
Soil, that unassuming layer of earth beneath our feet, holds a wealth of secrets waiting to be unearthed. In the Field Trip Dig It! program, students embark on a journey to discover the hidden wonders of soil and gain a deeper understanding of its vital role in our ecosystem. This article serves as an answer key, providing a comprehensive guide to the questions and mysteries revealed during the excursion.
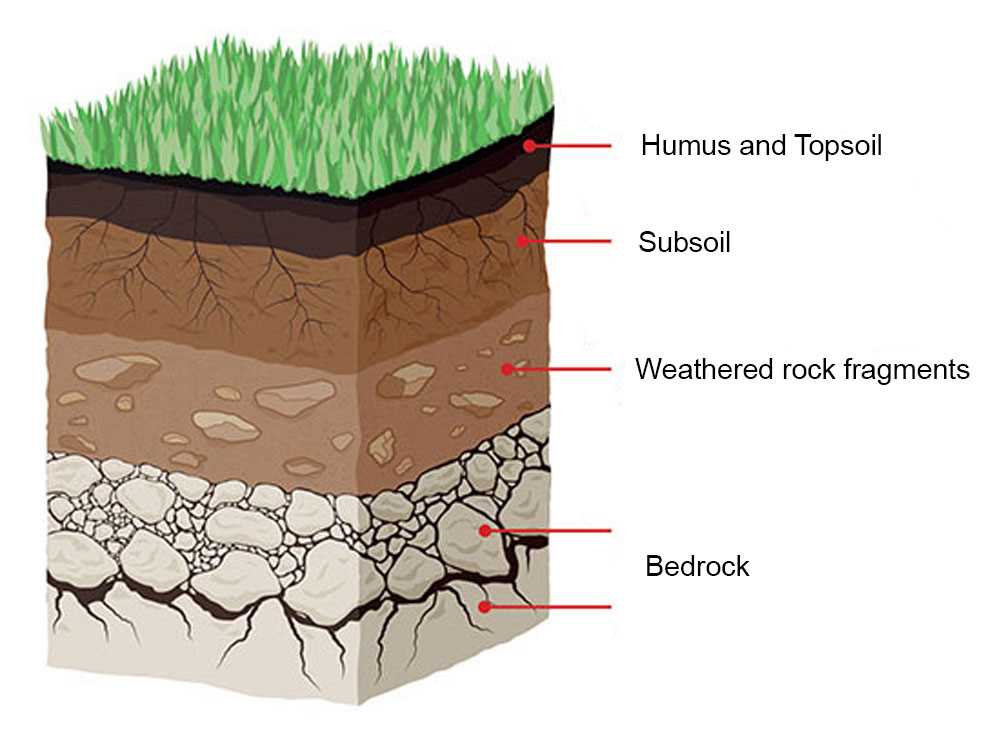
The journey begins with an exploration of the different layers of soil found in a typical landscape. Students learn to identify the distinct characteristics of each layer, ranging from the rich organic matter of topsoil to the compacted clay of the subsoil. Armed with this knowledge, they can decipher the stories that the soil layers tell about the history and composition of the land they are standing on.
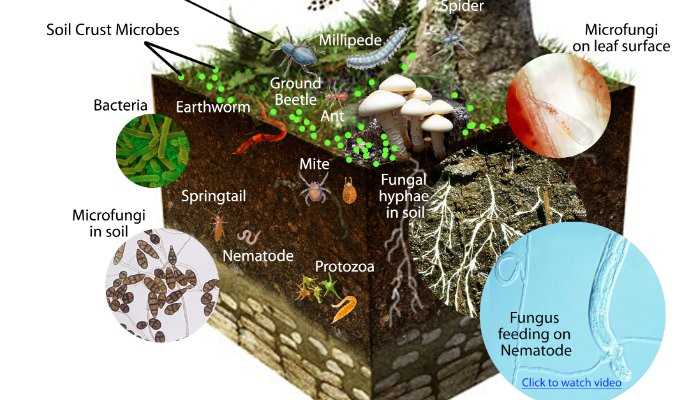
One of the main focuses of the Field Trip Dig It! program is investigating the diverse organisms that call soil their home. Students get hands-on experience in collecting soil samples and examining them under microscopes. They are astounded to discover the myriad of microscopic life forms, such as bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, that play a crucial role in decomposing organic matter and cycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Another captivating aspect of the program is uncovering the geological secrets buried within the soil. Through the careful examination of soil composition and texture, students can deduce valuable information about the geological processes that shaped the land. They learn how the interaction of weathering, erosion, and deposition over millions of years has given rise to the diverse landscapes we see today.
The Field Trip Dig It! program offers a remarkable opportunity for students to develop a deeper appreciation for the often-overlooked wonders of soil. By unearthing its secrets, they gain a greater understanding of its importance in supporting life on Earth and the delicate balance that exists within our ecosystem. Armed with this newfound knowledge, they are empowered to become champions for soil conservation and environmental stewardship.
