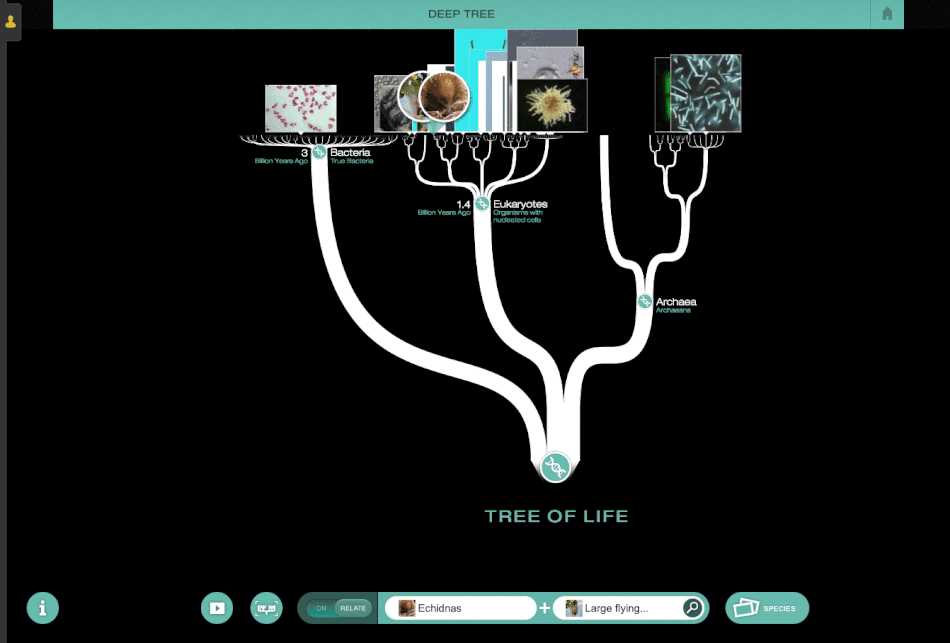
Evolution Lab Build a Tree Mission 4 is an exciting and challenging activity that aims to unravel the complexities of the tree of life. In this mission, participants are tasked with organizing and building a phylogenetic tree that accurately represents the evolutionary relationships between different species. By carefully analyzing and interpreting genetic and morphological data, participants can uncover the fascinating interconnectedness of all living organisms.
In this mission, participants are introduced to the concepts of common ancestry and speciation, two fundamental principles of evolutionary biology. Through the guide of the Evolution Lab software, participants navigate through a vast array of species and their traits, carefully examining the similarities and differences between them. By identifying shared traits and analyzing DNA sequences, participants can reconstruct the evolutionary history of various species and construct an accurate phylogenetic tree.
Through the Evolution Lab Build a Tree Mission 4, participants learn the importance of molecular and morphological data in understanding the evolutionary relationships between species. They also gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the tree of life and the vast diversity of life forms on our planet. By completing this mission, participants not only enhance their critical thinking and analytical skills but also develop a better understanding of the fundamental processes that shape the natural world.
What is Evolution Lab Build a Tree?
Evolution Lab Build a Tree is an interactive online activity that allows users to explore the concept of evolutionary relationships between different species. The main goal of the lab is to build an accurate phylogenetic tree that represents the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The lab provides users with various tools and resources to analyze genetic data and make informed decisions about the relationships between different species.
The lab consists of several missions, each focusing on a specific aspect of evolutionary biology. Mission 4, in particular, emphasizes the role of mutations and genetic variation in the process of evolution. Users are presented with a set of DNA sequences from different species and must compare the sequences to identify similarities and differences. Based on these comparisons, users can then construct a phylogenetic tree that reflects the evolutionary relationships between the species.
The Importance of Evolution Lab Build a Tree
Evolution Lab Build a Tree is an essential tool for teaching and learning about evolutionary biology. By providing an interactive and engaging platform, the lab allows users to actively participate in the process of building a phylogenetic tree. This hands-on approach helps to reinforce the concepts and principles of evolutionary biology and promotes a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Furthermore, Evolution Lab Build a Tree helps to develop critical thinking and data analysis skills. Users must carefully analyze and interpret genetic data, make logical connections between different species, and make informed decisions about the branching patterns on the phylogenetic tree. These skills are valuable not only in the field of biology but also in various other scientific disciplines and real-world applications.
In conclusion, Evolution Lab Build a Tree is a valuable educational resource for exploring the concept of evolutionary relationships. It provides users with an interactive platform to analyze genetic data, construct phylogenetic trees, and deepen their understanding of evolutionary biology. By engaging in this virtual lab, students and educators can enhance their knowledge and develop important skills related to data analysis and critical thinking.
