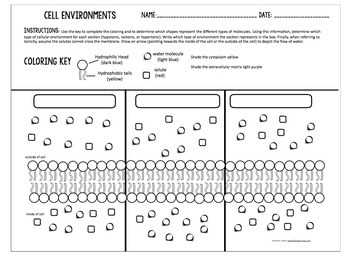
When studying cells, it is important to understand the different environments they exist in and how these environments influence their functions and behaviors. The cell environments worksheet answer key provides a comprehensive overview of these environments and the processes that take place within them.
One of the key concepts covered in the worksheet is the cell membrane and its role in maintaining the cell’s internal environment. The cell membrane acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. It also houses various proteins and receptors that allow the cell to communicate with its surroundings and respond to external signals.
The worksheet also explores the importance of the cytoplasm, which is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. This environment is rich in nutrients, proteins, and other essential molecules that support the cell’s metabolic processes. It is within the cytoplasm that many of the cell’s organelles, such as the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum, are located.
Furthermore, the cell environments worksheet answer key delves into the nucleus, the control center of the cell. This organelle houses the cell’s DNA and is responsible for controlling the cell’s activities and regulating gene expression. Understanding the role of the nucleus in cellular functions is crucial for comprehending how cells develop, function, and respond to changes in their environments.
In conclusion, the cell environments worksheet answer key provides valuable insights into the different environments within a cell and their impact on cell function. By understanding these concepts, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the complexity and importance of cells in living organisms.
Cell Environments Worksheet Answer Key

In this answer key for the Cell Environments Worksheet, we will provide the correct answers and explanations for each question. This worksheet focuses on understanding the different types of environments that cells can live in and how they adapt to those environments.
Question 1: What is an environment?
Answer: An environment refers to the surrounding conditions, both physical and biological, in which an organism or a cell lives.
Question 2: Name three types of cell environments.
Answer: The three types of cell environments are aquatic (water), terrestrial (land), and aerial (air).
Question 3: How do aquatic cells adapt to their environment?
Answer: Aquatic cells have adaptations to help them survive in water, such as the presence of specialized structures like gills or fins in aquatic organisms. They may also have a streamlined shape to reduce drag and move efficiently in water.
Question 4: How do terrestrial cells adapt to their environment?
Answer: Terrestrial cells have adaptations to withstand the challenges of living on land. One common adaptation is the presence of a protective outer layer, such as the cuticle in plant cells, to prevent water loss. Terrestrial cells also have structures like roots and leaves to absorb water and nutrients from the soil and carry out photosynthesis.
Question 5: How do aerial cells adapt to their environment?
Answer: Aerial cells have adaptations to survive in the air. For example, they may have specialized structures like wings or feathers for flight in animals, or structures like trichomes in plants to reduce water loss and provide support.
Question 6: Give an example of a cell that can live in both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Answer: One example is the amphibian cell, found in organisms like frogs and salamanders. These cells have adaptations that allow them to live in water during their larval stage and on land during their adult stage.
Question 7: Discuss the importance of cell adaptations to different environments.
Answer: Cell adaptations to different environments are crucial for the survival and success of organisms. These adaptations allow cells to function optimally and meet their physiological needs, such as obtaining nutrients, eliminating waste products, and reproducing. Without the appropriate adaptations, cells may not be able to survive or thrive in their respective environments.
The Importance of Cell Environments
Cell environments play a crucial role in the functioning and survival of cells. Every cell, whether it be a human cell, a plant cell, or a bacterial cell, operates within a specific environment that provides the necessary conditions for its proper functioning. The cell environment encompasses the chemical, physical, and biological factors that surround and interact with the cell.
Intraсellular environment: The intracellular environment refers to the conditions within the cell itself. It includes factors such as the concentration of various molecules, pH levels, temperature, and the availability of nutrients and energy sources. Maintaining an optimal intracellular environment is vital for cellular processes like metabolism, protein synthesis, signal transduction, and DNA replication.
