In today’s society, eating disorders are unfortunately common and can have serious consequences. They affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, and can be caused by a variety of factors such as genetics, psychological issues, and societal pressure. It is crucial to raise awareness and understanding of eating disorders to promote early intervention and proper treatment.
BrainPOP, an educational platform, offers quizzes on various subjects, including eating disorders. These quizzes provide an opportunity to test your knowledge and learn more about these mental health conditions. This article will provide answers to the Eating Disorders BrainPOP Quiz to help you consolidate your knowledge and gain a better understanding of eating disorders.
One of the questions in the Eating Disorders BrainPOP Quiz asks about the most common eating disorder. The correct answer is “Bulimia Nervosa.” Bulimia Nervosa is characterized by episodes of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors such as purging, excessive exercise, or fasting. It often involves a preoccupation with body weight and shape and can have severe medical consequences.
Eating Disorders Brainpop Quiz Answers: Discover the Solutions!
Are you struggling to find the correct answers to the Eating Disorders Brainpop Quiz? Look no further! We have compiled a list of solutions to help you ace the quiz and gain a deeper understanding of eating disorders and their impact on individuals.
1. General Knowledge:
- Question: What are the three main types of eating disorders?
- Answer: The three main types of eating disorders are anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder.
2. Identification and Symptoms:
- Question: What are some common signs and symptoms of anorexia nervosa?
- Answer: Common signs and symptoms of anorexia nervosa include extreme weight loss, intense fear of weight gain, distorted body image, and denial of hunger.
- Question: How can you identify someone with bulimia nervosa?
- Answer: People with bulimia nervosa often have a cycle of binge eating followed by purging, such as induced vomiting or excessive exercise. They may also have fluctuations in weight and may try to hide their eating habits.
3. Health Consequences:
- Question: What are some potential health consequences of binge eating disorder?
- Answer: Binge eating disorder can lead to obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease.
4. Treatment Options:
- Question: What are some common treatments for eating disorders?
- Answer: Treatment for eating disorders often involves a combination of therapy, nutritional counseling, medical monitoring, and support groups.
By familiarizing yourself with these answers, you can enhance your knowledge of eating disorders and their impact on mental and physical health. Remember, there is no shame in seeking help if you or someone you know is struggling with an eating disorder. Reach out to healthcare professionals for guidance and support.
Understanding Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that can have serious consequences for both physical and emotional well-being. They are characterized by abnormal eating habits and distorted thoughts about body weight and shape. These disorders often involve a combination of factors, including genetics, psychological factors, societal pressures, and cultural influences.
There are several types of eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder, and other specified feeding or eating disorders (OSFED). Anorexia nervosa is characterized by severe restriction of food intake, intense fear of gaining weight, and a distorted body image. Bulimia nervosa involves episodes of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors such as vomiting or excessive exercise. Binge eating disorder is characterized by recurrent episodes of uncontrollable overeating without compensatory behaviors.
- Causes: While the exact causes of eating disorders are unknown, they are believed to be influenced by a combination of genetic, psychological, and environmental factors. Biological factors may play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to developing an eating disorder. Psychological factors, such as low self-esteem, perfectionism, and body dissatisfaction, can contribute to the development of disordered eating behaviors. Societal pressures, including media ideals of beauty and societal emphasis on thinness, can also influence the development of eating disorders.
- Signs and Symptoms: Some common signs and symptoms of eating disorders include extreme weight loss or gain, preoccupation with food and weight, excessive exercising, self-esteem heavily influenced by body image, distorted body image, fear of gaining weight, purging behaviors (such as vomiting or using laxatives), and social withdrawal.
- Treatment: Treatment for eating disorders typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medical, psychological, and nutritional interventions. Medical treatment may be necessary to address any physical complications resulting from the eating disorder. Psychological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), can help individuals identify and change unhealthy thoughts and behaviors related to food and body image. Nutritional counseling can also play a crucial role in helping individuals develop a healthy relationship with food.
