
Understanding the concept of comparative advantage and trade is crucial in the field of macroeconomics. This topic explores the idea that countries can benefit from specializing in producing goods and services that they have a lower opportunity cost for, and trading with other countries who have a higher opportunity cost for those goods and services.
The worksheet answers for Ap Macro Topic 1 3 Comparative Advantage and Trade provide insights into how countries can determine their comparative advantage and make decisions about international trade. By analyzing the production possibilities frontier and calculating opportunity costs, economists can identify the most efficient allocation of resources and understand the benefits of trade.
The answers to the worksheet illustrate the importance of trade in promoting economic growth and improving living standards. Through specialization and trade, countries can take advantage of their strengths and have access to a wider range of goods and services. This not only promotes efficiency and innovation but also increases consumer choice and overall welfare.
What is Comparative Advantage?
Comparative advantage is a concept in economics that explains why countries specialize in the production of certain goods and services. It is based on the idea that countries should focus on producing goods and services that they can produce at a lower opportunity cost than other countries.
In other words, comparative advantage means that a country can produce a good or service with a lower relative cost compared to other countries. This cost can be measured in terms of the resources, such as labor and capital, that are required to produce the good or service.
For example, if Country A can produce 1 unit of wheat with 10 hours of labor, while Country B can produce 1 unit of wheat with 15 hours of labor, Country A has a comparative advantage in wheat production. On the other hand, if Country B can produce 1 unit of steel with 5 hours of labor, while Country A can produce 1 unit of steel with 8 hours of labor, Country B has a comparative advantage in steel production.
Comparative advantage is the basis for international trade, as countries can specialize in producing goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage and trade them with other countries. This allows countries to benefit from the differences in their relative production efficiencies and leads to a more efficient allocation of resources globally.
In summary, comparative advantage is the ability of a country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost compared to other countries. It explains why countries specialize in certain industries and engage in international trade to benefit from their relative efficiencies in production.
Understanding the Concept
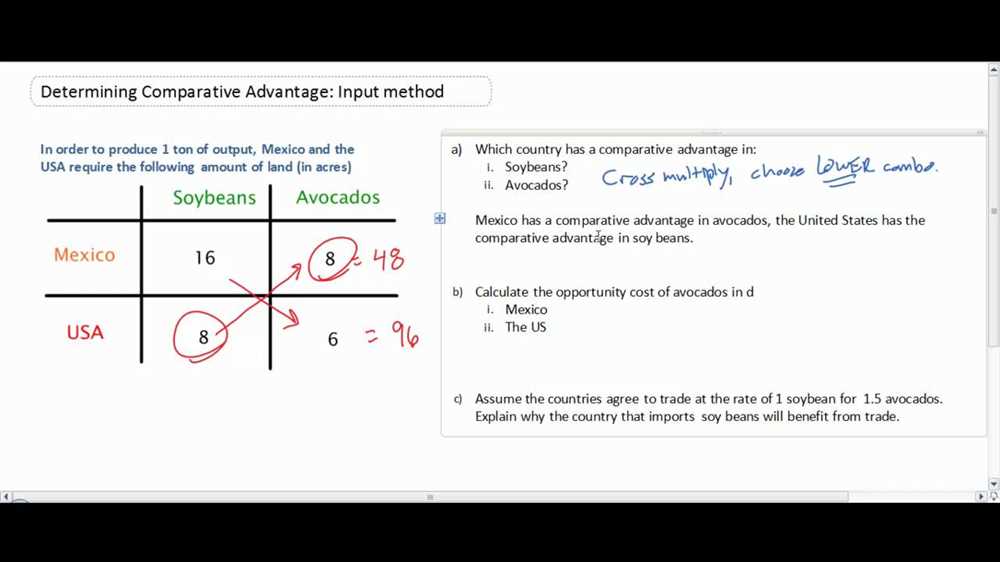
The concept of comparative advantage and trade is a fundamental principle in economics that explains the benefits of specialization and exchange between countries. In simple terms, comparative advantage refers to the ability of a country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost compared to another country.
When two countries have different comparative advantages, it creates an opportunity for mutually beneficial trade. By specializing in the production of goods or services where they have a comparative advantage, countries can increase their overall efficiency and productivity. This leads to higher levels of economic growth and prosperity.