Extracellular environment: The extracellular environment refers to the surroundings of the cell outside its plasma membrane. It can vary depending on the type of organism and its habitat. For example, human cells are bathed in interstitial fluid, while plant cells are surrounded by the cell wall and live in soil or water. The extracellular environment influences cell behavior, growth, and differentiation through factors such as nutrient availability, chemical signaling molecules, physical cues, and interactions with neighboring cells.
Cell membrane: The cell membrane acts as a selective barrier and plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s internal environment. It regulates the exchange of substances between the cell and its surroundings, ensuring that only essential molecules enter and exit the cell. The cell membrane also contains various transport proteins, receptors, and channels that facilitate communication and allow cells to respond to changes in their environment.
Cellular homeostasis: The proper functioning of cells relies on maintaining a stable internal environment, known as cellular homeostasis. Cells must regulate the concentrations of ions, pH levels, and nutrient levels within narrow ranges to ensure optimal cellular function. Imbalances in cell environments can have detrimental effects on cell viability and can lead to various diseases and disorders.
In summary, cell environments are essential for maintaining cellular health and functionality. Cells rely on their intracellular and extracellular environments to provide the necessary conditions for survival, growth, and proper functioning. Understanding the importance of cell environments is crucial for advancing our knowledge of cell biology and developing strategies for treating diseases that arise from imbalances in cellular environments.
Cell Environments and Cellular Processes
In order to understand how cells function and carry out their various tasks, it is important to consider the environments in which they exist. Cells are incredibly dynamic and versatile, adapting to their surroundings and responding to different stimuli in order to maintain homeostasis and perform their essential functions.
One key aspect of cell environments is the presence of specific molecules and chemicals that cells require for their biochemical processes. These molecules can include nutrients, such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, which cells use for energy production and building blocks for cellular structures. Additionally, cells require a constant supply of oxygen, which is essential for aerobic respiration and energy production.
Cells also rely on the presence of water in their environments. Water is an essential solvent for many cellular processes, allowing molecules to dissolve and react with one another. It also helps to maintain cellular structure and provides a medium for the transport of nutrients, waste products, and signaling molecules. Without water, cellular processes would not be able to occur efficiently.
Furthermore, the physical characteristics of the cell environment, such as temperature and pH, play a crucial role in cellular processes. Cells have specific temperature and pH ranges in which they can function optimally. Deviations from these optimal conditions can disrupt cellular processes and even lead to cell death. Therefore, cells have mechanisms in place to regulate and maintain these environmental factors within a narrow range.
In summary, cell environments are complex and dynamic, providing cells with the necessary molecules, chemicals, and physical conditions for their survival and function. Understanding these environments and how cells adapt to them is fundamental to studying cellular processes and their regulation in both normal and disease states.
Exploring Cell Environments
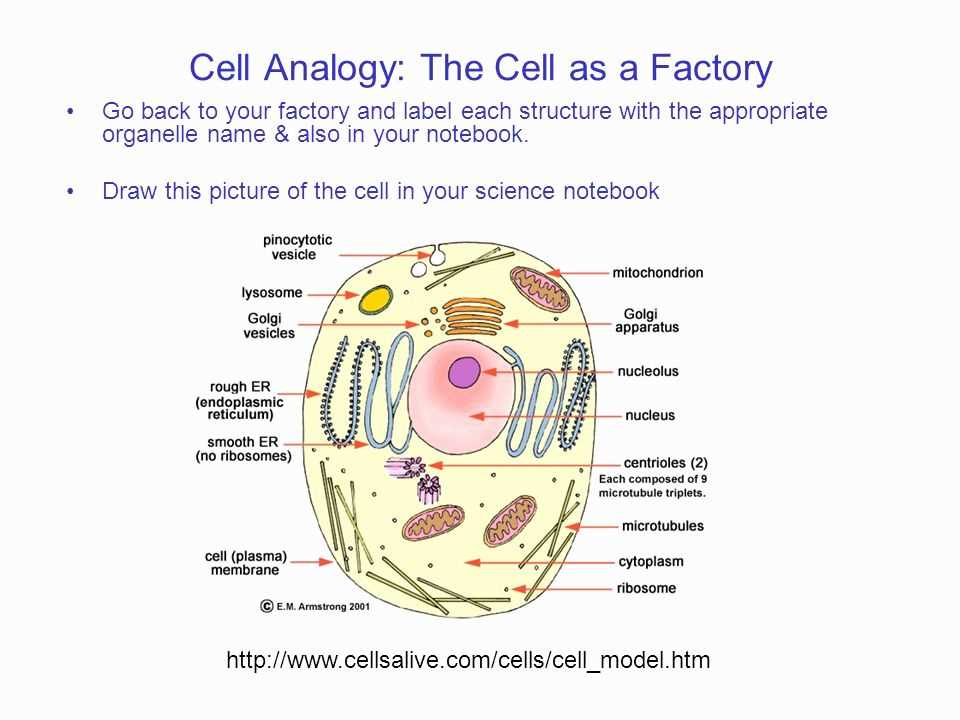
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms, and each cell has its own unique environment that allows it to function properly. By understanding and exploring these cell environments, scientists can gain valuable insights into the workings of cells and how they contribute to overall biological processes.
