
As the end of the semester approaches, students taking Algebra 2 are gearing up for their final exams. This crucial test encompasses the knowledge acquired throughout the semester and can have a significant impact on a student’s overall grade. To help students prepare, a comprehensive answer key for the Algebra 2 semester 1 final exam review has been devised to ensure mastery of the fundamentals.
Algebra 2 is a branch of mathematics that builds upon the concepts learned in Algebra 1, delving deeper into equations, functions, and mathematical manipulations. It is a critical step in a student’s mathematical journey, serving as a foundation for advanced math courses, including calculus and trigonometry. Therefore, a successful understanding of the material covered in the semester 1 final exam is vital for future success.
The answer key for the Algebra 2 semester 1 final exam review provides students with a valuable resource to gauge their understanding of the material before the actual exam. This comprehensive guide covers various topics, such as linear equations, quadratic functions, polynomials, and rational expressions. By reviewing the answer key, students can identify areas of weakness and focus their studying efforts accordingly.
Algebra 2 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answer Key

In the Algebra 2 Semester 1 Final Exam Review, students were given a variety of questions that covered topics from the first semester of Algebra 2. The answer key provides the correct solutions and explanations for each question, allowing students to check their work and identify any areas where they may need further review.
The answer key is organized by section, with each problem labeled and its solution provided. This allows students to easily navigate to the specific problems they want to review or check, making it a valuable resource for individual study or group review sessions.
Students who use the answer key can compare their answers to the correct solutions and identify any errors or misunderstandings. They can also review the accompanying explanations to better understand the steps and concepts involved in each problem.
The Algebra 2 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answer Key is a comprehensive and reliable resource for students studying Algebra 2. It helps students gauge their understanding of the material and provides them with the opportunity to correct any mistakes before taking the final exam. By using this answer key, students can feel more confident and prepared for their upcoming exam.
Overview
The Algebra 2 semester 1 final exam is a comprehensive test that assesses students’ understanding of various algebraic concepts covered throughout the semester. This exam covers topics such as linear equations, quadratic equations, exponential functions, systems of equations, inequalities, and more.
Students should expect the final exam to consist of a combination of multiple-choice, short answer, and problem-solving questions. The exam is designed to evaluate students’ ability to apply mathematical concepts to real-world situations, as well as their problem-solving skills and critical thinking abilities.
Key Topics Covered:
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Quadratic equations and functions
- Exponential functions and logarithms
- Systems of equations and inequalities
- Polynomials and polynomial functions
- Rational expressions and equations
- Radical and complex numbers
- Sequences and series
Students are encouraged to review their class notes, textbooks, and homework assignments in preparation for the final exam. It is also recommended to practice solving various types of algebraic problems and to seek clarification on any concepts or topics that may still be unclear. With thorough preparation and diligent studying, students can perform well on the Algebra 2 semester 1 final exam.
Simplifying Expressions

In algebra, simplifying expressions involves combining like terms and applying the appropriate rules of operations to reduce the expression to its simplest form. By simplifying an expression, we can make it easier to work with and understand.
One of the first steps in simplifying an expression is to identify and combine like terms. Like terms are terms that have the same variable raised to the same power. For example, in the expression 3x + 2x – 5y + 7x, the terms 3x, 2x, and 7x are like terms because they all have the variable x raised to the power 1. We can combine these terms by adding their coefficients, which gives us 12x. Similarly, the terms -5y can be simplified to -5y.
In addition to combining like terms, we also need to apply the rules of operations to simplify expressions. These rules include the commutative property, associative property, distributive property, and the rules of exponents. The commutative property allows us to change the order of addition or multiplication, while the associative property allows us to group terms together without changing the result.
The distributive property is particularly useful when simplifying expressions that involve multiplication and addition. It states that a(b + c) is equal to ab + ac. For example, in the expression 2(3x + 4y), we can distribute the 2 to both terms inside the parentheses, giving us 6x + 8y.
By simplifying expressions, we can make them easier to evaluate, solve equations involving them, or graph them on a coordinate plane. It is an important skill in algebra that allows us to manipulate and understand mathematical expressions more effectively.