For example, imagine a scenario where Country A has a comparative advantage in producing wheat, while Country B has a comparative advantage in producing steel. If both countries were to produce both goods, they would be less efficient compared to specializing in their respective areas of comparative advantage. Country A can produce wheat at a lower opportunity cost than Country B, and Country B can produce steel at a lower opportunity cost than Country A.
By specializing in the production of wheat and steel, and then trading with each other, both countries can benefit from the lower production costs of the goods they import. This allows them to consume more goods with the same amount of resources, leading to an increase in overall welfare. Additionally, trade allows countries to take advantage of economies of scale, leading to further cost reductions and increased competitiveness in the global marketplace.
In conclusion, understanding the concept of comparative advantage and trade is crucial for analyzing the benefits of specialization and exchange between countries. By embracing their respective comparative advantages, countries can maximize their efficiency, increase overall welfare, and promote economic growth.
Exploring the Benefits of Comparative Advantage
The concept of comparative advantage is a fundamental principle in economics that states that countries should focus on producing goods and services in which they have a lower opportunity cost compared to other countries. This principle allows countries to specialize in producing goods and services at which they are relatively more efficient, resulting in overall higher productivity and economic growth.
One of the main benefits of comparative advantage is increased trade. When countries specialize in producing goods and services they are relatively more efficient at, they can trade with other countries that specialize in producing goods and services that they are relatively less efficient at. This allows for the exchange of goods and services that each country needs, leading to a more efficient allocation of resources and increased overall welfare.
Another benefit of comparative advantage is increased market access. By focusing on producing goods and services at which they have a comparative advantage, countries can enter new markets and export their products to other countries. This not only increases their revenue and economic growth but also allows them to benefit from economies of scale and learn from foreign markets, leading to technological advancements and increased competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Additionally, comparative advantage promotes specialization and division of labor, which are key drivers of economic efficiency. By allocating resources to the production of goods and services at which they have a comparative advantage, countries can maximize their productivity and output. This specialization and division of labor enable countries to fully exploit their available resources and create a competitive advantage in specific industries, leading to increased efficiency, innovation, and economic development.
In conclusion, comparative advantage is a powerful concept that offers numerous benefits to countries. Through specialization, increased trade, market access, and division of labor, countries can harness their strengths, optimize resource allocation, and foster economic growth. By understanding and embracing the principle of comparative advantage, countries can unlock their full potential and prosper in the global economy.
The Importance of Trade
Trade plays a crucial role in the global economy, enabling countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. Comparative advantage refers to a country’s ability to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost compared to other countries. By focusing on producing goods and services in which they excel, countries can maximize their efficiency and productivity, leading to economic growth and improved living standards.
One key benefit of international trade is the access it provides to a wider variety of goods and services. Through trade, countries can import products that are not produced domestically, allowing consumers to enjoy a greater selection of goods. This promotes competition, which can lead to lower prices and improved quality. Additionally, trade enables countries to export their surplus production and generate income, thereby stimulating economic activity and creating jobs.
Another advantage of trade is its potential to foster economic development and reduce poverty. Trade can provide opportunities for developing countries to tap into global markets, allowing them to export their goods and attract foreign investment. This can contribute to economic diversification and drive sustainable growth. Moreover, by participating in international trade, countries can gain access to technology, knowledge, and expertise from other nations, which can further enhance their productivity and competitiveness.
- Trade can also contribute to the diffusion of ideas and promote cultural exchange between nations. Through the exchange of goods and services, countries have the opportunity to interact and learn from each other, fostering mutual understanding and cooperation.
- However, it is important to note that trade also presents challenges and risks. For instance, countries may face competition from foreign producers, which can threaten domestic industries and employment. Additionally, trade imbalances and protectionist policies can lead to trade disputes and hinder international cooperation.
In conclusion, trade plays a vital role in the global economy, offering numerous benefits such as increased productivity, access to a wider range of goods and services, and opportunities for economic development. However, it is important to manage the challenges and risks associated with trade to ensure equitable and sustainable economic growth for all participating countries.
How Trade Impacts Economic Growth

Trade plays a crucial role in driving economic growth and fostering prosperity. When countries engage in international trade, they can specialize in producing goods and services that they have a comparative advantage in, and then exchange those goods and services with other countries. This specialization allows countries to allocate their limited resources more efficiently, leading to increased productivity and economic growth.