- Prevention: While not all cases of eating disorders can be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. Promoting a positive body image, fostering self-esteem and body acceptance, and challenging unrealistic beauty ideals can help create a healthier environment. Educating individuals about the dangers of excessive dieting and the importance of balanced nutrition can also be beneficial in prevention efforts.
Eating disorders are serious mental health conditions that require professional intervention and support. Understanding the causes, signs, and symptoms of these disorders is crucial in order to provide appropriate help and support to individuals affected by them.
Common Types of Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are serious mental health conditions that can have severe physical and emotional consequences. They are characterized by abnormal eating behaviors and distorted body image. Here are some of the most common types of eating disorders:
Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight and a distorted body image. People with anorexia nervosa severely restrict their food intake, leading to significant weight loss and malnutrition. They may also engage in excessive exercise and engage in other behaviors to control their weight. Anorexia nervosa can have serious health complications and can even be life-threatening.
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by episodes of binge eating followed by purging behaviors, such as self-induced vomiting or excessive exercise. People with bulimia nervosa often feel a lack of control during binge episodes and may experience intense shame and guilt afterward. The cycle of bingeing and purging can negatively impact both physical and mental health.
Binge Eating Disorder
Binge eating disorder is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of uncontrollable overeating, often followed by feelings of guilt and shame. People with binge eating disorder do not engage in purging behaviors, unlike those with bulimia nervosa. Binge eating can lead to significant weight gain and obesity, as well as physical and emotional health problems.
Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorders (OSFED)
OSFED is a category of eating disorders that do not fit the specific criteria for anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, or binge eating disorder. For example, individuals may exhibit symptoms of disordered eating or have a dysfunctional relationship with food and their body image that does not meet the full diagnostic criteria for the other eating disorders. Although their behaviors may not fit neatly into a specific diagnosis, they still require treatment and support.
It is important to seek professional help if you or someone you know is struggling with an eating disorder. These disorders can have serious consequences and should be treated by a healthcare professional specializing in eating disorders.
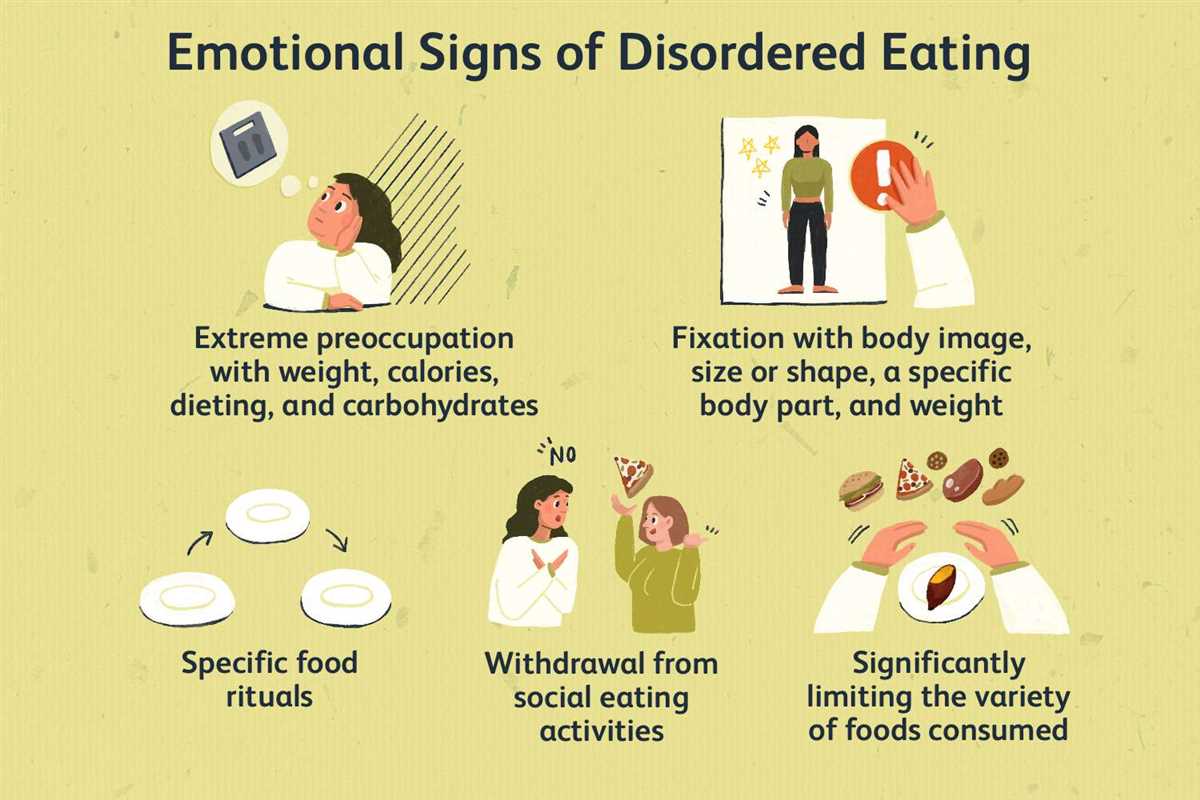
Identifying Warning Signs
When it comes to eating disorders, it is important to be able to recognize the warning signs. Early identification can greatly increase the chances of successful intervention and treatment. Here are some key indicators to look out for:
Extreme weight loss or gain:
One of the most obvious warning signs of an eating disorder is a significant and unexplained change in weight. This can involve the individual losing a large amount of weight in a short period of time, or gaining weight rapidly. Pay attention to any extreme fluctuations in weight, as they may be a sign of an underlying issue.
Obsession with food and body image:
People with eating disorders often have an unhealthy preoccupation with food and their appearance. They may constantly talk about or think about food, count calories obsessively, or engage in restrictive eating habits. They may also have a distorted perception of their body image, seeing themselves as overweight even when they are dangerously underweight.
Avoidance of social situations involving food:
Individuals with eating disorders may exhibit avoidance behaviors when it comes to food-related social situations. They may make excuses to avoid meals or gatherings where food is present, or they may engage in behaviors such as hiding food, playing with it instead of eating it, or taking small bites and then claiming to be full. These actions can be a sign of underlying issues with food and body image.
Changes in eating patterns:
Watch out for drastic changes in eating patterns or rituals. Someone with an eating disorder may suddenly start refusing food, skipping meals, or only eating very small portions. On the other hand, they may also engage in binge-eating episodes, consuming large quantities of food in a short amount of time and feeling out of control during these episodes.
Mood swings and emotional instability:
Eating disorders often go hand in hand with emotional distress and instability. Look out for sudden mood swings, irritability, depression, anxiety, and a general sense of low self-esteem. These emotional changes may be linked to the individual’s relationship with food and body image.
It is important to keep in mind that these warning signs may vary and can manifest differently in each individual. If you suspect someone may be struggling with an eating disorder, it is crucial to approach the situation with sensitivity and encourage them to seek professional help.
Seeking Help and Support
If you or someone you know is struggling with an eating disorder, it is important to seek help and support as soon as possible. Eating disorders can have serious physical and mental health consequences, and early intervention is key to recovery.
Medical professionals: The first step in seeking help is to reach out to a medical professional, such as a doctor or a therapist, who specializes in eating disorders. They can provide a thorough assessment and diagnosis, as well as develop an individualized treatment plan.
Support groups: Joining a support group can be beneficial for individuals with eating disorders. These groups provide a safe space to share experiences, receive support, and learn coping strategies from others who have gone through or are going through similar challenges.
Therapy: Individual therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), can be helpful in addressing the underlying issues that contribute to disordered eating behaviors. Therapy can also provide tools and techniques to develop a healthier relationship with food and body image.
Nutritional counseling: Working with a registered dietitian who specializes in eating disorders can be beneficial for individuals struggling with their relationship with food. A dietitian can provide guidance on meal planning, nutrition education, and support in developing a balanced and sustainable eating pattern.
Family support: Involving family members in the treatment process can be crucial, as they can provide support and understanding. Family therapy can help improve communication, address family dynamics, and foster a supportive environment for recovery.
Online resources: Numerous online resources, such as websites, forums, and helplines, are available for individuals seeking help for eating disorders. These resources can provide information, education, and anonymous support to those who may not be ready to seek professional help yet.