Solving Equations
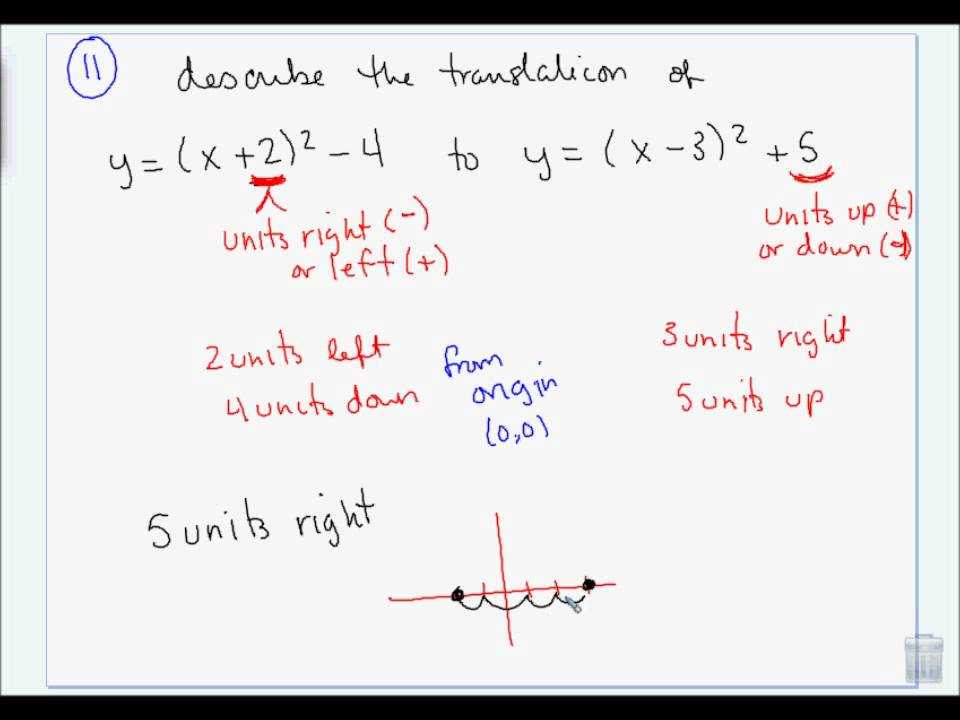
Solving equations is a fundamental skill in Algebra 2. In order to solve an equation, you need to isolate the variable on one side of the equation and find its value. This can be done through a series of steps, including simplifying the equation, combining like terms, and using inverse operations.
When solving equations, it is important to follow the order of operations and perform the same operation on both sides of the equation to maintain balance. This ensures that the equation remains true and that the variable is correctly isolated.
One common type of equation is a linear equation, which has the form y = mx + b. To solve a linear equation, you need to find the value of the variable (usually represented by x) that makes the equation true. This can be done by rearranging the equation and isolating the variable on one side.
Another type of equation is a quadratic equation, which has the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0. Quadratic equations can be solved using a variety of methods, including factoring, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula. These methods allow you to find the values of x that satisfy the equation.
Overall, solving equations is an essential skill in Algebra 2, as it allows you to find the values of variables and solve real-world problems. It requires a strong understanding of algebraic operations and the ability to follow a systematic approach to problem-solving. With practice and perseverance, you can become proficient at solving equations and succeed in your Algebra 2 studies.
Graphing Linear Equations
Graphing linear equations is a fundamental skill in algebra. It involves plotting points on a coordinate plane and connecting them to create a line. Linear equations can be written in the form y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept.
To graph a linear equation, start by identifying the slope and y-intercept. The slope can be determined by looking at the coefficient of x in the equation, while the y-intercept is the value of y when x is equal to 0. Once you have these values, plot the y-intercept on the y-axis and use the slope to find additional points on the line. You can do this by using the equation y = mx + b and substituting different values for x.
- If the slope is positive, the line will rise from left to right.
- If the slope is negative, the line will fall from left to right.
- If the slope is zero, the line will be horizontal.
- If the slope is undefined, the line will be vertical.