The Importance of Soil in Understanding Our Ecosystem
Soil is a critical component of our ecosystem and plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth. It is not just a medium for plants to grow, but also serves as a habitat for countless organisms, a source of nutrients, and a regulator of water and air quality. Understanding the properties and functions of soil is essential for maintaining and improving the health of our ecosystem.
One of the key functions of soil is its ability to provide a stable foundation for plant growth. Soil acts as a medium for roots to anchor and absorb water and nutrients. Different types of soil have varying levels of fertility, drainage capacity, and composition, which can directly impact the growth and health of plants. By studying the characteristics of soil, scientists and farmers can make informed decisions on crop selection, irrigation practices, and fertilization methods to optimize plant productivity.
Moreover, soil is a complex ecosystem in itself, hosting a vast array of organisms such as bacteria, fungi, insects, worms, and small mammals. These organisms decompose organic matter, recycle nutrients, and maintain soil structure. They also contribute to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem. By studying the interactions between soil organisms and their environment, scientists can gain insights into the intricate web of life and the ecological processes that shape our world.
Additionally, soil acts as a natural filter and regulator of water and air quality. It absorbs and retains water, preventing runoff and erosion, and replenishing groundwater supplies. It also serves as a buffer against pollutants, filtering and degrading harmful substances before they reach water bodies or the atmosphere. Understanding the role of soil in water and air purification is crucial for maintaining the health and sustainability of our environment.
In conclusion, soil is a fundamental component of our ecosystem with multifaceted functions. It supports plant growth, nurtures a diverse range of organisms, and provides essential services in regulating water and air quality. By understanding and valuing soil, we can better protect and manage our environment, ensuring its health and sustainability for future generations.
Exploring the Field Trip Dig It Activity
Field Trip Dig It is an interactive activity designed to teach students about the secrets of soil. The activity allows students to explore different aspects of soil, such as its composition, layers, and the organisms that live within it. The activity consists of various stations, each focusing on a specific aspect of soil.
At the composition station, students learn about the different components that make up soil, including minerals, organic matter, water, and air. They have the opportunity to examine samples of soil under a microscope and identify the different particles present. This hands-on experience helps students develop a deeper understanding of soil composition and its importance for plant growth.
Layers of Soil
Another station focuses on the layers of soil, also known as soil horizons. Students learn about the different layers, such as topsoil, subsoil, and bedrock. They have the chance to dig into the soil and observe the distinct characteristics of each layer. This activity helps students understand how soil develops over time and the role each layer plays in supporting plant life.
Organisms in Soil
The station dedicated to organisms in soil introduces students to the wide variety of organisms that live within it. They explore the microorganisms that contribute to soil fertility, such as bacteria and fungi, as well as larger organisms like earthworms and insects. Students get to observe these organisms through microscopes and learn about their roles in the soil ecosystem. This station highlights the importance of biodiversity in soil and its impact on agricultural productivity.
The Field Trip Dig It activity provides an engaging and hands-on approach to learning about soil. Students have the opportunity to explore the different aspects of soil and develop a deeper understanding of its composition, layers, and the organisms that inhabit it. Through this activity, students gain valuable knowledge about the vital role that soil plays in sustaining life on Earth.
Gathering the Clues: Understanding the Soil Sample Analysis
During our field trip to explore the secrets of soil, we gathered various soil samples from different locations. Now, it’s time to analyze these samples and unravel the hidden information within them. By understanding the results of the soil sample analysis, we can gain insights into the composition, fertility, and health of the soil.
Chemical Composition: One of the key aspects of soil analysis is studying its chemical composition. The analysis reveals the presence and concentration of various nutrients, minerals, and elements in the soil. This information helps us understand the soil’s ability to support plant growth and its potential limitations in terms of nutrient availability.
Physical Properties: Apart from its chemical composition, analyzing the physical properties of the soil is also crucial. This includes studying the soil’s texture, structure, and moisture content. Texture refers to the relative proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles in the soil, while structure relates to how these particles are organized. Understanding these properties can provide valuable information about the soil’s drainage, aeration, and water-holding capacity.
By performing a thorough soil analysis, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the soil’s condition and its suitability for different purposes. This knowledge can help farmers and gardeners make informed decisions about crop selection, land management practices, and soil improvement techniques. Additionally, it allows scientists and researchers to monitor soil health, identify potential issues, and develop strategies for sustainable land use.
Unlocking the Secrets: The Key Findings from the Soil Sample Analysis
During our field trip to investigate the secrets of soil, we collected multiple soil samples from various locations. These samples were meticulously analyzed in the laboratory, revealing fascinating findings that shed light on the hidden world beneath our feet.
