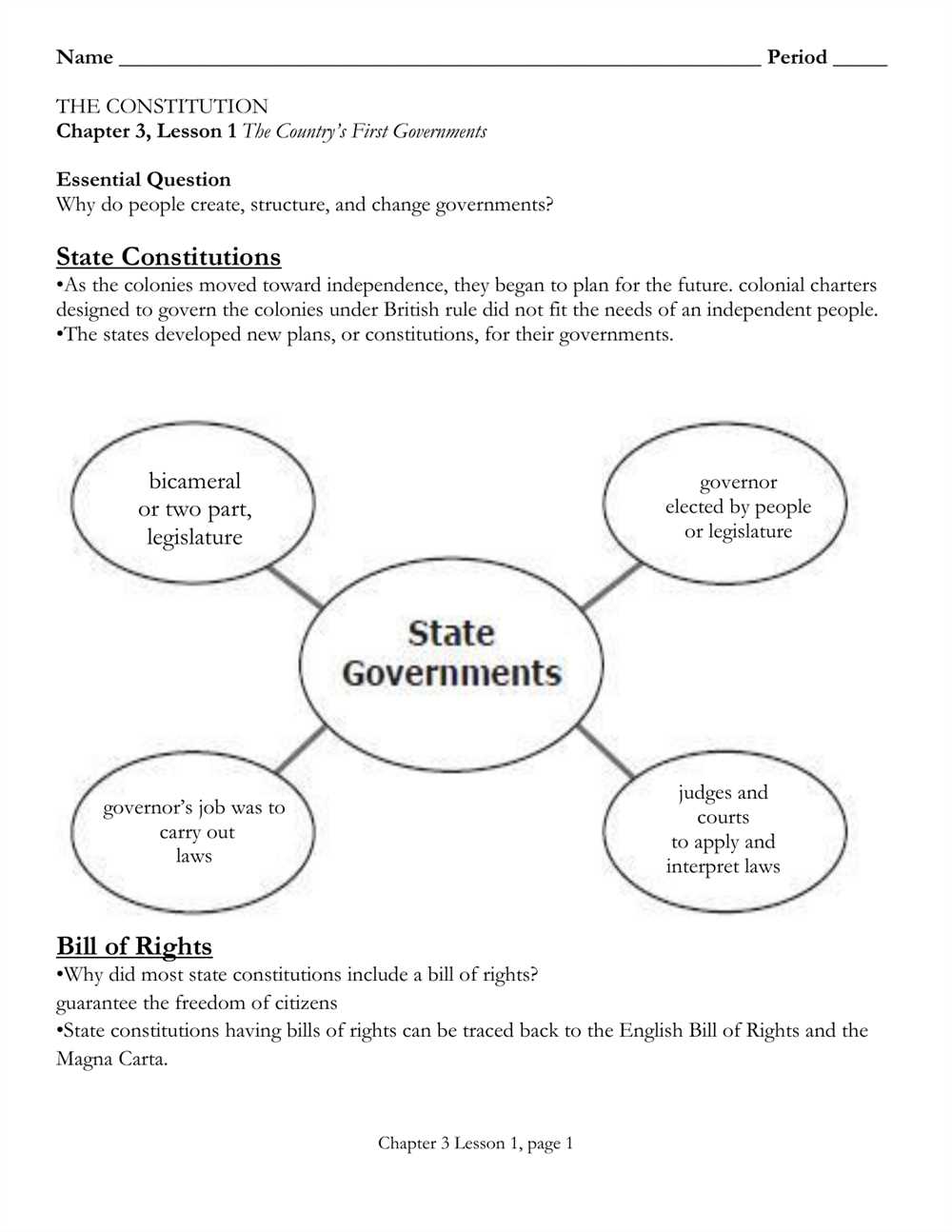
Private Property Rights: Another essential component of a market economy is the recognition and protection of private property rights. This means that individuals and businesses have the right to own, use, and dispose of property and resources as they see fit. The existence of private property rights provides individuals with an incentive to work hard, innovate, and invest in order to maximize their own self-interest.
Competition: Competition plays a crucial role in a market economy as it encourages efficiency, innovation, and lower prices. When multiple businesses compete for customers, they are driven to improve the quality of their products or services, offer better prices, and find new ways to meet consumers’ needs. This dynamic competition benefits consumers by giving them more choices and lower prices.
Profit Motive: The profit motive is another key component of a market economy. In this system, businesses are driven by the desire to make a profit. Profit is the reward for taking risks, making investments, and successfully meeting consumers’ demands. The pursuit of profit encourages businesses to be efficient, allocate resources wisely, and innovate in order to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Government Regulation: While a market economy is based on the principles of free markets and limited government intervention, government regulation is still necessary to ensure fair competition and protect consumers. Regulations may include measures such as antitrust laws to prevent monopolies, consumer protection laws, and environmental regulations. The role of government in a market economy is to create a level playing field and provide the necessary infrastructure and public goods.
