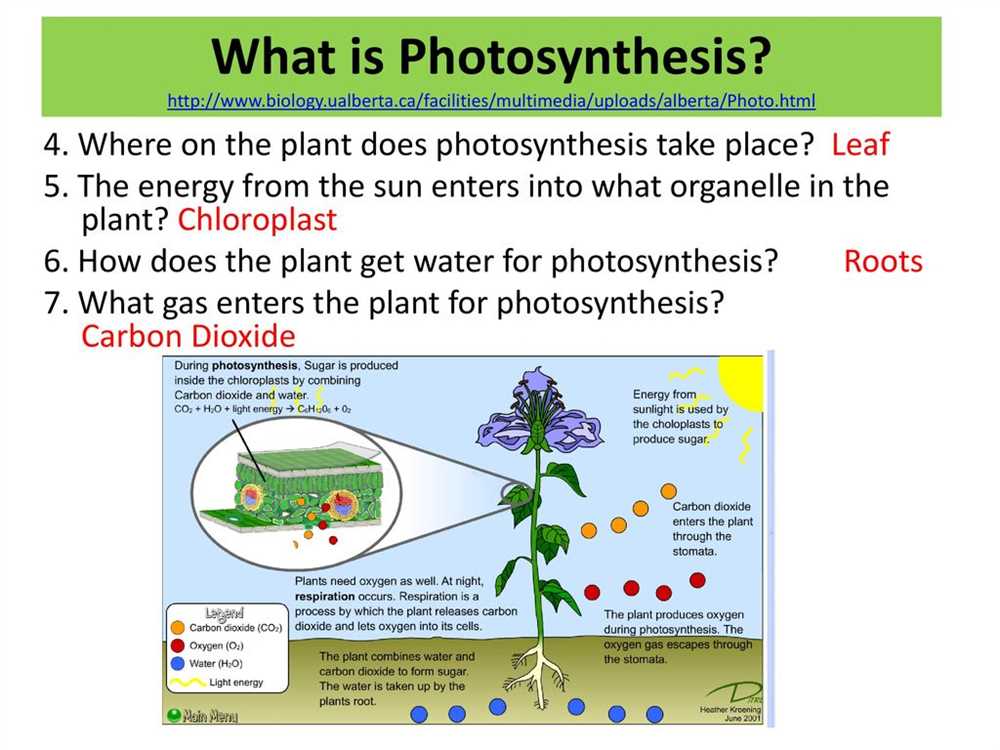
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that allows plants to convert light energy into chemical energy, ultimately fueling life on Earth. Understanding the intricacies of photosynthesis is essential for anyone studying biology, as it provides insight into how organisms obtain energy and sustain themselves.
Vanessa Jason, a renowned biologist, has dedicated her research to unraveling the mysteries of photosynthesis. Her groundbreaking work has shed light on the key components and mechanisms involved in this vital process. By studying the roots of photosynthesis, Vanessa has provided valuable answers to long-standing questions in the field.
In her research, Vanessa has focused on unraveling the complexities of the pigments involved in photosynthesis. These pigments, such as chlorophyll, are responsible for capturing light energy and initiating the chemical reactions that produce energy-rich molecules. By understanding their structure and function, Vanessa has been able to explain how plants optimize photosynthesis under different environmental conditions.
Additionally, Vanessa’s work has delved into the role of enzymes in photosynthesis. Enzymes play a critical part in catalyzing the chemical reactions that drive photosynthesis, and understanding their mechanisms is crucial for improving crop yields and developing sustainable energy sources. Through her meticulous experiments and rigorous analysis, Vanessa has provided key insights into how enzymes function in photosynthesis.
In conclusion, Vanessa Jason’s contributions to the study of photosynthesis have been invaluable. Her research on the roots of photosynthesis, including the pigments and enzymes involved, has provided answers to important questions in biology. By furthering our understanding of this fundamental process, Vanessa’s work has opened new avenues for research and has the potential to impact agriculture and renewable energy in the future.
