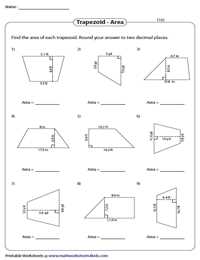
What are the key properties of trapezoids? How can we identify and describe these unique quadrilaterals? In this worksheet answer key, we will explore the various characteristics that define a trapezoid, providing a comprehensive understanding of their properties and how to solve related problems.
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. It is important to identify these parallel sides in order to determine the shape as a trapezoid. Furthermore, the non-parallel sides of a trapezoid are known as legs, while the parallel sides are called bases. Understanding these terms is crucial to correctly solving problems related to trapezoids.
One key property of trapezoids is that the opposite angles, those formed by the intersection of the legs and the bases, are congruent. This means that if we know the measure of one of these angles, we can easily determine the measure of the remaining congruent angle. Additionally, the sum of the measures of the angles in any trapezoid is always equal to 360 degrees.
Another property of trapezoids is that the lengths of the two bases are not necessarily equal. This allows for further classification of trapezoids into isosceles trapezoids, where the legs are congruent, and scalene trapezoids, where the legs have different lengths. These distinctions are vital when working with trapezoids and solving problems that involve their properties.
Properties of Trapezoids Worksheet Answer Key
In this worksheet, we will explore the properties of trapezoids and how to find their different measurements. A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides. The other two sides are not parallel and may have different lengths.
The key concepts covered in this worksheet include:
- Base angles: The base angles of a trapezoid are the angles formed by the non-parallel sides and the bases. They are congruent to each other.
- Base angles sum: The sum of the base angles of a trapezoid is always 180 degrees.
- Median: The median of a trapezoid is a segment that connects the midpoints of the non-parallel sides. It is parallel to the bases and its length is equal to the average of the lengths of the bases.
- Height: The height of a trapezoid is the perpendicular distance between the bases. It can be found using the Pythagorean theorem or by using the length of the median.
- Area: The area of a trapezoid can be found by multiplying the length of the median by the height and dividing by 2.
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a trapezoid can be found by adding the lengths of all four sides.
This worksheet provides several examples and practice problems to reinforce these concepts. It also includes an answer key that allows students to check their work and verify their solutions. By completing this worksheet, students will develop a solid understanding of the properties of trapezoids and gain experience in applying them to solve problems.
Note: It is important to pay attention to the given information in each problem and carefully follow the steps and formulas discussed in class to obtain the correct answers and solutions.
Definition and Characteristics of Trapezoids
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. It is a unique shape that has distinct properties and characteristics. Understanding these properties can help us identify, classify, and solve problems related to trapezoids.
A trapezoid can be identified by its parallel sides. These sides are called bases, and they are the two opposite sides of the trapezoid. The other two sides are called legs. The bases can be of different lengths, but the legs are non-parallel and have different measures. This distinguishing feature sets the trapezoid apart from other quadrilaterals.
Key Characteristics of Trapezoids:
- Parallel Sides: A trapezoid has one pair of parallel sides.
- Non-parallel Sides: The other two sides, called legs, are non-parallel.
- Base Angles: The angles formed between the bases and the legs are called base angles. The base angles are congruent in an isosceles trapezoid and can be different in a non-isosceles trapezoid.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a trapezoid intersect each other and form four triangles. The intersection point is called the midsegment point.
- Area: The area of a trapezoid can be found by multiplying the average length of the bases by the height, which is the distance between the bases.
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of its four sides.
These are some of the main characteristics that define and distinguish trapezoids. By understanding these properties, we can easily identify and classify trapezoids and utilize them in various mathematical problems and real-life situations.
Identifying the Bases and Legs of a Trapezoid
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides. In order to understand and solve problems related to trapezoids, it is important to be able to identify the bases and legs of a trapezoid.
The bases of a trapezoid are the two parallel sides. These sides are often referred to as the top base and bottom base, or the longer base and shorter base. The bases play a crucial role in determining the area and perimeter of the trapezoid. The length of the bases can be found by measuring the corresponding sides of the trapezoid or by using the given measurements.
The legs of a trapezoid are the non-parallel sides that connect the bases. These sides are often referred to as the slant height or lateral sides. The length of the legs can be found using the given measurements of the trapezoid, such as the height or the lengths of the base and the other side.
By correctly identifying and understanding the bases and legs of a trapezoid, one can effectively solve problems related to the various properties of trapezoids, such as finding the area, perimeter, or missing side lengths. It is important to pay attention to the parallel sides and the non-parallel sides when working with trapezoids in order to correctly apply the formulas and solve the given problems.
Finding the Perimeter of a Trapezoid
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. To find the perimeter of a trapezoid, we need to sum the lengths of all its sides. There are a few different formulas that can be used depending on the information given.
