Geometry is a fascinating branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, sizes, and properties of figures. It plays a crucial role in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and design. In this article, we will delve into the world of geometry and explore the answers to 8 2 practice A geometry questions on page 269, aiming to deepen our understanding of this intriguing subject.
The study of geometry allows us to analyze the relationships between different shapes and how they interact with each other. By understanding various geometric concepts such as angles, lines, and polygons, we can solve complex problems and find practical applications in the real world.
As we navigate through 8 2 practice A geometry answers on page 269, we will encounter a wide range of questions that require us to apply our knowledge of geometric principles. From finding missing angles in triangles to determining the lengths of line segments, each question presents a unique challenge that will test our problem-solving skills.
By exploring these answers, we can not only sharpen our geometry skills but also gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of geometry in our everyday lives. Whether we are constructing buildings, creating computer graphics, or simply appreciating the beauty of geometrical patterns, geometry is an integral part of our world.
2 Practice A Geometry Answers Page 269
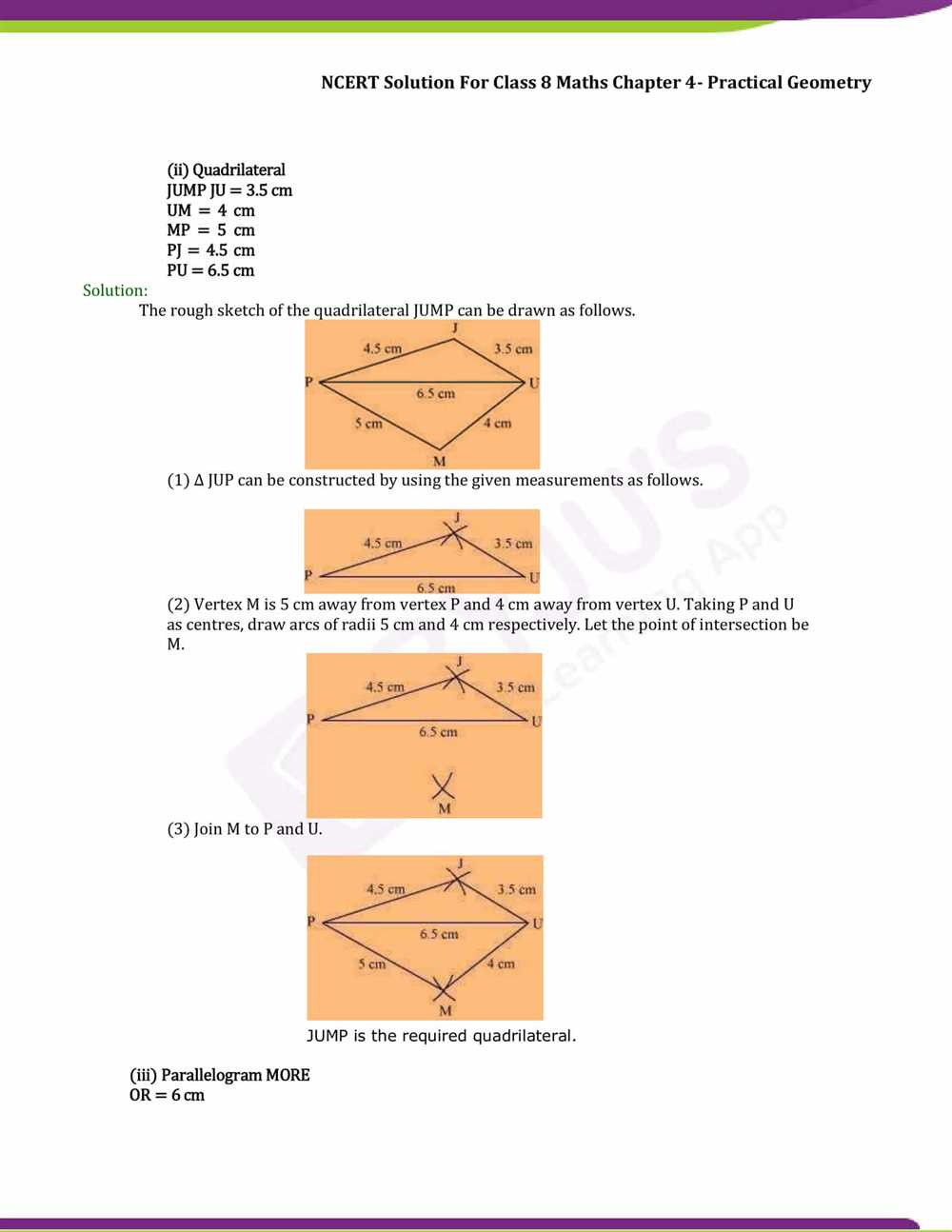
In 2 Practice A of Geometry, on page 269, students are given various geometry problems to solve. These problems cover a range of topics including angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles. By practicing these problems, students can sharpen their understanding of these geometric concepts and improve their problem-solving skills.