Overall, a market economy is characterized by the interaction of supply and demand, private property rights, competition, the profit motive, and government regulation. These key components work together to create a system that allows for the efficient allocation of resources, encourages innovation, and provides individuals with the opportunity to pursue their own self-interest in a competitive marketplace.
The Role of Supply and Demand in a Market Economy
In a market economy, the forces of supply and demand play a crucial role in determining the prices of goods and services. Supply refers to the quantity of a product that producers are willing to offer for sale at a given price, while demand represents the quantity of a product that consumers are willing to purchase at a given price.
Supply is influenced by factors such as the cost of production, availability of resources, and government regulations. If the cost of production decreases, producers are more likely to supply a larger quantity of goods. Conversely, if the cost of production increases, producers may reduce their supply. Similarly, if resources are scarce or restricted, supply may be limited. On the other hand, if resources are abundant and easily accessible, the supply may be higher.
For example, in the market for smartphones, if the cost of producing the latest model decreases due to advancements in technology, smartphone manufacturers may increase their supply to meet the growing demand from consumers who now find the product more affordable.
Demand is influenced by factors such as price, income levels, consumer preferences, and population size. When the price of a product decreases, consumers tend to demand more of it, assuming all other factors remain constant. Conversely, when the price of a product increases, consumers may reduce their demand. Additionally, as income levels rise, consumers often have more disposable income, which can lead to increased demand for goods and services.
For instance, if the price of gasoline rises significantly, consumers may reduce their demand for gas by using public transportation or carpooling. On the other hand, if income levels increase and consumers have more money to spend, they may have a higher demand for luxury cars.
In a market economy, the interaction between supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity of goods and services. When supply is greater than demand, prices tend to decrease. Conversely, when demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. The equilibrium price and quantity represent a point where supply and demand are balanced, and it indicates the most efficient allocation of resources.
For example, if there is an oversupply of apples in the market, the price of apples may decrease. As a result, consumers may be more inclined to buy apples, leading to an increase in demand and ultimately restoring the equilibrium price.
In conclusion, supply and demand are essential components of a market economy. They determine the prices and quantities of goods and services, and their interaction helps allocate resources efficiently. Understanding the dynamics of supply and demand is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers in making informed decisions and fostering a vibrant market economy.
How Prices are Determined in a Market Economy
In a market economy, prices play a crucial role in determining the allocation of resources and the behavior of producers and consumers. Prices act as signals that convey information about the relative scarcity and demand for goods and services. Understanding how prices are determined is essential to comprehending the functioning of a market economy.
The forces of supply and demand interact to determine prices in a market economy. When the demand for a product or service exceeds the available supply, prices tend to rise. This increase in price signals to producers that there is an opportunity for profit, leading them to increase production to meet the demand. On the other hand, when the supply of a product or service exceeds the demand, prices tend to fall. This decrease in price signals to producers that they are producing more than what consumers are willing to buy, prompting them to reduce production.
- Supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that producers are willing and able to sell at different prices.
- Demand refers to the quantity of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices.
When the forces of supply and demand are in equilibrium, meaning that the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied at a particular price, the market is said to clear. This equilibrium price, also known as the market price, is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. Prices in a market economy are flexible and adjust based on changes in supply and demand conditions.
Overall, the determination of prices in a market economy is a dynamic process that reflects the interaction of supply and demand. Prices serve as signals that guide producers and consumers in their economic decision-making, ensuring efficient allocation of resources and promoting economic growth and prosperity.
The Importance of Competition in a Market Economy
Competition plays a vital role in a market economy, driving innovation, efficiency, and better quality products or services. When multiple businesses compete for customers, they are forced to constantly improve and find ways to differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Increase in innovation: Competition fosters innovation as businesses strive to develop new products, technologies, and processes to gain a competitive edge. They invest in research and development, which leads to advancements that benefit not only the businesses but also the overall economy. Without competition, businesses may become complacent and fail to invest in innovation.
Efficiency and lower prices: In a competitive market, businesses are motivated to become more efficient in order to reduce costs and offer their products or services at lower prices. This benefits consumers, as they have more choices and can purchase goods and services at competitive prices. Additionally, competition prevents businesses from engaging in monopolistic practices, ensuring that prices remain fair and affordable.
Quality improvement: Competition drives businesses to constantly improve the quality of their products or services to attract and retain customers. They are compelled to provide excellent customer service, offer better warranties, and deliver superior products that meet or exceed customer expectations. Without competition, businesses may not have the same incentive to prioritize quality.
Consumer choice: Competition in a market economy gives consumers the freedom to choose from a variety of products or services available in the market. This promotes diversity and allows consumers to find the best options that suit their individual needs and preferences. It also encourages businesses to cater to different customer segments, leading to a more diverse and inclusive market.
In conclusion, competition is essential in a market economy as it drives innovation, efficiency, quality improvement, and offers consumers a wider array of choices. It is through healthy competition that businesses are motivated to constantly improve and deliver value to customers, ensuring the overall growth and vitality of the economy.