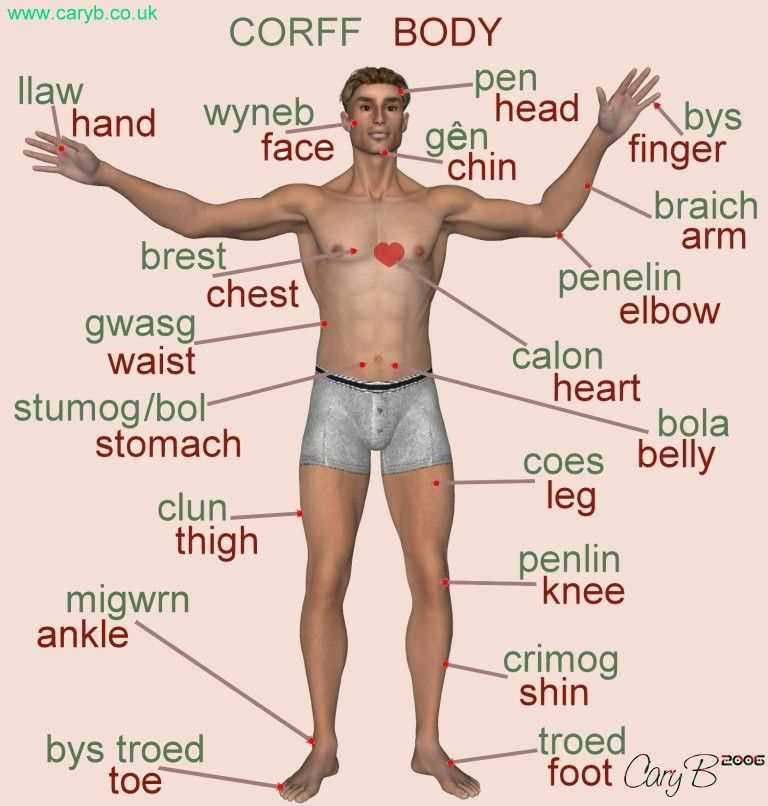
Physical examination is an important part of medical care that allows healthcare professionals to evaluate a patient’s overall health and detect any potential medical conditions. It involves systematically examining the body, usually starting with a review of the patient’s medical history and then progressing to a series of specific tests and observations.
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will assess the patient’s vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature. They may also examine the patient’s eyes, ears, nose, throat, and skin, looking for any abnormalities or signs of disease.
The physical examination may also involve palpation, which is the process of using touch to feel various parts of the body. For example, the healthcare provider may palpate the patient’s abdomen to check for any tenderness or masses. They may also perform a neurological examination, testing the patient’s reflexes, coordination, and sensory function.
In addition to these general examinations, a physical examination may also include specific tests based on the patient’s individual circumstances. For example, if the patient is complaining of chest pain, the healthcare provider may order an electrocardiogram or an echocardiogram to evaluate the heart.
What is a Physical Exam?

A physical exam is a comprehensive evaluation of a person’s overall health, performed by a healthcare professional. It involves a series of examinations, tests, and observations to assess the physical condition of an individual.
During a physical exam, a healthcare provider will typically begin by reviewing the person’s medical history, including any previous or existing medical conditions, allergies, medications, and family history of diseases. This information helps the healthcare provider understand the individual’s health background and any potential risk factors.
The physical exam itself usually involves the healthcare provider examining various parts of the body, such as the head, neck, chest, abdomen, limbs, and back. This may include measurements of vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature.
The healthcare provider may also perform specific tests or screenings to evaluate certain aspects of the individual’s health, such as blood tests, urine tests, or imaging studies. These tests can help detect any underlying health conditions or abnormalities.
Overall, a physical exam serves as an important tool for healthcare providers to gather information about a person’s health, detect early signs of potential health issues, and provide preventive care recommendations. It helps ensure that individuals receive appropriate medical attention and interventions to maintain their overall well-being.
Understanding the Purpose and Importance
In the field of medicine, the physical examination is a crucial part of the diagnostic process. It involves a systematic and thorough evaluation of a patient’s body systems to identify any abnormalities or signs of disease. The purpose of conducting a physical examination is to gather important clinical information that can help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis, develop an appropriate treatment plan, and monitor the patient’s progress.