One example problem on page 269 asks students to determine the measure of an angle formed by two intersecting lines. To solve this problem, students can use the properties of angles formed by intersecting lines, such as the Vertical Angle Theorem and the Linear Pair Postulate. By applying these theorems, students can find the missing angle measure and provide their solution.
Another problem on this page involves finding the area of a triangle using the given side lengths. Students can apply the formula for the area of a triangle, which is 1/2 times the base times the height. By substituting the given lengths into the formula, students can calculate the area of the triangle and write their answer.
In addition to these specific problems, page 269 also provides students with an opportunity to practice general problem-solving strategies in geometry. By approaching each problem systematically, students can develop a logical and organized approach to solving geometry problems. This can include identifying given information, drawing accurate diagrams, applying relevant theorems, and checking their answers for reasonableness.
Overall, 2 Practice A of Geometry on page 269 offers students a range of challenging problems to reinforce their understanding of geometry concepts and develop their problem-solving abilities. By carefully working through these problems, students can improve their skills and gain confidence in their geometry knowledge.
Explanation and Breakdown of Practice A Geometry Activity

In practice A of the geometry activity, students are presented with a series of geometry problems that focus on various concepts, such as angles, lines, and polygons. The activity is designed to provide students with an opportunity to apply their understanding of these concepts and deepen their knowledge of geometry through problem-solving.
The activity begins with a set of multiple-choice questions that test students’ knowledge of basic geometry concepts. These questions require students to identify angles, lines, and shapes based on their properties. By answering these questions, students can gauge their understanding of the fundamental principles of geometry and identify areas where they may need further practice.
Next, the activity progresses to a set of short-answer questions that require students to apply their knowledge in more complex scenarios. These questions often involve problem-solving skills to determine unknown angles or properties of figures. Students are encouraged to use their understanding of geometry principles along with logical reasoning to solve these questions.
The activity concludes with a few challenging questions that require students to think critically and analyze geometric properties in real-world contexts. These questions aim to develop students’ ability to apply geometry concepts to practical situations and make connections between theoretical knowledge and real-life scenarios.
In summary, practice A of the geometry activity offers students an opportunity to practice and consolidate their understanding of geometry concepts through a diverse range of questions. By engaging in problem-solving and critical thinking, students can strengthen their geometry skills and develop a deeper understanding of the subject.
Step-by-Step Solutions for Practice A Geometry Questions on Page 269
In Practice A Geometry questions on page 269, students are presented with a variety of geometric problems to solve. These questions cover topics such as angles, lines, polygons, and congruence. To successfully answer these questions, it is important to understand the specific concepts and formulas related to each problem.
One example of a question on page 269 is: “Find the measure of angle A in triangle ABC.” To solve this problem, students can use the angle sum property of triangles, which states that the sum of the angles in a triangle is always equal to 180 degrees. By subtracting the given measures of angles B and C from 180 degrees, students can find the measure of angle A.
Another question may ask students to find the length of a diagonal in a rectangle. To solve this problem, students can use the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two legs. By identifying the legs of the right triangle formed by the diagonal and the sides of the rectangle, students can set up an equation and solve for the length of the diagonal.