One key aspect of cell environments is the presence of various nutrients and molecules that are necessary for cellular growth and metabolism. For example, cells need access to glucose, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals in order to carry out essential functions such as energy production, protein synthesis, and DNA replication. Without these nutrients, cells may not be able to function optimally and can even die.
In addition to the presence of essential nutrients, the physical structure and organization of cell environments also play a crucial role in cell function. Cells are often surrounded by a protective extracellular matrix, which provides structural support and helps regulate cell behavior. This extracellular matrix is made up of proteins, carbohydrates, and other molecules that form a complex network, creating a unique environment for cells to interact with.
Furthermore, cell environments can vary greatly depending on the specific tissue or organ where the cells are located. For instance, cells in muscle tissue require a different environment compared to cells in nerve tissue. These different environments provide the necessary cues and signals for cells to differentiate into specific cell types and carry out specialized functions. Understanding and recreating these tissue-specific environments in the laboratory is an ongoing challenge for researchers in the field of tissue engineering.
In conclusion, exploring cell environments is essential for understanding the intricacies of cellular function and how cells contribute to the overall functioning of living organisms. By investigating the presence of essential nutrients, the physical structure of cell environments, and tissue-specific variations, scientists can gain valuable insights that can be applied to various fields, including medicine, biology, and tissue engineering.
Cell Environments and Cell Function
In order for cells to carry out their functions effectively, they need to be in the right environment. Cells are highly specialized and have specific requirements for temperature, pH, and nutrient availability. The extracellular environment surrounding cells plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and supporting cell function.
Temperature: Cells function optimally within a specific temperature range. Extreme temperatures can disrupt cell membranes, denature proteins, and disrupt the overall function of the cell. For example, in extremely cold temperatures, cell membranes can become rigid and lose their fluidity, impairing the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. On the other hand, high temperatures can cause proteins to unfold and lose their structure, rendering them non-functional.
pH: Cells also require a specific pH level to function properly. pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Most cells function best in a slightly alkaline environment, around pH 7.4. Changes in pH can disrupt the structure and function of proteins and enzymes within the cell, which are critical for cellular processes. For example, highly acidic conditions can lead to the denaturation of proteins, while highly alkaline conditions can interfere with enzyme activity.
Nutrient Availability: Cells need a constant supply of nutrients to carry out their metabolic processes. Nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals are essential for cell growth, energy production, and maintenance. The extracellular environment provides the necessary nutrients through diffusion and active transport mechanisms. Inadequate nutrient availability can lead to impaired cell function and ultimately cell death.
In conclusion, the environment in which cells exist greatly influences their function. Maintaining optimal temperature, pH, and nutrient availability is crucial for cells to carry out their specialized functions effectively. Any disruption in the cell environment can have detrimental effects on cellular processes and overall cell health.