Remember: It takes courage to seek help, and recovery is possible. If you or someone you know is struggling with an eating disorder, don’t hesitate to reach out for support. You are not alone, and there are people who can help you on your journey to recovery.
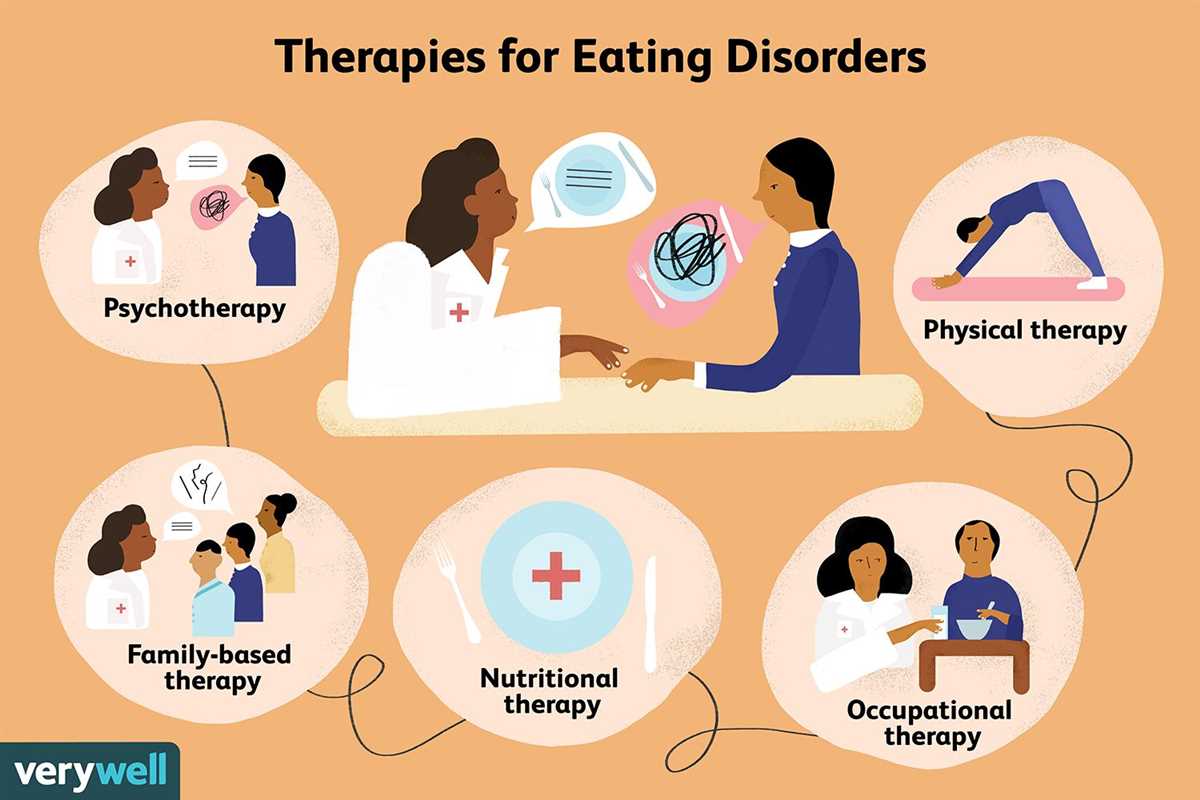
Treatment Options for Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that require specialized treatment. There are several treatment options available to help individuals suffering from eating disorders regain a healthy relationship with food and their bodies.
1. Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a common treatment for eating disorders. This form of therapy helps individuals gain insight into their thoughts and behaviors related to food, body image, and self-esteem. Psychotherapy can be conducted individually, in a group setting, or with family members involved.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- CBT helps individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their eating disorder.
- It focuses on developing healthy coping mechanisms, improving self-esteem, and establishing a positive body image.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
- DBT combines elements of CBT with mindfulness techniques. It helps individuals regulate their emotions, manage stress, and improve interpersonal relationships.
- It also promotes self-acceptance and self-compassion.