It is important for students to carefully read each question, identify the given information, and determine the appropriate formulas or concepts to apply. Additionally, it is helpful to sketch diagrams or use visual aids to better understand the problem and visualize the solution. By following these steps and applying the relevant geometric principles, students can successfully solve the Practice A Geometry questions on page 269.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Practice A Geometry Activity
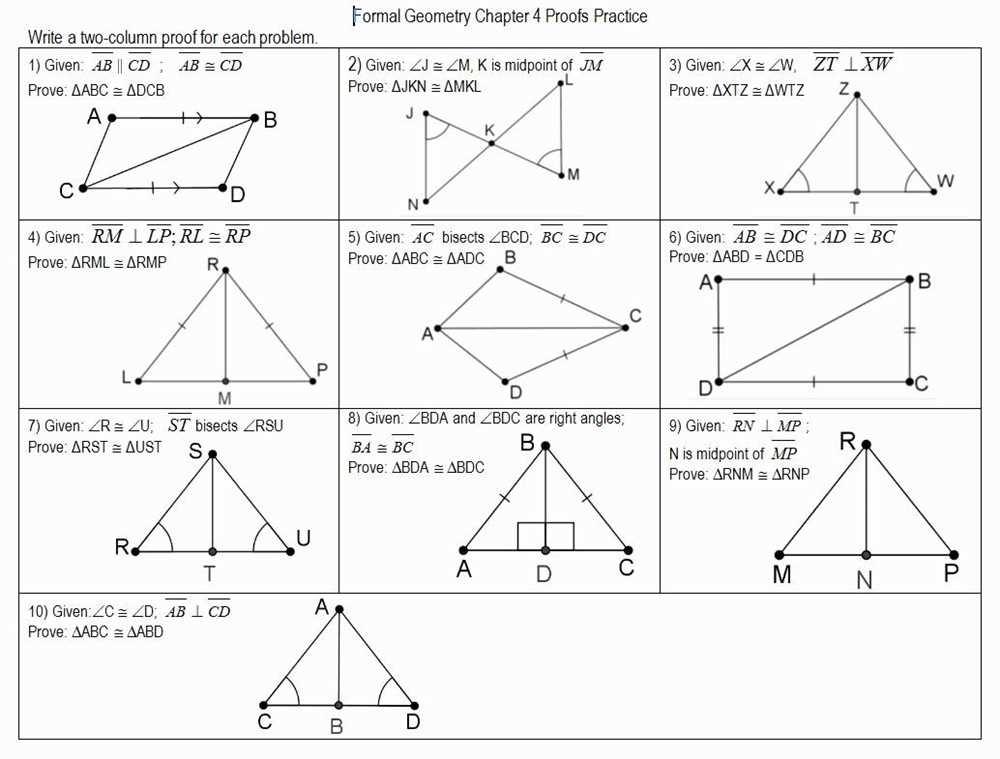
In the practice A geometry activity, there are a few common mistakes that students often make. By identifying and avoiding these mistakes, students can improve their understanding and performance in geometry.
1. Misunderstanding the Problem: One common mistake is misunderstanding the problem given in the activity. Students might misinterpret the provided information or fail to identify the specific question being asked. It is essential to read the problem carefully and take note of all the given information and requirements before attempting to solve it.
2. Misusing Formulas and Relationships: Another mistake students make is misusing formulas and relationships in geometry. Students might incorrectly apply the wrong formula or fail to recognize the relevant relationship between different geometric concepts. It is crucial to review and understand the formulas and relationships before attempting to solve problems.
3. Failing to Show All Steps: Many students make the mistake of not showing all the steps in their solutions. Geometry problems often require logical reasoning and a series of steps to reach the final answer. Failing to show these steps can lead to confusion and make it difficult for others to follow the solution. It is essential to show all the steps and explain the reasoning behind each step.
4. Careless Calculation Errors: Careless calculation errors are another common mistake in geometry. Students might make errors in basic arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Taking the time to double-check calculations and being mindful of potential errors can help avoid these mistakes.
5. Ignoring Units and Labeling: Students often overlook the importance of units and labeling in geometry problems. Forgetting to include units or properly label the given figures can lead to incorrect answers. It is crucial to pay attention to units and label all relevant measurements and figures accurately.
In conclusion, understanding and avoiding these common mistakes in the practice A geometry activity can improve students’ performance and overall understanding of geometry. By being attentive to the problem, correctly using formulas and relationships, showing all steps, avoiding careless calculation errors, and paying attention to units and labeling, students can enhance their problem-solving abilities in geometry.
Tips and Techniques for Solving Practice A Geometry Questions
Geometry can be a challenging subject, but with the right strategies and techniques, you can successfully solve practice questions. Whether you are preparing for a test or simply trying to improve your understanding of geometry, here are some tips to help you navigate through Practice A Geometry questions.
1. Understand the problem: Before you start solving a geometry question, make sure you fully understand the problem statement. Read the question carefully and identify any given information, such as measurements, angles, or relationships between figures. Pay attention to keywords or phrases that might provide clues about the solution.
2. Draw accurate diagrams: Drawing an accurate diagram is crucial in geometry problem-solving. Take your time to sketch the given figures and label any known measurements, angles, or points. Use a ruler or protractor if needed to ensure accuracy. This visual representation will help you visualize the problem and identify any geometric properties or relationships.