Understanding the Role of Cell Environments

Cells are the building blocks of life, and they exist in a wide range of environments. The environment in which a cell resides plays a crucial role in determining its structure and function. From the temperature and pH levels to the availability of nutrients and oxygen, each aspect of the cell’s environment influences its ability to carry out essential processes.
One key factor in cell environments is temperature. Different organisms thrive in different temperature ranges, and cells have adapted to function optimally within these specific temperature conditions. For example, extremophile organisms, such as those found in hot springs or deep-sea vents, have cells that are designed to withstand extremely high temperatures. On the other hand, cells in the Arctic tundra are adapted to function in freezing temperatures. The temperature of the environment significantly impacts the rate of chemical reactions within the cells, affecting their metabolism and overall activity.
The pH level of the environment is another critical aspect that cells must contend with. The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, and cells have evolved to function within specific pH ranges. For example, human cells function optimally at a slightly alkaline pH of around 7.4. Changes in pH outside of this optimal range can disrupt cellular processes and even lead to cell death. Some extreme environments, such as highly acidic or alkaline habitats, harbor organisms with cells that can survive and thrive in these hostile conditions.
The availability of nutrients and oxygen in the cell’s environment is also essential for its survival and function. Cells require a constant supply of nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, to carry out their metabolic processes. Additionally, oxygen is crucial for cellular respiration, the process by which cells produce energy. Cells in different environments have adapted unique strategies to obtain and utilize these essential resources.

In conclusion, understanding the role of cell environments is fundamental to comprehending cellular biology. The temperature, pH level, and availability of nutrients and oxygen in an environment all influence how cells function and adapt to their surroundings. By studying and analyzing these factors, scientists can gain insights into the complexities of cellular life and the intricate mechanisms that allow cells to thrive in various environments.
Key Takeaways on Cell Environments
Understanding the different environments in which cells exist is crucial for comprehending their functions and behaviors. Here are the key takeaways on cell environments:
- Extracellular environment: This is the environment outside the cell and includes the extracellular matrix, which provides structural support to cells. Signals from the extracellular environment can influence cell behavior and decision-making.
- Intracellular environment: This is the environment inside the cell and consists of various organelles, proteins, and other cellular components. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cell homeostasis and carrying out essential cellular processes.
- Cell membrane: The cell membrane acts as a selective barrier, regulating the exchange of substances between the extracellular and intracellular environments. It is composed of phospholipids and proteins.
- Cell signaling: Cells communicate with each other and respond to their environments through a process called cell signaling. This can involve both direct cell-cell interactions and the release of signaling molecules that bind to specific receptors.
- Tissue and organ environments: Cells exist within specific tissue and organ environments, which provide specialized conditions for their functioning. These environments can vary greatly depending on the tissue or organ type.
- Cellular adaptations: Cells can adapt to different environments through various mechanisms such as changing gene expression, altering cell shape, or modifying metabolic processes. These adaptations allow cells to survive and function optimally in different conditions.
Overall, the study of cell environments is essential for understanding the complex and dynamic nature of cells, their interactions, and their role in various biological processes. By gaining insights into the unique characteristics of different cell environments, scientists can further unravel the mysteries of cell biology and potentially develop new strategies for treating diseases and improving human health.
Q&A:
What is a cell environment?
A cell environment refers to the conditions, surroundings, and factors that affect the growth, functioning, and behavior of a cell.
What are the different types of cell environments?
There are various types of cell environments, including extracellular environments, intracellular environments, and specialized environments such as stem cell niches.
How do extracellular environments affect cells?
Extracellular environments provide cells with essential nutrients, oxygen, and signaling molecules. They also play a role in cell adhesion, communication, and regulation of cell behavior and function.
What is the significance of specialized cell environments like stem cell niches?
Specialized cell environments, such as stem cell niches, provide the necessary signals and cues for stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. These environments play a crucial role in regulating stem cell maintenance and tissue regeneration.