Once you have plotted enough points, connect them to form a line. It’s important to extend the line beyond the plotted points to accurately represent the entire line. Additionally, you can use additional tools such as a ruler or a graphing calculator to help you create a straight line.
Graphing linear equations is a useful skill for solving real-world problems and analyzing relationships between variables. It allows us to visually represent mathematical equations and make predictions based on the graphed data. By understanding the concepts and techniques involved in graphing linear equations, you will be better equipped to solve more complex algebraic problems.
Quadratic Functions

A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree 2. It is an important concept in algebra and has many real-world applications. Quadratic functions can be written in the form:
f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c
where a, b, and c are constants. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. Depending on the value of the coefficient a, the parabola can open upwards or downwards. The coefficient a also determines whether the parabola is narrow or wide.
The vertex of a parabola is a point on the graph where it reaches its minimum or maximum value. The x-coordinate of the vertex can be found using the formula:
x = -b/2a
The y-coordinate of the vertex can be found by substituting the x-coordinate into the equation.
To solve quadratic equations, we can use various methods such as factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. Factoring involves finding two binomials that multiply to give the quadratic expression. Completing the square is a method that allows us to rewrite a quadratic equation in a perfect square trinomial form. The quadratic formula is a formula that gives us the roots of a quadratic equation.
- Factoring: If we have a quadratic equation in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, we can factor it into (mx + r)(nx + s) = 0.
- Completing the Square: To solve a quadratic equation of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, we can rewrite it as (x + p)^2 = q.
- Quadratic Formula: The quadratic formula gives the solutions of a quadratic equation in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0 as x = (-b ± √(b^2 – 4ac)) / 2a.
Quadratic functions are used in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics. They help model and analyze real-life situations where different variables are related quadratically. Understanding quadratic functions is essential for solving problems and making predictions based on data.
Exponents and Radicals
Exponents and radicals are important concepts in algebra and are often used in solving equations and simplifying expressions. Understanding how to work with exponents and radicals is crucial for success in algebra and beyond.
Exponents: An exponent is a small number written above and to the right of a base number, indicating how many times the base should be multiplied by itself. For example, in the expression 32, the base is 3 and the exponent is 2. This means that 3 should be multiplied by itself 2 times, resulting in 9. Exponents can also be negative or fractions, representing division or roots, respectively.
Radicals: A radical is a symbol, typically the square root (√) or cube root (3√), that represents the operation of finding the root of a number. For example, the square root of 16 is written as √16 and equals 4, because 4 multiplied by itself equals 16. Radicals can be simplified by finding perfect square or cube factors within the number being rooted.
When working with exponents and radicals, there are several rules and properties that can be applied. These include the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, and simplification rules. These rules allow for the simplification of expressions and the solving of equations involving exponents and radicals.
In conclusion, understanding and mastering exponents and radicals is important for success in algebra. By knowing how to work with these concepts, students can simplify expressions, solve equations, and gain a deeper understanding of mathematical principles. Regular practice and review of these concepts will lead to proficiency and confidence in algebraic calculations.
Systems of Equations
In algebra, a system of equations refers to a set of two or more equations that have common solutions. Solving systems of equations involves finding the values of the variables that satisfy all the equations in the system.
There are three possible scenarios for a system of equations:
- No solution: In this case, the system of equations represents parallel lines that do not intersect. The equations are inconsistent, and there is no common solution.
- One solution: This is when the system has a unique solution, where the lines intersect at a single point. The equations are consistent, and there is only one solution.
- Infinitely many solutions: When the equations in the system represent the same line or overlapping lines, the system is dependent, and there are infinitely many solutions.
To solve systems of equations, various methods can be used:
- Graphing: Plotting the equations on a coordinate plane and visually determining the point of intersection.
- Substitution: Solving one equation for one variable and substituting it into the other equation to solve for the remaining variable.
- Elimination: Adding or subtracting the equations to eliminate one variable and solve for the other.
Systems of equations are widely applicable in various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and biology. They provide a mathematical framework for solving real-world problems that involve multiple unknown quantities.
Understanding systems of equations and the methods to solve them is crucial in algebra and higher-level mathematics. Mastering these concepts can help in problem-solving and analyzing situations with multiple variables.