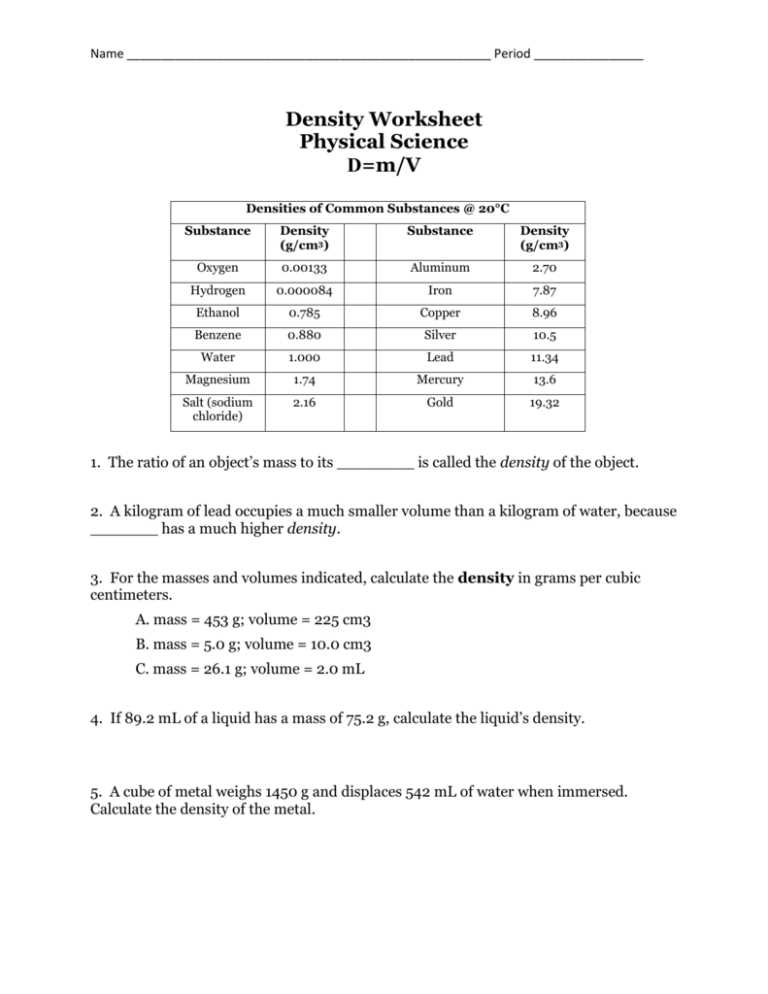
Are you having trouble understanding the concept of density? Do you find it challenging to solve density-related problems? Look no further! In this article, we will provide you with the answer key to Density Worksheet 2, along with a comprehensive explanation of the concept of density.
Density is a fundamental concept in science and is defined as the amount of mass per unit volume. It is a characteristic property of a substance and can be used to identify and compare different materials. The formula for density is density = mass/volume, and it is expressed in units such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) or kilograms per liter (kg/L).
Worksheet 2 is designed to help you practice calculating density using the given mass and volume measurements. With the provided answer key, you can check your answers and understand the steps involved in solving each problem. Additionally, the answer key will also explain any related concepts or formulas that are necessary for finding the correct solution.
Density Worksheet 2 Answer Key

In the field of science, density is a key concept that helps us understand the physical properties of different substances. It is defined as the ratio of an object’s mass to its volume. The density of a substance can be used to determine its buoyancy, as well as its ability to float or sink in a given medium.
When working with density, it is important to remember that it is an intensive property, meaning it does not depend on the size or amount of the substance. This means that no matter how much or how little of a substance you have, its density will remain the same. Density is commonly measured in units such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per liter (kg/L).
Answer Key:
- Question 1: The density of an object is calculated by dividing its mass by its volume.
- Question 2: The density of water is approximately 1 gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Question 3: If an object’s density is less than the density of water, it will float.
- Question 4: The volume of an object can be calculated by dividing its mass by its density.
- Question 5: If two objects have the same volume but different masses, the object with the greater mass will have a higher density.
Understanding the concept of density is crucial in various scientific fields, including chemistry, physics, and materials science. It allows scientists to classify and compare different substances based on their physical characteristics, and can be used to predict how a substance will behave in different environments. Density also plays a role in everyday life, such as determining whether an object will sink or float in water, or how much space an object occupies.
Objective of the Worksheet

The objective of the Density Worksheet 2 is to reinforce the understanding of density, its calculation, and its relationship to mass and volume. This worksheet provides students with various problems and questions that require them to apply their knowledge of density in different scenarios.
The worksheet begins with a review of the formula for calculating density, which is density = mass/volume. Students are then presented with a series of problems that require them to calculate density using this formula. These problems involve different units of measurement for mass and volume, allowing students to practice converting units and applying the appropriate formula.
The worksheet also includes questions that test students’ understanding of the concept of density. These questions ask students to determine the relationship between the density of an object and its ability to float or sink in a liquid. Students are also asked to explain why different substances have different densities and how density can be used to identify substances.
The Density Worksheet 2 aims to assess students’ comprehension of density and their ability to apply this concept in various situations. By completing this worksheet, students will reinforce their understanding of the relationship between mass, volume, and density, and develop their problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
What is Density?