Importance of Mission 4 in Evolution Lab Build a Tree
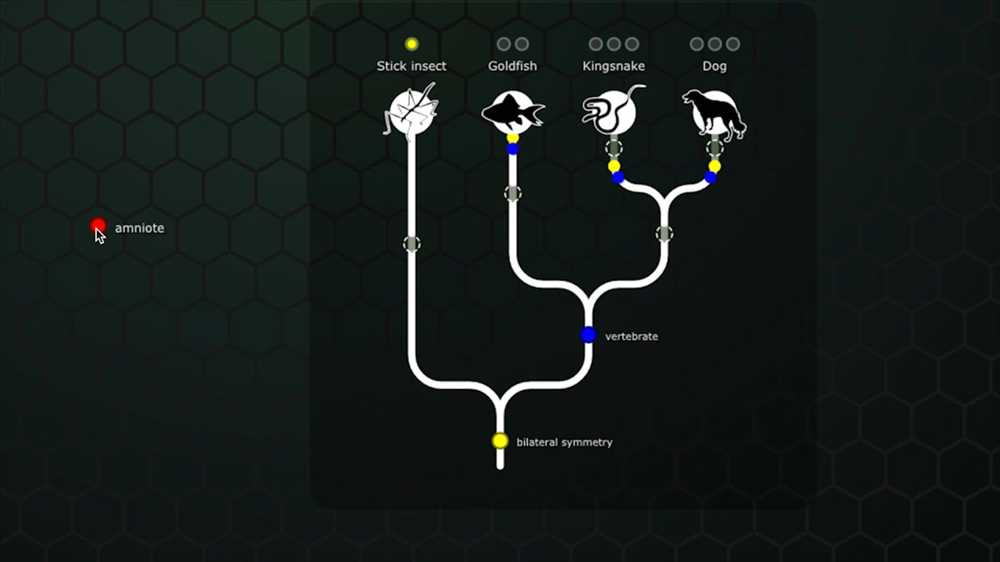
Mission 4 in Evolution Lab Build a Tree is a crucial step in understanding the process of evolution and the tree of life. This mission allows students to apply their knowledge of traits, adaptations, and common ancestry to construct a more accurate representation of the evolutionary relationships between various species.
The importance of Mission 4 lies in its role in helping students grasp the concept of phylogenetic trees. These trees visually represent the evolutionary history and relationships between different organisms. By completing this mission, students learn how to create and interpret phylogenetic trees, which are essential tools in studying evolutionary biology.
Mission 4 prompts students to carefully analyze the traits and characteristics of different species and organize them into a branching diagram. By doing so, they develop a better understanding of how organisms have diversified over time and how species are related to one another through common ancestry.
In addition to teaching students about the basics of phylogenetic trees, Mission 4 also emphasizes the importance of evidence-based reasoning and critical thinking. Students must evaluate the traits of each species and use that information to determine where they should be placed on the phylogenetic tree. This exercise encourages students to think scientifically and make logical connections based on observable data.
Overall, Mission 4 in Evolution Lab Build a Tree plays a crucial role in enhancing students’ understanding of evolutionary relationships and the process of constructing phylogenetic trees. By completing this mission, students develop important skills in data analysis, critical thinking, and scientific reasoning, which are essential for success in the field of evolutionary biology.
Understanding Evolution Lab Build a Tree Mission 4

In the Evolution Lab Build a Tree Mission 4, students are tasked with constructing a phylogenetic tree based on genetic similarity data of various species. This activity helps students understand the process of constructing a phylogenetic tree and the evolutionary relationships between different species.
The mission begins with students selecting multiple species and collecting genetic similarity data for each pair. They can then use this data to determine the degree of genetic relatedness between different species. Based on this information, students can start building a tree by placing the most closely related species together and branching out to include more distantly related species.
One important aspect of Mission 4 is the concept of homologous traits. Homologous traits are traits that are shared between species and inherited from a common ancestor. By identifying shared traits, students can further refine their tree construction and infer evolutionary relationships.
The Evolution Lab Build a Tree Mission 4 also introduces the concept of a common ancestor. A common ancestor is a hypothetical organism from which two or more different species have evolved. By analyzing the genetic similarity data, students can determine which species share a more recent common ancestor and arrange them accordingly in the tree diagram.
This activity provides a hands-on and interactive approach to understanding the process of constructing a phylogenetic tree. It allows students to apply their knowledge of genetics and evolution to analyze and interpret data, reinforcing their understanding of evolutionary relationships between species.
Overview of Mission 4
In Mission 4 of the Evolution Lab Build a Tree activity, you will continue learning about the process of evolution and how new species are formed. This mission focuses specifically on the concept of speciation, which is the creation of new species over time through the accumulation of small changes in populations. You will explore the different mechanisms of speciation and learn how they contribute to the diversity of life on Earth.
1. Geological Time Scale: The mission begins with an introduction to the Geological Time Scale, which divides Earth’s history into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. You will learn about the major events that occurred during each time period and how they influenced the evolution of species.
2. Types of Speciation: Next, you will explore the different types of speciation: allopatric, sympatric, and parapatric. Allopatric speciation occurs when populations become geographically isolated and evolve separately. Sympatric speciation occurs when new species arise in the same geographic area. Parapatric speciation occurs when populations are not completely isolated, but have limited gene flow between them.