A physical examination typically includes various components such as assessing vital signs (such as blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature), inspecting the body for abnormalities, palpating different organs and body structures, and listening to sounds produced by the body (using a stethoscope). These components can provide valuable clues about a patient’s overall health status and help the healthcare provider pinpoint the underlying cause of any symptoms or complaints.
- Diagnostic Tool: The physical examination serves as an essential diagnostic tool, allowing healthcare providers to gather objective data about a patient’s physical condition. It helps identify possible causes of symptoms and guides further diagnostic testing or referrals to specialists.
- Establishing Rapport: The physical examination also plays a crucial role in establishing a strong rapport between healthcare providers and patients. The hands-on approach of the physical examination allows healthcare providers to engage with patients, address their concerns, and build trust, thereby improving the overall patient experience and satisfaction.
- Early Detection and Prevention: Through a comprehensive physical examination, healthcare providers can identify early signs of diseases that might not be apparent through symptoms alone. This early detection can enable timely intervention and preventive measures, helping to prevent the progression of diseases and improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the physical examination is a fundamental aspect of healthcare practice. It serves as a diagnostic tool, establishes rapport with patients, and enables early detection and prevention of diseases. By conducting a thorough and systematic physical examination, healthcare providers can gather vital clinical information and provide quality care to their patients.
The Components of a Physical Exam

A physical exam, also known as a medical examination, is a routine check-up performed by healthcare professionals to assess a person’s overall health condition. This examination typically involves several components which help evaluate different aspects of a person’s physical well-being.
1. Vital Signs: One of the first steps in a physical exam is measuring the vital signs, including the person’s temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate. These measurements provide important information about a person’s general health and can indicate any underlying medical conditions.
2. General Appearance: In this component, the healthcare provider observes the patient’s overall appearance, including their skin color, body build, and any visible abnormalities. They may also assess the person’s level of alertness, mental status, and signs of distress or discomfort.
3. Head and Neck Examination: This part of the physical exam focuses on evaluating the person’s head and neck for any abnormalities. It may include an examination of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat, as well as palpation of the lymph nodes and assessment of the person’s neck movements.
4. Cardiovascular Examination: The cardiovascular exam involves assessing the person’s heart and blood vessels. This may include listening to the heart sounds using a stethoscope, checking for any irregularities or murmurs, palpating the pulse, and assessing the blood flow in the extremities.
5. Respiratory Examination: This component involves evaluating the person’s respiratory system, including the lungs and breathing. The healthcare provider may listen to the person’s lung sounds, check for any abnormalities or signs of respiratory distress, and assess the person’s breathing pattern and efficiency.
6. Abdominal Examination: In this part of the physical exam, the healthcare provider examines the person’s abdomen for any abnormalities, tenderness, or masses. They may use palpation techniques to feel for organs, such as the liver, spleen, and kidneys, and assess for any signs of gastrointestinal issues.
7. Musculoskeletal Examination: The musculoskeletal exam focuses on evaluating the person’s muscles, joints, and bones. The healthcare provider may assess the person’s range of motion, perform specific tests to evaluate strength and stability, and check for any signs of inflammation, injuries, or deformities.
8. Neurological Examination: This component involves assessing the person’s nervous system, including their cranial nerves, sensation, reflexes, and coordination. The healthcare provider may perform various tests to evaluate the person’s neurological function, such as assessing their grip strength, testing their reflexes, and observing their balance and coordination.
Overview of the Different Tests and Assessments
When conducting a physical examination, there are various tests and assessments that healthcare professionals utilize to gather important information about a patient’s overall health and well-being. These tests can help identify any potential issues or abnormalities that may require further investigation or treatment.
1. Vital signs: The first step in any examination is to assess the patient’s vital signs, which include measurements such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and body temperature. These measurements provide valuable information about the patient’s baseline health and can help detect any signs of illness or distress.
2. General inspection: During the examination, healthcare providers carefully observe the patient’s appearance, posture, and behavior. They may look for signs of pain, discomfort, or abnormal findings such as rashes, swelling, or discoloration. This general inspection can provide initial clues about the patient’s overall health and specific areas of concern.
3. Physical palpation: Palpation involves using the hands to feel and assess various parts of the body. During this assessment, healthcare professionals may feel for abnormalities in the organs, lymph nodes, and other structures. They may also assess tissue texture, temperature, and tenderness, which can help determine the presence of inflammation or other underlying conditions.