If all the sides of the trapezoid are given, then we can simply add them up. For example, if the lengths of the four sides are 10 cm, 15 cm, 12 cm, and 8 cm, then the perimeter would be 10 + 15 + 12 + 8 = 45 cm.
In some cases, only the lengths of the non-parallel sides and the height of the trapezoid are given. In this situation, we can use the formula P = a + b + c + d, where P is the perimeter and a, b, c, and d are the lengths of the sides. For example, if the lengths of the non-parallel sides are 10 cm and 15 cm, and the height is 6 cm, then the perimeter would be 10 + 15 + 10 + 15 = 50 cm.
Another scenario is when the lengths of the parallel sides and the height are given. In this case, we can use the formula P = 2a + 2b, where P is the perimeter and a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides. For instance, if the lengths of the parallel sides are 8 cm and 12 cm, and the height is 5 cm, then the perimeter would be 2 × 8 + 2 × 12 = 40 cm.
It’s important to remember that the units of measurement should be consistent in order to obtain an accurate perimeter. Whether the measurements are in centimeters, inches, or any other unit, they must be the same for all sides.
- When finding the perimeter of a trapezoid, you may need to use different formulas depending on the given information.
- If all the sides are known, simply add them up to find the perimeter.
- If only the lengths of the non-parallel sides and the height are given, use the formula P = a + b + c + d.
- If the lengths of the parallel sides and the height are known, use the formula P = 2a + 2b.
- Make sure to use consistent units of measurement throughout the calculation.
Calculating the Area of a Trapezoid
When it comes to finding the area of a trapezoid, there are a few key steps you need to follow. First, recall that a trapezoid is a quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides. To calculate its area, you need to know the lengths of both the parallel sides (base 1 and base 2) and the height of the trapezoid.
Once you have the necessary measurements, you can use the following formula to find the area of a trapezoid:
Area = (base 1 + base 2) * height / 2
To calculate the area, simply add the lengths of the two parallel sides, then multiply the sum by the height of the trapezoid. Finally, divide the result by 2.
It is important to note that the units of measurement used for the bases and the height should be the same. For example, if the bases are measured in inches, the height should also be measured in inches.
If you are given a trapezoid with missing measurements, you may need to use other formulas or find additional information to solve for the missing values. However, if you are given all the necessary measurements, calculating the area of a trapezoid becomes a straightforward process using the formula mentioned above.
Understanding the Midsegment of a Trapezoid
The midsegment of a trapezoid is a line segment that connects the midpoints of the two non-parallel sides of the trapezoid. It is also known as the midline or the midparallel. Understanding the midsegment is essential in geometry as it helps us to analyze and solve various trapezoid-related problems.
The midsegment of a trapezoid has several important properties. Firstly, it is parallel to the bases of the trapezoid. This means that the midsegment will have the same slope as the bases, and its equation can be determined using the midpoint formula. Secondly, the length of the midsegment is equal to the average of the lengths of the bases. This property can be used to find the length of the midsegment when the lengths of the bases are known.
Another property of the midsegment is that it divides the trapezoid into two smaller trapezoids with equal areas. This property can be proven using the concept of the area of parallelograms. By dividing the trapezoid into two smaller parts, we can apply the area formula for parallelograms to find the area of each smaller trapezoid.
Understanding the midsegment of a trapezoid is crucial for solving problems involving trapezoids, such as finding missing lengths or angles, determining areas, and proving geometric relationships. By recognizing the properties and characteristics of the midsegment, we can confidently approach and solve various trapezoid-related questions.
Applying the Trapezoid Midline Theorem
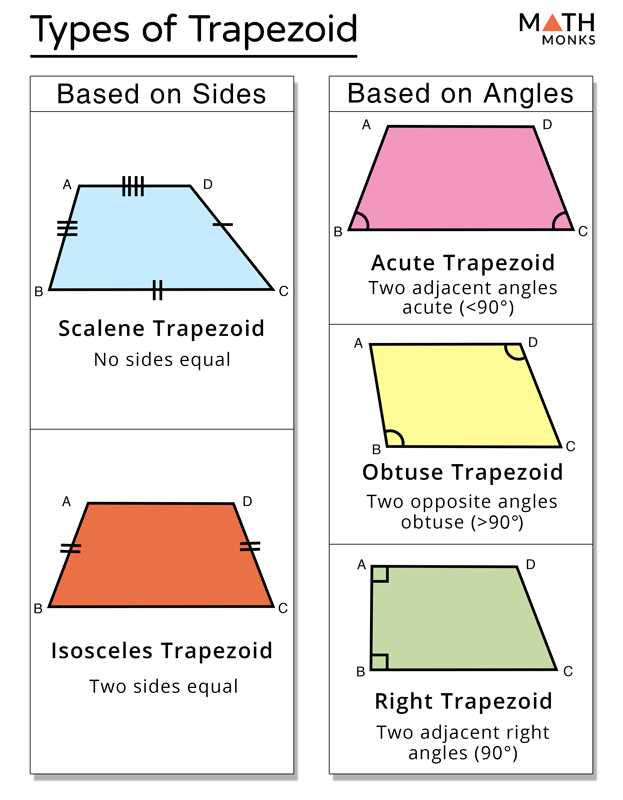
The Trapezoid Midline Theorem states that the midline of a trapezoid is equal to the average of the lengths of its bases. This theorem is a useful tool in solving geometry problems involving trapezoids.