2. Medical Monitoring: For individuals with severe eating disorders, medical monitoring is necessary to ensure their physical health and safety. Inpatient or outpatient programs may include regular check-ups, nutritional assessments, and medical interventions to address any health complications caused by the eating disorder.
3. Nutritional Counseling: Nutritionists or dietitians can help individuals develop a balanced and healthy approach to food. They provide education about proper nutrition, meal planning, and portion control. Nutritional counseling also aims to address any unhealthy beliefs or behaviors related to food and eating.
4. Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed as part of the treatment plan for eating disorders. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, or mood stabilizers may be prescribed to help manage underlying mental health conditions that contribute to the eating disorder.
5. Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide individuals with a sense of community and understanding. These groups allow individuals to share their experiences, receive support, and learn from others who have faced similar challenges. Support groups can be invaluable in promoting recovery and preventing relapses.
In conclusion, treatment options for eating disorders involve a multidisciplinary approach, including psychotherapy, medical monitoring, nutritional counseling, medication, and support groups. It is important for individuals with eating disorders to seek professional help and work with a team of healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits their specific needs.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-term Recovery

Recovering from an eating disorder involves making significant lifestyle changes that promote long-term recovery. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Establish a Supportive Network
Building a strong support system is crucial for long-term recovery. Surround yourself with a network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals who understand your struggles and are willing to provide support and encouragement.
2. Seek Professional Help
Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a therapist, nutritionist, or doctor specialized in eating disorders, can be extremely beneficial. They can evaluate your condition, provide guidance, and develop a customized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
3. Adopt Healthy Eating Habits
Working with a nutritionist to develop a balanced meal plan that nourishes your body with essential nutrients is an essential part of long-term recovery. Understanding portion sizes, learning to listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, and finding enjoyable ways to incorporate a variety of foods are important steps towards a healthier relationship with food.
4. Practice Self-Care
Self-care activities, such as engaging in hobbies, practicing relaxation techniques, and prioritizing restful sleep, can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being. Finding healthy coping mechanisms and developing self-compassion are essential tools for maintaining long-term recovery.
5. Challenge Negative Thoughts
Addressing and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs about yourself, your body, and food is crucial for long-term recovery. Engaging in therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help you identify and reframe these destructive thoughts, promoting positive self-image and improved body acceptance.
Overall, long-term recovery from an eating disorder requires dedication, perseverance, and ongoing support. By making these lifestyle changes and committing to self-care, individuals can work towards a healthier relationship with food, their bodies, and themselves.
Q&A:
What lifestyle changes can help with long-term recovery?
Lifestyle changes that can help with long-term recovery include practicing healthy habits such as regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, managing stress, avoiding negative influences, and seeking support from friends, family, or support groups.
How does regular exercise contribute to long-term recovery?
Regular exercise can contribute to long-term recovery by helping to reduce stress, improve mood, increase energy levels, promote better sleep, and enhance overall physical health and well-being.
Why is a balanced diet important for long-term recovery?
A balanced diet is important for long-term recovery because it provides the necessary nutrients to support physical and mental health, boost energy levels, strengthen the immune system, and promote overall well-being.
How does managing stress aid in long-term recovery?
Managing stress is crucial for long-term recovery because it helps to prevent relapse, improves mental and emotional well-being, enhances coping mechanisms, and promotes overall relaxation and balance in life.
Why is it important to seek support from others in long-term recovery?
Seeking support from others in long-term recovery is important because it provides a sense of community, understanding, and encouragement. It allows individuals to share their experiences, gain valuable insights, learn coping strategies, and establish a strong support network that can help them maintain their recovery journey.
What lifestyle changes can help with long-term recovery?
There are several lifestyle changes that can contribute to long-term recovery. These include maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, getting enough sleep, managing stress effectively, surrounding oneself with a supportive social network, and avoiding relapse triggers.
How can a healthy diet aid in long-term recovery?
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in long-term recovery. It provides the body with the necessary nutrients to support physical and mental well-being. Certain foods can also help regulate mood and reduce cravings. Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can promote overall health and support recovery.