What is Vanessa Jason Biology Roots Photosynthesis Answer Key?
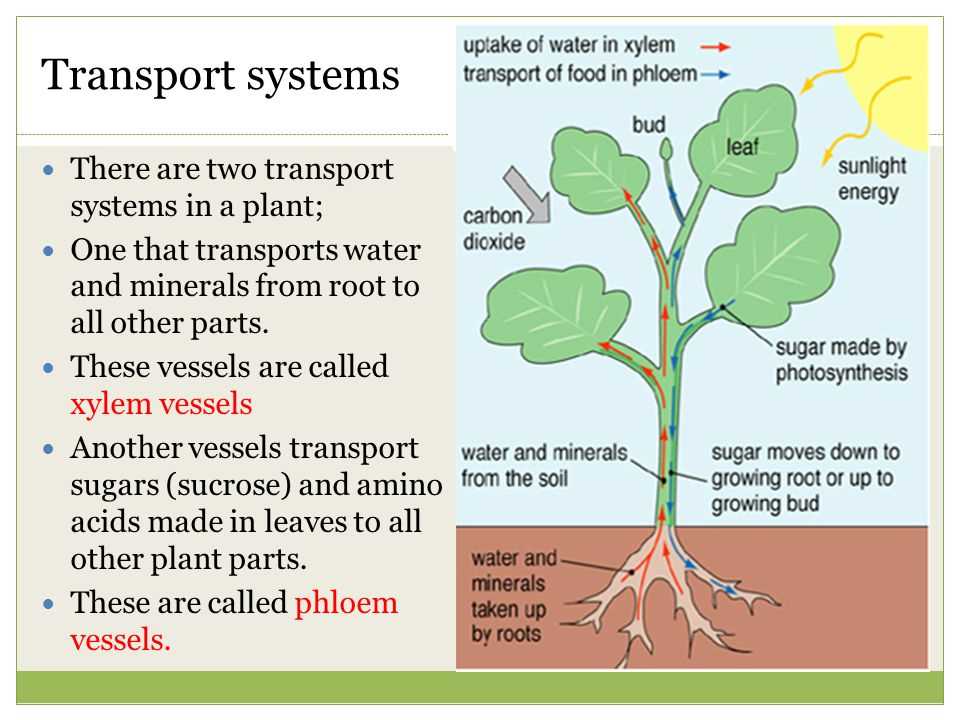
Vanessa Jason Biology Roots Photosynthesis Answer Key is a comprehensive resource that provides answers to questions and exercises related to the topic of photosynthesis. This answer key is designed to accompany the Vanessa Jason Biology Roots Photosynthesis textbook or workbook and serves as a helpful tool for students and teachers alike.
The answer key covers a wide range of topics related to photosynthesis, including the process of photosynthesis, the role of chlorophyll, the different factors that affect photosynthesis, and the biochemical pathways involved. It provides clear and concise explanations for each question, allowing students to better understand the concepts and principles of photosynthesis.
The Vanessa Jason Biology Roots Photosynthesis Answer Key is organized in a user-friendly manner, making it easy for students to find the answers they need. It includes a table of contents that outlines the different chapters and sections, allowing students to quickly navigate to the specific topic they want to review. Additionally, the answer key may include helpful diagrams, illustrations, and charts to further enhance understanding.
Overall, the Vanessa Jason Biology Roots Photosynthesis Answer Key is an invaluable resource for students studying photosynthesis. It provides clear and accurate answers to help students check their understanding and ensures that they are on the right track in their studies. Whether used independently or in conjunction with the textbook or workbook, the answer key serves as a valuable tool to support learning and reinforce important concepts in photosynthesis.
Understanding the Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a vital process that occurs in plants, algae, and some types of bacteria. It is the process by which these organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose, while also releasing oxygen into the atmosphere. This process is essential for the survival of life on Earth, as it is the primary source of the oxygen we breathe and the energy that fuels the ecosystem.
