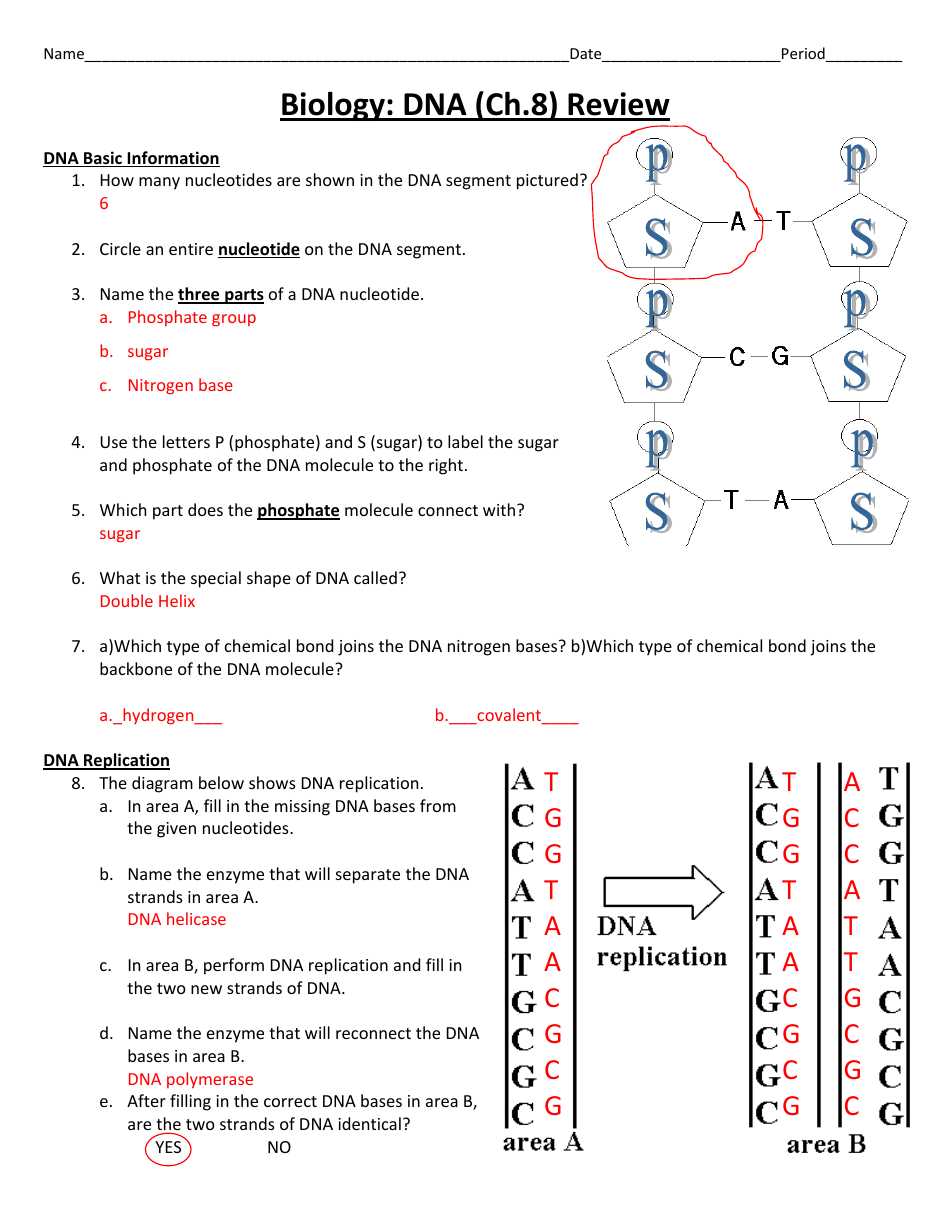
Understanding the structure of DNA is crucial for understanding how genetic information is stored and transmitted in living organisms. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a long molecule that contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. It is made up of smaller units called nucleotides, which are composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
In this lab, students constructed a paper model of DNA to explore its structure and gain a better understanding of its components. The model consisted of two long strands of paper representing the DNA molecule, with smaller pieces of colored paper representing the nucleotides. By following the instructions and matching the nucleotides correctly, students were able to see how the base pairs (adenine paired with thymine, and guanine paired with cytosine) held the strands together.
This hands-on lab activity allowed students to visualize the three-dimensional structure of DNA and understand how the double helix shape is formed. By building and manipulating the paper model, students were able to see how the nucleotides are connected to form the long strands, and how the base pairs interact to hold the strands together. This visual representation helped reinforce the concept of complimentary base pairing and the overall structure of the DNA molecule.
Overall, the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab provided students with a tangible way to learn about the structure of DNA, enhancing their understanding of genetics and how genetic information is passed from one generation to the next. By actively engaging in the construction and manipulation of the paper model, students were able to grasp the concepts more easily and make meaningful connections to the real-life applications of DNA research.
What is a DNA Structure Paper Model Lab?
A DNA Structure Paper Model Lab is a hands-on activity that allows students to create a three-dimensional model of DNA using paper and other materials. This lab provides students with a visual representation of the double helix structure of DNA, helping them to better understand its organization and function.