To apply the Trapezoid Midline Theorem, we first need to identify the bases of the trapezoid. The bases are the parallel sides of the trapezoid. Once we have identified the bases, we can calculate their lengths by measuring the corresponding sides or using other geometric methods.
Next, we calculate the average of the lengths of the bases. This can be done by adding the lengths of the bases and dividing the sum by 2. The result of this calculation gives us the length of the midline of the trapezoid.
The Trapezoid Midline Theorem can be used to find missing lengths or solve for unknown variables in trapezoid problems. For example, if we know the lengths of the bases and want to find the length of the midline, we can use the theorem to calculate it. Conversely, if we know the length of the midline and one of the bases, we can use the theorem to find the length of the other base.
Overall, the Trapezoid Midline Theorem provides a straightforward method for solving problems involving trapezoids. By understanding and applying this theorem, we can confidently solve geometry problems and further explore the properties of trapezoids.
Solving Problems Involving Trapezoids
When working with trapezoids, it is important to understand the properties and formulas associated with this quadrilateral shape. By utilizing these properties, you can solve a variety of problems involving trapezoids.
One key property of a trapezoid is that it has one pair of parallel sides. This property allows us to calculate the area of a trapezoid using the formula: Area = (base1 + base2) * height / 2. By knowing the lengths of the bases and the height, we can easily find the area of the trapezoid.
Another property of a trapezoid is that the angles at the bases are supplementary. This means that the sum of the measures of the two adjacent angles at the bases is equal to 180 degrees. Using this property, we can solve problems involving the measures of these angles, such as finding the measure of an angle given the measure of its adjacent angle.
To further illustrate how these properties can be applied, let’s consider an example problem. Suppose we are given a trapezoid with base1 measuring 10 cm, base2 measuring 15 cm, and a height of 8 cm. We are asked to find the area of the trapezoid.
- First, we can use the given values to identify the base lengths and height needed to calculate the area.
- Plugging the values into the formula, we have: Area = (10 + 15) * 8 / 2 = 25 * 8 / 2 = 100 cm^2.
By applying the formula for the area of a trapezoid, we find that the area of the given trapezoid is 100 cm^2.
In conclusion, understanding the properties of trapezoids and utilizing the relevant formulas allows us to solve various problems involving these quadrilaterals. Whether it’s finding the area, calculating angles, or determining other measurements, applying these properties and formulas helps us effectively solve problems related to trapezoids.
Working with Trapezoids in Real-Life Scenarios
Trapezoids are a common shape that we encounter in various real-life scenarios. Understanding the properties of trapezoids can help us solve practical problems and make accurate measurements.
Architecture: Architects often come across trapezoids when designing buildings. The shape of roofs, windows, and doors can sometimes be trapezoidal. By knowing the properties of trapezoids, architects can determine the angles and lengths of different sections, ensuring structural integrity and functionality.
Civil Engineering: In civil engineering, trapezoids are frequently encountered when designing roads, bridges, and canals. The shape of road sections, river channels, and irrigation canals can often be approximated as trapezoids. Engineers use the properties of trapezoids to determine the volume of earthworks, calculate the water flow rate, and design stable slopes.
- Geometry: In geometry, trapezoids are essential in understanding polygons and the relationships between sides and angles. By studying trapezoids, mathematicians can deduce formulas for finding the area, perimeter, and height of trapezoids. These formulas are then applied to solve problems in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and physics.
- Physics: Trapezoids also play a role in physics when calculating moments of inertia for rigid bodies. The moment of inertia for a trapezoidal shape can be derived by using the parallel axis theorem. This knowledge is crucial in analyzing the stability and dynamics of rotating objects.
- Statistics: In statistics, trapezoids are used in numerical integration techniques, such as the trapezoidal rule. This rule approximates the area under a curve by dividing it into trapezoids. By summing up the areas of these trapezoids, statisticians can estimate the integral of a function and make accurate predictions.
Overall, understanding the properties and applications of trapezoids is valuable in various fields. Whether you’re an architect, engineer, mathematician, physicist, or statistician, knowledge of trapezoids enables you to solve real-life problems and contribute to the advancement of your respective field.