Density is a physical property of matter that describes how much mass is contained within a given volume. It is the measure of how tightly packed the particles of a substance are. The formula for density is density = mass/volume.
Density is an intensive property, which means it does not depend on the amount of substance present. For example, a small piece of steel will have the same density as a larger piece of steel. Density is often used to identify substances and can be used to compare the densities of different materials.
The units of density are commonly expressed in grams per milliliter (g/mL) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), although other units such as kilograms per liter (kg/L) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) can also be used.
It is important to note that density is affected by changes in temperature and pressure. As temperature increases, the particles of a substance typically move faster, causing the substance to expand and its density to decrease. When pressure increases, the particles of a substance are pushed closer together, resulting in an increase in density.
Objects with higher densities will sink in liquids or other substances with lower densities, while objects with lower densities will float. This is the principle behind why ice cubes float in water.
Understanding How to Calculate Density

Density is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry that measures the amount of mass in a given volume. It is calculated by dividing the mass of an object by its volume. Understanding how to calculate density is essential in various scientific fields, as it helps to determine the properties and characteristics of different substances.
Calculating density involves a straightforward formula: density = mass/volume. Mass refers to the amount of matter in an object, usually measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg). Volume, on the other hand, measures the space occupied by an object and is typically expressed in cubic units such as cubic centimeters (cm³) or liters (L).
When working with density calculations, it is crucial to ensure that the units of mass and volume are consistent. For example, if the mass is given in grams, the volume should be in cubic centimeters. If the mass is in kilograms, the volume needs to be in liters. This step is essential for obtaining accurate and meaningful density values.
To illustrate how to calculate density, let’s consider an example. Suppose we have a sample of gold with a mass of 50 grams and a volume of 10 cubic centimeters. Using the formula density = mass/volume, we can calculate the density as follows:
Density = 50g / 10cm³ = 5g/cm³.
In this example, the density of the gold sample is 5 grams per cubic centimeter. This value tells us that gold is a dense material, meaning it has a large amount of mass packed into a relatively small volume. Understanding density allows scientists and researchers to compare and classify materials based on their physical properties.
In conclusion, calculating density is a fundamental skill for understanding the properties of different substances. By knowing how to divide an object’s mass by its volume, scientists can determine how compact or spread out the matter is. Whether working in physics, chemistry, or other scientific fields, a solid understanding of density calculations is crucial for accurate analysis and interpretation of data.
Practical Application of Density
Density is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry and has numerous practical applications in various fields. It is a physical property that relates the mass of an object to its volume, and can be used to identify and characterize different materials.
1. Identifying Unknown Substances: Density can be used to identify unknown substances. By measuring the density of a sample and comparing it to known densities of different materials, scientists can determine the composition of the substance. This is particularly useful in forensic science and environmental analysis, where identifying unknown substances is important for solving crimes or assessing pollution levels.
Example: If an unknown liquid has a higher density than water, it could be identified as a heavy organic solvent such as chloroform or gasoline. On the other hand, if its density is lower than water, it could be identified as a lighter liquid like alcohol or acetone.
2. Quality Control in Manufacturing: Density measurements are used in manufacturing processes to ensure consistent product quality. By monitoring the density of raw materials or final products, manufacturers can detect variations or impurities that could affect the performance or safety of their products.
Example: In the production of pharmaceuticals, density measurements are performed to ensure that the concentration of active ingredients is within the specified range. Deviations from the desired density values may indicate a batch of substandard or contaminated product.
3. Determining Purity of Substances: Density can also be used to determine the purity of substances. By comparing the density of a sample to the theoretical density of a pure substance, scientists can evaluate the degree of impurities or contaminants present in the sample.
Example: In the analysis of metals, density measurements can help assess the purity of the material. A sample with a density lower than the theoretical density of the pure metal may indicate the presence of alloying elements or impurities.
Overall, the practical applications of density span across various disciplines and industries, playing a crucial role in material identification, quality control, and purity assessment. Its measurement and understanding are essential for scientists, engineers, and technicians working in fields such as chemistry, physics, manufacturing, and environmental science.
Answer Key for Density Worksheet 2
In this article, we have provided the answer key for Density Worksheet 2. This worksheet focuses on calculating density using the formula: density = mass/volume. It includes various practice problems that require students to find the density of different substances.
Here is the answer key for Density Worksheet 2:
- Problem 1: The mass of an object is 50 grams and its volume is 25 cubic centimeters. Calculate the density.
- Problem 2: The mass of a substance is 120 kilograms and its volume is 80 liters. Calculate the density.
- Problem 3: The mass of a liquid is 75 grams and its volume is 50 milliliters. Calculate the density.
- Problem 4: The mass of a gas is 0.5 grams and its volume is 2 liters. Calculate the density.
Answer: density = mass/volume = 50 g / 25 cc = 2 g/cc
Answer: density = mass/volume = 120 kg / 80 L = 1.5 kg/L
Answer: density = mass/volume = 75 g / 50 mL = 1.5 g/mL
Answer: density = mass/volume = 0.5 g / 2 L = 0.25 g/L
By using the formula for density and the given mass and volume values, students can calculate the density of various substances. This helps them understand the concept of density and its importance in identifying different materials based on their physical properties. It also reinforces their problem-solving skills and mathematical abilities.
Overall, Density Worksheet 2 provides valuable practice for students to better understand and apply the concept of density, and the answer key serves as a useful resource for checking their work and verifying their answers.