The first key finding was the diversity of microorganisms present in the soil. Through DNA sequencing, we identified a wide range of bacteria, fungi, and other microscopic organisms. This diversity plays a vital role in nutrient cycling and soil health, highlighting the importance of maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Further analysis revealed the soil’s chemical composition, with particular attention to the presence of essential nutrients. We discovered that the soil samples contained high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, the primary macronutrients necessary for plant growth. This confirms the fertility of the soil and its suitability for agriculture.
Additionally, we examined the soil’s texture to determine its composition of sand, silt, and clay particles. The results showed that the soil samples varied in texture, with some being more sandy while others were clayey. This variation has significant implications for water retention and drainage, affecting the overall health of plants and the ecosystem as a whole.
In conclusion, our soil sample analysis provided valuable insights into the composition and quality of the soil. The diversity of microorganisms, abundance of essential nutrients, and variation in texture all contribute to the intricate web of life hidden beneath the surface. By understanding and appreciating these secrets, we can make informed decisions to protect and enhance the soil for future generations.
Understanding Soil Composition: The Role of Minerals, Organisms, and Organic Matter
Soil is a complex and dynamic part of our ecosystem that plays a crucial role in supporting life on Earth. Its composition is made up of various components, including minerals, organisms, and organic matter. By understanding the role of these elements, we can gain insight into the health and fertility of soil, as well as its ability to sustain plant and animal life.
The Role of Minerals
Minerals are an essential component of soil composition. They are derived from rocks and minerals, and their presence in soil provides important nutrients for plants. Minerals such as calcium, potassium, and phosphorus are necessary for plant growth and development. They also contribute to the physical properties of soil, such as its texture and structure, which affects its ability to retain water and support root growth. Understanding the mineral content of soil is key to determining its fertility and suitability for different types of crops.
The Role of Organisms
Soil is teeming with life, from microscopic bacteria to earthworms and insects. These organisms play a vital role in the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients. They break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms that can be absorbed by plants, thus contributing to the nutrient cycle. Additionally, soil organisms improve soil structure through their burrowing activities, which enhances water infiltration and aeration. Their presence is indicative of a healthy and thriving soil ecosystem.
The Role of Organic Matter
Organic matter is another important component of soil composition. It consists of dead plant and animal material, as well as substances derived from their decay. Organic matter contributes to soil fertility by providing essential nutrients, improving soil structure, and enhancing its ability to retain moisture. It also supports the growth of beneficial soil organisms, which further contribute to soil health. A lack of organic matter can result in poor soil fertility and reduced crop productivity. Therefore, the addition of organic matter through practices such as composting and crop rotation is essential to maintaining healthy and productive soils.
Conclusion

The composition of soil is a complex interplay between minerals, organisms, and organic matter. Understanding the role of each component is crucial for assessing soil fertility and health. By promoting the presence of minerals, fostering a diverse and thriving soil organism population, and maintaining adequate levels of organic matter, farmers and gardeners can ensure the long-term sustainability and productivity of the soil.
Soil Health and Sustainability: Impacts of Human Activity and Ways to Improve
Soil health is crucial for the sustainability of our planet and for ensuring long-term food security. However, human activities have had a significant impact on soil health and have posed challenges to its sustainability. One of the main threats is soil erosion, which occurs due to the removal of vegetation cover for agriculture, deforestation, and construction. This erosion leads to the loss of topsoil, which is rich in nutrients and organic matter, and can result in decreased soil fertility and productivity.
Another human activity that affects soil health is the excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture. While these inputs can increase crop yields in the short term, they can also have negative effects on soil health. They can lead to the accumulation of toxic substances in the soil, reduce beneficial soil organisms, and increase soil acidity. Additionally, poor land management practices such as over-tilling, overgrazing, and improper irrigation can contribute to soil degradation and erosion.
To improve soil health and ensure its sustainability, it is important to adopt sustainable land management practices. These include practices such as conservation tillage, crop rotation, and the use of cover crops. Conservation tillage reduces soil erosion by leaving crop residues on the soil surface and minimizing or eliminating plowing. Crop rotation helps break pest cycles and improves soil fertility by alternating crops with different nutrient requirements. Cover crops, such as legumes, help prevent erosion, add organic matter to the soil, and fix atmospheric nitrogen.
In addition to sustainable land management practices, soil conservation efforts should also focus on improving soil organic matter content. This can be achieved through practices such as adding organic amendments (e.g., compost), practicing crop residue management, and incorporating crops with deep root systems. Increasing soil organic matter improves soil structure, water holding capacity, nutrient cycling, and promotes the growth of beneficial soil organisms, leading to healthier and more productive soils.
Overall, soil health and sustainability are critical for ensuring the long-term productivity of our soils and the availability of food for future generations. Through the implementation of sustainable land management practices and the promotion of soil conservation efforts, we can mitigate the negative impacts of human activities on soil health and ensure the preservation of this vital resource.