Photosynthesis provides oxygen: One of the key benefits of photosynthesis is the production of oxygen. Through this process, plants and other photosynthetic organisms release oxygen gas into the atmosphere as a byproduct. Oxygen is essential for the survival of most living organisms, as it is required for cellular respiration, the process by which organisms convert oxygen and glucose into energy. Without photosynthesis, the oxygen levels in our atmosphere would dramatically decrease, impacting the health and well-being of all living beings.
Photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain: Another crucial role of photosynthesis is in the production of glucose, which serves as the primary source of energy for organisms in the food chain. Plants use the glucose they produce during photosynthesis to fuel their own growth and development. This energy is then transferred to other organisms when they consume plant material, such as leaves or fruits. Herbivores, in turn, are eaten by carnivores, creating a chain of energy transfer that starts with photosynthesis. Without photosynthesis, the food chain would collapse, leading to widespread ecosystem instability.
Photosynthesis helps regulate the Earth’s climate: In addition to producing oxygen and supporting the food chain, photosynthesis also plays a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into glucose. This process helps to reduce the levels of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, in the atmosphere, thus mitigating the effects of global warming. Photosynthesis acts as a natural carbon sink, helping to maintain a balance in the Earth’s carbon cycle and preventing the rapid accumulation of carbon dioxide.
In conclusion, photosynthesis is an essential process for the survival of life on Earth. It not only provides us with oxygen to breathe but also serves as the basis for the food chain and helps regulate the Earth’s climate. Understanding the importance of photosynthesis allows us to appreciate the vital role that plants and other photosynthetic organisms play in sustaining life on our planet.
The Role of Photosynthesis in the Ecosystem

Photosynthesis is a vital process in the ecosystem, as it is responsible for converting sunlight into energy that can be utilized by life forms on Earth. This process takes place in plants, algae, and some bacteria, and plays a crucial role in sustaining life on our planet.
Key players: Plants are the primary organisms involved in photosynthesis. They contain specialized structures called chloroplasts, which house the green pigment chlorophyll that captures sunlight. Algae and certain bacteria also have chlorophyll and can perform photosynthesis.
What happens during photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, plants absorb light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This energy is stored in the plant’s cells and can be used for various life processes. The process involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
- Light-dependent reactions: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts. Chlorophyll captures sunlight, and its energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere, while the hydrogen is used in the next stage.
- Calvin cycle: In this stage, the energy-carrying molecules produced in the light-dependent reactions are used to synthesize glucose. The carbon dioxide captured from the atmosphere is also used in this process. The glucose produced can either be used immediately by the plant for energy or stored for future use.
Importance to the ecosystem:
Photosynthesis is essential for the survival of all life forms on Earth. It is the primary process through which energy enters the ecosystem. Plants, algae, and certain bacteria serve as the foundation of the food chain, as they produce their own food through photosynthesis. Organisms that cannot perform photosynthesis, such as animals, rely on these autotrophs for their energy needs.
Furthermore, photosynthesis serves as a major source of oxygen production. The oxygen released during photosynthesis is essential for the respiration of both plants and animals, sustaining their life processes. It also contributes to the oxygen content in the atmosphere, ensuring its availability for other forms of life.
In summary, photosynthesis is a fundamental process in the ecosystem, driving energy production, providing food for organisms, and contributing to oxygen production. Understanding the mechanisms and importance of photosynthesis is crucial for comprehending the intricate web of life on Earth.
How Photosynthesis Works
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. It is one of the most important biological processes on Earth, as it produces the oxygen we breathe and is the primary source of energy for all life forms.
Photosynthesis occurs in a specialized organelle called the chloroplast, which contains a pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun and uses it to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose. This process is divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
In the light-dependent reactions, sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll and the energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The oxygen is released as a byproduct, while the hydrogen ions are used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are energy-rich molecules that will be used in the next stage.