3. Modes of Speciation: You will also learn about the modes of speciation, including gradualism and punctuated equilibrium. Gradualism suggests that speciation occurs slowly and gradually over long periods of time, while punctuated equilibrium proposes that species evolve in rapid bursts, separated by periods of little or no change.
4. Case Studies: Throughout the mission, you will explore various case studies to understand how speciation occurs in real-life scenarios. These case studies involve different organisms, such as birds, insects, and plants, and demonstrate the different mechanisms and modes of speciation in action.
5. Tree-building Activity: Finally, you will have the opportunity to apply your knowledge by completing a tree-building activity. You will analyze the similarities and differences between different species, determine their evolutionary relationships, and construct a phylogenetic tree to illustrate these relationships.
By the end of Mission 4, you will have a deeper understanding of speciation and how it contributes to the diversity of life on Earth. You will also have acquired the skills to analyze and interpret data to construct phylogenetic trees, a fundamental tool in evolutionary biology.
Objectives of Mission 4
Mission 4 in the Evolution Lab Build a Tree activity focuses on the concept of convergent evolution. The main objective of this mission is to investigate and analyze the evolutionary relationships between different species based on their physical and genetic traits. By completing this mission, students will gain a deeper understanding of how convergent evolution can lead to the development of similar traits in unrelated species.
In Mission 4, students will be presented with a tree that represents the relationships between various species. Their task is to use the evidence provided, such as anatomical features, DNA sequences, and fossil records, to infer the evolutionary relationships between the species and construct their own tree. They will also need to identify the key adaptive traits that have emerged in different lineages and explain how convergent evolution has played a role in shaping these traits.
To successfully complete Mission 4, students will need to carefully analyze the provided evidence, make logical inferences, and critically evaluate the similarities and differences between species. They will also need to demonstrate their understanding of convergent evolution by accurately documenting the instances where it has occurred and explaining the underlying mechanisms that have led to the development of similar traits. Overall, Mission 4 serves as an opportunity for students to apply their knowledge of evolutionary concepts and practice their analytical and critical thinking skills in a real-world context.
Answering the Questions in Mission 4
Mission 4 of the Evolution Lab Build a Tree activity requires answering a series of questions based on the evolutionary relationships of organisms. These questions help to reinforce the concepts of common ancestry, speciation, and classification. By correctly answering the questions, students can gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary history of different species.
Question 1
Question 1 asks about the closest living relative to the domestic dog. The answer is the gray wolf. Through genetic and morphological analysis, scientists have determined that the domestic dog (Canis lupus familiaris) shares a common ancestor with the gray wolf (Canis lupus) and diverged from a common ancestor approximately 15,000 years ago.
Question 2
Question 2 centers around the classification of humans. Humans belong to the taxonomic order Primates and are classified as Homo sapiens. Within the order Primates, humans belong to the family Hominidae, which includes great apes such as chimpanzees and orangutans. The classification of humans as primates reflects our evolutionary relationship with other primates, and the similarities in anatomy, behavior, and genetics shared among primates.
Question 3
Question 3 focuses on the concept of speciation. Speciation is the process by which new species arise from a common ancestor. It occurs when populations of a single species become reproductively isolated and diverge genetically over time. Speciation can be driven by a variety of factors, including geographic isolation, ecological divergence, or reproductive barriers. By studying the genetic and morphological differences between different species, scientists can understand the patterns and processes of speciation.
In conclusion, answering the questions in Mission 4 of the Evolution Lab Build a Tree activity allows students to explore and understand the evolutionary relationships of different organisms. By examining genetic and morphological data, along with concepts such as common ancestry and speciation, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of life on Earth and the processes that have shaped it over millions of years.
Question 1: [Question]
Question 1 in the Evolution Lab’s Build a Tree mission 4 prompts players to analyze the provided information about four different species and determine the type of evidence that would be most useful in building an accurate phylogenetic tree for these species.
To answer this question, players should carefully consider the characteristics and traits of the species, as well as their evolutionary relationships. They should also evaluate the different types of evidence that can be used to construct phylogenetic trees, such as morphological similarities, genetic data, and fossil records.
Based on the information provided, the most useful type of evidence to build an accurate phylogenetic tree for these species would likely be genetic data. This is because genetic data can provide insights into the evolutionary relationships between species by analyzing the similarities and differences in their DNA sequences. By comparing the genetic information of the four species, players can determine their genetic relatedness and construct a phylogenetic tree that represents their evolutionary history.
However, players should also consider other types of evidence, such as morphological similarities and fossil records. These can provide additional insights into the evolutionary relationships between species and help to corroborate the findings based on genetic data. Therefore, a combination of genetic data, morphological similarities, and fossil records would provide the most comprehensive and accurate picture of the phylogenetic relationships between the four species.