The lab typically begins with an introduction to the structure of DNA, including the concepts of base pairing and complementary base sequences. Students are then provided with a template or instructions for creating their paper model, which may involve cutting out and coloring different components of the DNA molecule.
The key components of a DNA Structure Paper Model Lab include:
- Template or instructions for creating the model
- Paper or cardstock for constructing the model
- Scissors for cutting out the components
- Markers or colored pencils for coloring the components
- Tape or glue for assembling the model
During the lab, students will carefully cut out the different components of the DNA molecule, such as the sugar-phosphate backbone and the nitrogenous bases. They will then color each component according to a key or guide, highlighting the different nucleotides and the pairing of adenine with thymine, and guanine with cytosine.
Once all the components are colored, students will assemble the model by attaching the backbone and connecting the complementary base pairs. This process allows students to visually see how DNA strands are held together by hydrogen bonds and how the double helix structure is formed.
The DNA Structure Paper Model Lab is an effective way for students to engage with and understand the complex structure of DNA. By actively constructing the model, students are able to visualize the arrangement of nucleotides, comprehend base pairing, and comprehend the overall structure and function of DNA.
Importance of Understanding DNA Structure
Understanding DNA structure is crucial in many fields of science and medicine as it provides the foundation for the functioning and replication of genetic material. The discovery of the double helix structure of DNA by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 revolutionized the field of genetics and laid the groundwork for many subsequent breakthroughs in molecular biology.
Genetic research: DNA structure is of paramount importance in genetic research as it allows scientists to study and manipulate genes. By understanding how DNA is organized and how its different components interact, researchers can identify mutations and genetic variations that are associated with diseases. This knowledge has paved the way for the development of targeted therapies and personalized medicine.
Forensic science: DNA structure is also crucial in forensic science as it allows for the identification of individuals through DNA profiling. DNA samples found at crime scenes or on different objects can be analyzed to determine the identity of the person who left the sample behind. This technology has been instrumental in solving countless criminal cases and has contributed to the advancement of justice.
Evolutionary biology: Understanding DNA structure is essential in studying the evolution of species. Through comparative genomics, scientists can compare the DNA sequences of different organisms and identify similarities and differences. This information helps to construct evolutionary trees and understand the relationships between different species.
Medical diagnostics: DNA structure plays a critical role in medical diagnostics. Many diseases and disorders have a genetic component, and by analyzing an individual’s DNA, doctors can make accurate diagnoses and determine the most effective treatment options. DNA testing has become a routine part of medical practice and has improved patient care.
Biotechnology and genetic engineering: Understanding DNA structure has revolutionized the field of biotechnology and genetic engineering. Researchers can manipulate DNA sequences to create modified organisms with desired traits, such as disease-resistant crops or bacteria that produce important pharmaceuticals. This technology has the potential to address global challenges related to food security and healthcare.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of DNA structure is essential in various scientific disciplines and has led to numerous advancements in research, medicine, and technology. It has opened up new avenues for studying genetics, solving crimes, understanding evolution, diagnosing diseases, and improving agriculture and healthcare. Continuing to explore and expand our understanding of DNA structure will undoubtedly lead to future breakthroughs and advancements in the field of molecular biology.
Overview of the Paper Model Lab

The DNA structure paper model lab is a hands-on activity designed to help students understand the structure of DNA, one of the most important molecules in living organisms. This activity involves constructing a three-dimensional model of DNA using paper cutouts, which allows students to visualize the double helix structure of DNA and its components.
The lab begins with an introduction to the basic concepts of DNA, such as the nucleotides that make up its structure and the base pairing rules. Students are provided with a set of paper cutouts representing the four nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine) and are instructed to assemble them in a specific order to create a DNA strand. This activity helps students understand how the base pairing rules determine the complementary pairing between nucleotides in DNA.
Once students have created a single DNA strand, they are then guided to create a second complementary strand using the base pairing rules. By aligning the two strands and twisting them in a helical fashion, students can visualize the double helix structure of DNA. This activity emphasizes the importance of base pairing and demonstrates how the two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds.
In addition to constructing the DNA structure, students are also introduced to the concept of DNA replication. They learn that DNA can replicate itself by separating the two strands and using each strand as a template to synthesize a new complementary strand. This process is crucial for the transmission of genetic information during cell division and is replicated in every cell of an organism.
Overall, the DNA structure paper model lab provides a hands-on and visual approach to learning about the structure and function of DNA. By constructing a three-dimensional model, students gain a deeper understanding of the double helix structure and the processes involved in DNA replication. This lab activity helps reinforce key concepts and allows students to actively engage in the learning process.
Key Components of the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab
The DNA Structure Paper Model Lab is an interactive activity that allows students to visually and kinesthetically understand the structure of DNA. This lab involves the use of colored paper cutouts representing the four nucleotides (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) and their complementary base pairings.