The light-independent reactions take place in the stroma of the chloroplast and do not require sunlight. In this stage, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is combined with the hydrogen ions and energy from ATP and NADPH to produce glucose. This glucose can be used by the plant as a source of energy, or it can be stored as starch for later use.
In conclusion, photosynthesis is a complex process that allows plants to use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. It is crucial for the survival of all life on Earth and is a fundamental process for the study of biology.
Exploring the Biology Roots of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process in biology that allows plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy. It is the process by which green plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This vital process plays a crucial role in the Earth’s ecosystems, as it is responsible for producing the oxygen we breathe and serving as the basis for most food chains.
The roots of photosynthesis can be traced back to the early days of life on Earth. It is believed that photosynthesis originated in cyanobacteria, some of the earliest known photosynthetic organisms. These primitive organisms used simple pigments to harness the energy from sunlight and produce organic molecules. Over time, photosynthetic organisms evolved complex structures and processes to optimize their ability to capture sunlight and carry out photosynthesis.
One key component of photosynthesis is chlorophyll, a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun and uses it to drive the biochemical reactions of photosynthesis. The structure of chlorophyll molecules has been shaped by millions of years of evolution, resulting in the specific arrangement of atoms that allows for efficient energy capture.
In addition to chlorophyll, photosynthesis involves several other complex biochemical pathways and enzymes. These include the light-dependent reactions, which occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts, and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, which occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts. These processes work together to convert light energy into chemical energy and produce glucose, the primary energy source for plants and other organisms.
Understanding the biology roots of photosynthesis is crucial for comprehending the intricate mechanisms and processes involved in this fundamental biological process. By studying the evolution and adaptations of photosynthetic organisms, scientists can gain insights into how life has evolved on Earth and how organisms have adapted to different environments. It also provides a foundation for research and advancements in fields such as agriculture, renewable energy, and biotechnology.
The History of Photosynthesis Research
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, has been the subject of scientific research for centuries. The study of photosynthesis has played a crucial role not only in understanding the fundamental processes of life on Earth, but also in developing technologies that harness the power of sunlight for various applications. Over the years, scientists have made significant discoveries and advancements in unraveling the complex mechanisms of photosynthesis.
One of the earliest experiments investigating photosynthesis was conducted by Jan Ingenhousz in the 18th century. Ingenhousz discovered that plants release oxygen when exposed to light, and that this process only occurs in the green parts of the plant. His findings laid the foundation for further research into the role of light in photosynthesis. Another important milestone in understanding photosynthesis came in the 19th century with the work of Julius von Sachs. Sachs demonstrated that the green pigment in plants, known as chlorophyll, is responsible for capturing light energy.
- Scientists: Jan Ingenhousz, Julius von Sachs
- Key Discoveries: Plants release oxygen when exposed to light, chlorophyll captures light energy
In the early 20th century, further progress was made in photosynthesis research with the work of C.B. van Niel. Van Niel studied bacteria that are capable of photosynthesis, and he proposed the idea that the process involves the splitting of water molecules. This mechanism, known as oxygenic photosynthesis, is now recognized as a fundamental process in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. In the 1940s, Nobel laureate Melvin Calvin and his team conducted groundbreaking experiments that identified the series of chemical reactions, known as the Calvin cycle, involved in carbon fixation during photosynthesis.
- Scientist: C.B. van Niel, Melvin Calvin
- Key Discoveries: Oxygenic photosynthesis involves splitting of water, Calvin cycle for carbon fixation
Today, photosynthesis research continues to be an active field of study. Scientists are exploring various aspects of photosynthesis, such as understanding the structures of photosynthetic proteins, optimizing photosynthetic efficiency for agricultural applications, and developing artificial photosynthesis techniques for renewable energy production. The ongoing research in photosynthesis promises to deepen our understanding of the natural world and open up new possibilities for sustainable technologies.