3. Apply relevant geometry theorems and formulas: Geometry is built on a foundation of theorems and formulas. Familiarize yourself with key theorems and formulas relevant to the given problem. For example, if the question involves finding angles in a triangle, remember the properties of triangles, such as the angle sum theorem or the triangle inequality theorem. Applying the appropriate theorems and formulas will guide you towards the correct solution.
4. Break down complex problems: If a geometry question seems complex or overwhelming, break it down into smaller, more manageable parts. Identify any subproblems or intermediate steps that can lead you towards the final solution. This step-by-step approach can help simplify the problem and make it easier to solve.
5. Practice using different problem-solving strategies: Geometry problems can often be solved using multiple strategies. Familiarize yourself with different problem-solving techniques, such as using algebraic equations, applying coordinate geometry, or using geometric transformations. Practice using these strategies to develop your problem-solving skills and become more comfortable with different types of geometry questions.
6. Check your answer: After solving a geometry question, always double-check your answer. Make sure that your solution aligns with the given problem statement and any given measurements or relationships. Verify your calculations and recheck your diagram for accuracy. Proofread your work to avoid any calculation errors or simple mistakes. Double-checking will help ensure that you have arrived at the correct solution.
By following these tips and techniques, you can approach Practice A Geometry questions with more confidence and improve your problem-solving skills.
The Importance of Practicing Geometry for Building Problem-solving Skills
Geometry is a fundamental branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, sizes, and properties of figures and spaces. It plays a crucial role in problem-solving, as it teaches students to analyze and reason using logical and spatial thinking. By practicing geometry, students develop critical thinking skills that can be applied to various real-life situations.
One of the key reasons why practicing geometry is essential for building problem-solving skills is that it enhances spatial reasoning abilities. Geometry helps individuals visualize objects in their mind and understand their relationships. This skill is valuable in many careers, such as architecture, engineering, and design, where professionals need to conceptualize and manipulate objects in three dimensions.
Geometry practice also fosters logical reasoning skills. When solving geometric problems, students have to apply deductive reasoning, identify patterns, and make accurate conclusions based on given information. This logical thinking skill set is not only valuable in mathematics but also in other subjects and everyday life. It allows individuals to analyze complex problems, evaluate evidence, and make informed decisions.
Moreover, practicing geometry improves problem-solving skills by promoting perseverance and problem persistence. Geometry involves solving challenging puzzles and proofs that require patience and determination. Students learn to break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps, persist through failures, and find alternative strategies to solve problems. These problem-solving skills are transferable to various domains and are beneficial for overcoming obstacles in both academic and professional settings.
In conclusion
Practicing geometry is crucial for building problem-solving skills. It enhances spatial reasoning, fosters logical thinking, and promotes perseverance. By honing these skills through geometry practice, individuals can become better problem solvers, equipped to tackle challenges in various areas of their lives.
Resources for Additional Practice and Study
When it comes to studying geometry, practice is key. If you find yourself in need of additional resources to help reinforce what you’ve learned or to further challenge yourself, there are several options available. Whether you prefer digital resources, textbooks, or interactive activities, you can find something to suit your learning style.
One convenient option is online practice websites. Websites such as Khan Academy, Mathway, and MathHelp offer a wide range of geometry practice problems and tutorials. You can work through these problems at your own pace, receiving instant feedback and explanations for any mistakes you make. These resources are accessible 24/7, making it easy to fit in some extra practice whenever you have free time.
If you prefer more traditional studying methods, there are also plenty of geometry textbooks and workbooks available. These resources often include a variety of practice problems, guided explanations, and step-by-step solutions. Some popular geometry textbooks include “Geometry: Concepts and Applications” by Glencoe and “Geometry” by McDougal Littell. These textbooks can be used as a supplement to your class materials or as a standalone study resource.
For those who enjoy a hands-on approach, there are also interactive geometry activities and games available. Websites like MathPlayground and Math Warehouse offer a variety of interactive games and puzzles that help reinforce geometry concepts in a fun and engaging way. These activities can be a great way to break up your study routine and make learning geometry more enjoyable.
Remember, the key to mastering geometry is practice, so take advantage of these additional resources to enhance your understanding and skills. Whether you choose to use online practice websites, textbooks, or interactive activities, the important thing is to find a method that works best for you and allows you to consistently practice and review the material. Good luck!