One way trade impacts economic growth is by expanding markets for goods and services. Through trade, countries gain access to a larger customer base, both domestically and internationally. This increased demand for products and services stimulates production and encourages businesses to invest in expanding their operations. As a result, economic growth is fueled, leading to more job opportunities, higher incomes, and improved living standards for citizens.
In addition, trade promotes innovation and technological advancements. When countries engage in trade, they are exposed to new ideas, technologies, and practices from other countries. This exposure encourages competition and fosters innovation as firms strive to improve their products and processes to gain a competitive advantage in the global market. As a result, trade acts as a catalyst for technological progress and drives economic growth.
Furthermore, trade allows countries to reap the benefits of specialization and economies of scale. By focusing on producing goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage, countries can achieve higher levels of efficiency and productivity. This efficiency leads to cost savings, which can be passed on to consumers in the form of lower prices. As a result, trade not only promotes economic growth but also enhances the purchasing power of consumers.
In conclusion, trade has a significant impact on economic growth. It enables countries to specialize, expand markets, promote innovation, and achieve efficiencies. By embracing trade and removing trade barriers, countries can maximize their economic potential, create wealth, and improve the overall well-being of their citizens.
The Role of Trade in Globalization
Trade plays a crucial role in the process of globalization. Globalization refers to the increasing integration and interdependence of economies, societies, and cultures around the world. It is driven by various factors such as advancements in technology, transportation, and communication. One of the key drivers of globalization is international trade, which allows countries to specialize in the production of goods and services that they have a comparative advantage in.
Comparative advantage refers to the ability of a country to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another country. By specializing in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage, countries can maximize their efficiency and productivity, leading to economic growth and development. Trade allows countries to exchange their specialized goods and services with one another, leading to a more efficient allocation of resources and increased variety of goods for consumers.
Trade also promotes competition and innovation. When countries engage in international trade, they are exposed to different market conditions and competition from abroad. This competition encourages domestic producers to become more efficient, reduce costs, and improve the quality of their products. It also fosters innovation as companies strive to differentiate themselves and stay ahead of their competitors.
In addition, trade can have significant social and cultural impacts. Through trade, countries have the opportunity to exchange not only goods and services, but also ideas, knowledge, and cultural practices. This exchange of ideas and cultural diversity contributes to the enrichment of societies and promotes understanding and cooperation among nations.
Overall, trade plays a vital role in driving globalization by facilitating economic integration, promoting efficiency and innovation, and fostering cultural exchange. It is an essential tool for countries to maximize their potential and contribute to the interconnected global economy.
Factors Affecting Comparative Advantage
Comparative advantage refers to a country’s ability to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another country. Several factors influence a country’s comparative advantage, including:
- Natural Resources: The availability of natural resources, such as fertile land, minerals, oil, and water, can give a country a comparative advantage in the production of certain goods. For example, a country rich in oil reserves may have a comparative advantage in the production of petroleum-based products.
- Technological Advancement: The level of technological development and innovation plays a significant role in determining a country’s comparative advantage. Advanced technology can increase productivity and efficiency, allowing a country to produce goods more quickly and at a lower cost than its competitors.
- Human Capital: The education, skills, and expertise of a country’s workforce can also affect its comparative advantage. A highly educated and skilled workforce is likely to be more productive and efficient in producing goods and services, giving the country a comparative advantage in industries that require specialized knowledge.
- Infrastructure: The quality and availability of infrastructure, such as transportation, communication, and utilities, can impact a country’s comparative advantage. Good infrastructure facilitates the movement of goods and services, reduces transportation costs, and improves overall efficiency, allowing a country to compete more effectively in international markets.
- Government Policies: Government policies, such as trade barriers, subsidies, and regulations, can either support or hinder a country’s comparative advantage. Protectionist measures, such as tariffs and import quotas, can limit competition and distort comparative advantage. On the other hand, policies that promote free trade and create a favorable business environment can enhance a country’s comparative advantage.
In conclusion, a country’s comparative advantage is influenced by a combination of natural resources, technological advancement, human capital, infrastructure, and government policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for countries to exploit their comparative advantages and maximize their gains from international trade.