Materials:
- Colored paper cutouts (in different shapes and sizes) representing the four nucleotides
- Scissors
- Glue
- Base pairings chart (to help students match the complementary nucleotides)
- Instructions or guidelines for building the DNA model
Procedure:
- Provide each student with the necessary materials, including the colored paper cutouts, scissors, and glue.
- Explain the basic structure of DNA, including the double helix shape and the complementary base pairings.
- Show students the base pairings chart and demonstrate how to match the complementary nucleotides.
- Give students clear instructions or guidelines on how to build the DNA model using the colored paper cutouts. This may involve cutting out specific shapes, gluing them together, and arranging them in the correct sequence.
- Allow students to work individually or in small groups to build their DNA models.
- Encourage students to discuss their models with their peers and compare their structures to ensure accuracy.
- Provide opportunities for students to explain their models and discuss the importance of the structure of DNA in genetic information.
Learning Outcomes:
The DNA Structure Paper Model Lab allows students to engage in a hands-on activity that promotes understanding of the key components of DNA. Through building their own DNA models, students gain a visual and tactile understanding of the double helix structure and the complementary base pairings. Additionally, this lab provides an opportunity for students to practice following instructions, working collaboratively, and discussing scientific concepts with their peers. Overall, this lab helps students deepen their understanding of the structure and function of DNA and its importance in genetics.
Understanding the Answer Key for the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab
The DNA Structure Paper Model Lab is a commonly used activity in biology classes to help students visualize and understand the structure of DNA. Students construct a three-dimensional model of the DNA molecule using cut-out templates and assemble the nucleotides, sugar-phosphate backbone, and hydrogen bonds.
In order to assess their understanding of the lab, students are usually given an answer key which provides the correct way to assemble the model. This answer key serves as a guide for students to compare their own models and check for errors or misconceptions. Understanding the answer key is essential for students to learn from their mistakes and improve their understanding of DNA structure.
The answer key typically includes step-by-step instructions on how to assemble the model, including the correct placement of each component. It may also include additional information and explanations about the structure and function of DNA. Students can use this information to enhance their understanding of DNA and the key features of its structure.
Key Components and Structures in the Answer Key
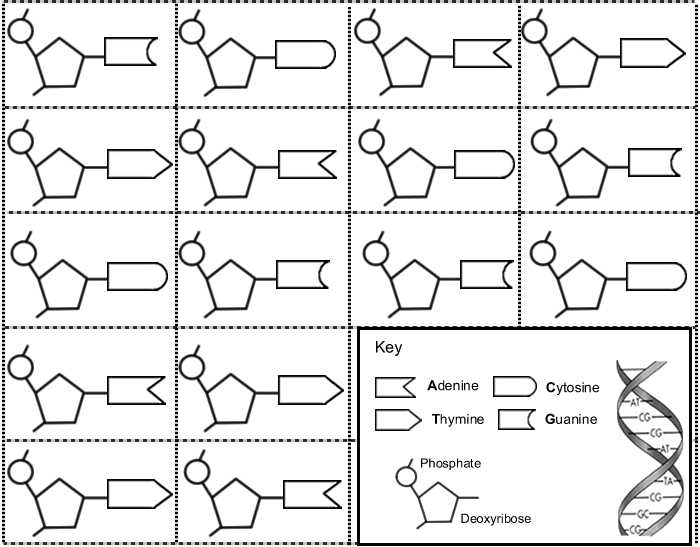
When examining the answer key, students will often find the following components and structures:
- Nucleotides: The basic building blocks of DNA, consisting of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- Sugar-Phosphate Backbone: The alternating sugar and phosphate groups that make up the sides of the DNA molecule.
- Hydrogen Bonds: The bonds that hold the two strands of DNA together.
- Base Pairs: The specific pairs of nitrogenous bases that form the rungs of the DNA ladder, such as adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine.
By comparing their model to the answer key, students can identify any mistakes or missing components in their own model. This helps them understand the correct arrangement of the components and reinforces their understanding of DNA structure.
Conclusion
The answer key for the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab is an essential tool for students to assess their understanding of DNA structure. By comparing their model to the answer key, students can identify any errors or misconceptions and improve their understanding of the key components and structures of DNA. This activity helps students visualize and comprehend the structure of DNA, a fundamental concept in biology.
Q&A:
What is the purpose of the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab?
The purpose of the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab is to help students understand the structure of DNA and how it is organized.
What is the answer key used for in the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab?
The answer key is used as a guide for students to check their models and ensure they have correctly assembled the DNA structure.
How does the answer key help students in the lab?
The answer key provides a visual representation of the correct assembly of the DNA structure, allowing students to compare their own models and make any necessary corrections.
What happens if a student’s model does not match the answer key?
If a student’s model does not match the answer key, they can review the instructions and identify any mistakes they may have made. They can then make the necessary corrections to accurately assemble the DNA structure.
Can the answer key be used to cheat or skip the lab activity?
No, the answer key is not intended for cheating or skipping the lab activity. It is meant to serve as a reference for students to check their work and ensure their understanding of the DNA structure.
What is the DNA Structure Paper Model Lab?
The DNA Structure Paper Model Lab is an experiment where students build a 3D model of the DNA molecule using paper and other materials.