4. Range of motion testing: Range of motion testing is done to assess the flexibility and mobility of joints and muscles. Healthcare professionals may ask the patient to perform specific movements or exercises to evaluate their range of motion and identify any limitations or abnormalities. This assessment can help diagnose conditions such as joint stiffness, muscle weakness, or joint instability.
5. Laboratory tests: Laboratory tests, such as blood tests, urine tests, and imaging studies (X-rays, MRIs, etc.), can provide valuable information about a patient’s internal health. These tests can help diagnose or monitor conditions such as infections, organ dysfunction, and metabolic disorders. They are often used in conjunction with other physical assessments to provide a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health status.
6. Neurological assessment: A neurological assessment is performed to evaluate the patient’s nervous system function. This assessment may include tests to assess cognitive function, motor skills, reflexes, sensation, and coordination. It can help identify any neurological abnormalities or diseases, such as neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, or stroke.
Overall, these tests and assessments are essential components of a physical examination. They help healthcare professionals gather important data, make accurate diagnoses, and develop appropriate treatment plans for their patients. Each assessment provides unique insights into different aspects of the patient’s health, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation and individualized care.
Preparing for a Physical Exam
Getting ready for a physical exam involves several important steps that can help ensure the process goes smoothly and effectively. First and foremost, it is essential to schedule an appointment with a healthcare professional who specializes in physical exams. This ensures that the exam will be conducted by a trained and experienced individual who can accurately assess your overall health and identify any potential issues.
Prior to the exam, it is important to gather any necessary medical records and documentation. This may include previous test results, vaccination records, and a list of any medications or supplements you are currently taking. These documents provide important background information for the healthcare professional and can help guide them in their assessment and recommendations.
On the day of the exam, it is advisable to wear comfortable clothing that allows for easy movement and access to different areas of your body. It is also a good idea to bring a list of questions or concerns you may have so that you can discuss them with the healthcare professional during the exam.
During the physical exam, the healthcare professional will typically take measurements such as height, weight, blood pressure, and heart rate. They may also examine different parts of your body, such as your eyes, ears, throat, and abdomen. Depending on your age and medical history, additional tests or screenings may be ordered, such as bloodwork or imaging studies.
Overall, preparing for a physical exam involves proactive steps such as scheduling an appointment, gathering necessary documentation, and wearing appropriate clothing. By being prepared and actively participating in the process, you can help ensure a thorough and beneficial exam that helps keep you on track with your health goals.
Helpful Tips and Guidelines for Patients
When visiting a physician or undergoing a physical examination, it’s important to be well-prepared and informed. Here are some helpful tips and guidelines for patients to ensure a smooth and productive experience:
1. Provide accurate medical history: Before your appointment, take some time to gather and organize your medical history. Include details about any past medical conditions, surgeries, medications, and allergies. Providing this information to your physician will help them make an accurate diagnosis and provide appropriate treatment.
2. Be honest and open: In order to receive the best possible care, it’s crucial to be honest and open with your physician. Share any symptoms you are experiencing, even if they seem insignificant. Be sure to mention any lifestyle habits, such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, as these can impact your health. Your physician is there to help, so don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns or questions you may have.
3. Follow instructions: Your physician may give you specific instructions before your physical examination or procedures. It’s important to carefully follow these instructions to ensure accurate results and minimize any risks. If you are unsure about any instructions or have questions, don’t hesitate to ask your physician for clarification.
4. Keep a record of your symptoms: If you are experiencing any symptoms or changes in your health, keep a record of them. Note down the date, time, duration, and any other relevant details. This will help your physician better understand your condition and provide appropriate treatment. Additionally, it’s important to inform your physician if any symptoms worsen or new ones arise.
5. Take a list of questions: Before your appointment, make a list of any questions or concerns you may have. This will ensure that you don’t forget to ask anything during your visit. Your physician is there to provide guidance and answer any questions you may have, so don’t hesitate to seek their advice.
6. Follow up on results: After your physical examination or any diagnostic tests, it’s important to follow up with your physician to discuss the results. This will help you to understand the findings and any recommended treatments or further tests. If you have any questions or concerns about the results, make sure to communicate them to your physician for further clarification.
By following these helpful tips and guidelines, patients can actively participate in their healthcare and ensure they receive the best possible care. Remember, effective communication and cooperation with your physician are key to maintaining good health.