
In today’s digital age, computers have become an essential tool for both personal and professional use. However, many users are still unfamiliar with the internal components that make these machines work. Understanding the different parts of a computer is crucial for troubleshooting, repairs, and upgrades. That’s where Lab 1-3 testing mode comes in.
Lab 1-3 testing mode is a hands-on training program designed to help individuals identify and understand the internal components of a computer. Through interactive exercises and real-life simulations, participants gain knowledge and practical skills needed to navigate the intricate inner workings of a computer system.
During the course, participants will learn to identify and describe key components such as the motherboard, CPU, RAM, storage devices, and power supply. They will also understand the purpose and function of each component, enabling them to troubleshoot and diagnose hardware issues effectively.
Lab 1-3 testing mode goes beyond theory by providing participants with a chance to examine real computer hardware up close. By dismantling and reassembling computers in a controlled environment, participants experience hands-on learning that reinforces theoretical knowledge and builds confidence in their understanding of computer internals.
Lab 1-3 Testing Mode: Identify Internal Components of a Computer
In Lab 1-3 Testing Mode, students will learn to identify the internal components of a computer. This exercise is crucial for anyone working with computers, as it provides a fundamental understanding of how they function and interact with each other.
During the lab, students will be introduced to various components such as the motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), hard drive, and power supply. They will learn to identify these components and understand their roles in the overall functioning of a computer system.
One of the key components students will focus on is the motherboard. The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer system, and it houses many critical components such as the CPU, RAM slots, expansion slots, and connectors for various peripherals. By learning to identify the motherboard and its components, students will gain a deeper understanding of how a computer system is structured and how its components communicate with each other.
Another important component students will learn about is the central processing unit (CPU). The CPU is often referred to as the “brain” of a computer, as it carries out most of the computations and instructions necessary for the computer to function. Students will be able to identify the CPU on the motherboard and understand its significance in determining the overall performance of a computer.
In addition to the motherboard and CPU, students will also learn about other internal components such as RAM, which is responsible for temporarily storing data that the CPU needs to access quickly, and the hard drive, which stores long-term data and programs. By understanding the functions of these components, students will be better equipped to troubleshoot and upgrade computer systems as needed.
In conclusion, Lab 1-3 Testing Mode provides students with a hands-on opportunity to identify internal components of a computer. By gaining a deeper understanding of how these components work together, students will be better prepared to work with computers and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Overview
The lab 1-3 testing mode is designed to help identify the internal components of a computer. By examining the different parts and their functions, technicians and users can better understand how the computer operates and diagnose any potential issues.
In this lab, participants will learn about the essential components of a computer, including the motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard drive, and power supply. They will also gain knowledge about how these components work together to perform various tasks and processes.
Through hands-on activities, participants will have the opportunity to physically examine and identify each component. They will learn to differentiate between the different types of RAM modules, identify the various ports and connectors on the motherboard, and recognize the different types of hard drives.
By the end of the lab, participants will have a solid understanding of the internal components of a computer and how they contribute to the overall functionality of the system. This knowledge will prove invaluable in troubleshooting and maintaining computer hardware, as well as in making informed decisions about upgrading or replacing components.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer. It is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. The CPU is one of the most important components of a computer system, as it controls all the operations and processes that occur within the system.
The CPU is made up of several components, including the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The control unit is responsible for fetching, decoding, and executing instructions. It is like the conductor of an orchestra, directing the flow of data and instructions within the system. The ALU is responsible for performing arithmetic and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, and comparison. Registers are small storage areas within the CPU that hold data and instructions that are currently being processed.
The CPU also interacts with other components of the computer system, such as the memory and input/output devices. It retrieves data and instructions from the memory, performs operations on them, and then sends the results back to the memory or output devices. The speed and performance of the CPU is measured in terms of clock speed, which indicates how many instructions it can execute per second. A higher clock speed generally means faster processing and better performance.
In summary, the CPU is the central component of a computer system that performs all the processing and calculation tasks. It consists of the control unit, ALU, and registers, and interacts with other components of the system to retrieve data, perform operations, and send results. The clock speed of the CPU determines its processing speed and overall performance.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of computer memory that is used to store data that is actively being used by the computer’s operating system and applications. It is a volatile memory, which means that the data stored in RAM is lost when the computer is powered off or restarted. RAM is an essential component of a computer system and plays a crucial role in its overall performance.
RAM is responsible for temporarily storing data that the computer needs to access quickly. This includes the operating system, application files, and data that is currently being processed. When a computer program is executed, the necessary files and data are loaded into RAM so that the CPU can quickly retrieve and process them. The more RAM a computer has, the more data it can store and access at any given time, which can improve overall system performance.
RAM is made up of individual memory cells, each of which can store a certain amount of data. These cells are organized into rows and columns, which form a grid-like structure. Each cell is made up of a capacitor and a transistor, which allow it to store a single bit of information. The capacitors hold a charge to represent a binary value of 0 or 1, and the transistors allow the data stored in the cells to be read or written by the computer’s CPU.
RAM is available in different capacities, typically measured in gigabytes (GB). The amount of RAM a computer needs depends on the operating system, applications, and tasks that will be run. For example, a computer used for basic tasks such as web browsing and word processing may only need 4GB of RAM, while a computer used for video editing or gaming may require 16GB or more of RAM. It is important to choose an appropriate amount of RAM for your specific needs in order to ensure optimal performance.
Overall, Random Access Memory (RAM) is a critical component of a computer system. It provides temporary storage for data that is actively being used, allowing the CPU to quickly access and process information. The amount of RAM a computer has can significantly impact its performance, so it is important to consider your specific needs when determining how much RAM is necessary for your system.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)

A Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a non-volatile storage device that is commonly used in computers and other electronic devices to store and retrieve large amounts of data. It is one of the essential components of a computer system and is responsible for storing the operating system, software applications, and user data.
The HDD consists of one or more rotating disks called platters, which are coated with a magnetic material. These platters are mounted on a spindle and can spin at high speeds, typically ranging from 5,400 to 15,000 revolutions per minute (RPM). Each platter has read/write heads that move across its surface to read or write data on concentric tracks.
The capacity of an HDD is determined by the number of platters it has and the areal density of the data that can be stored on each platter. Modern HDDs can store terabytes (TB) of data, making them suitable for storing large files such as high-definition videos, games, and multimedia content.
Key Features of Hard Disk Drives:
- Storage Capacity: HDDs offer a large storage capacity, ranging from several gigabytes (GB) to several terabytes (TB).
- Speed: The rotational speed (RPM) of the platters affects the performance of the HDD, with higher speeds allowing for faster data access.
- Durability: HDDs are prone to mechanical failures due to their moving parts, but advancements in technology have greatly improved their reliability.
- Cost: HDDs are generally more cost-effective compared to other storage technologies, such as Solid-State Drives (SSDs).
- Compatibility: HDDs can be easily installed and used with most computer systems and are compatible with various operating systems.
In conclusion, the Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a crucial internal component of a computer system, providing large storage capacity, long-term data retention, and compatibility with different hardware and software configurations. Despite the rise of alternative storage technologies, HDDs remain widely used for their affordability and proven reliability.
Motherboard
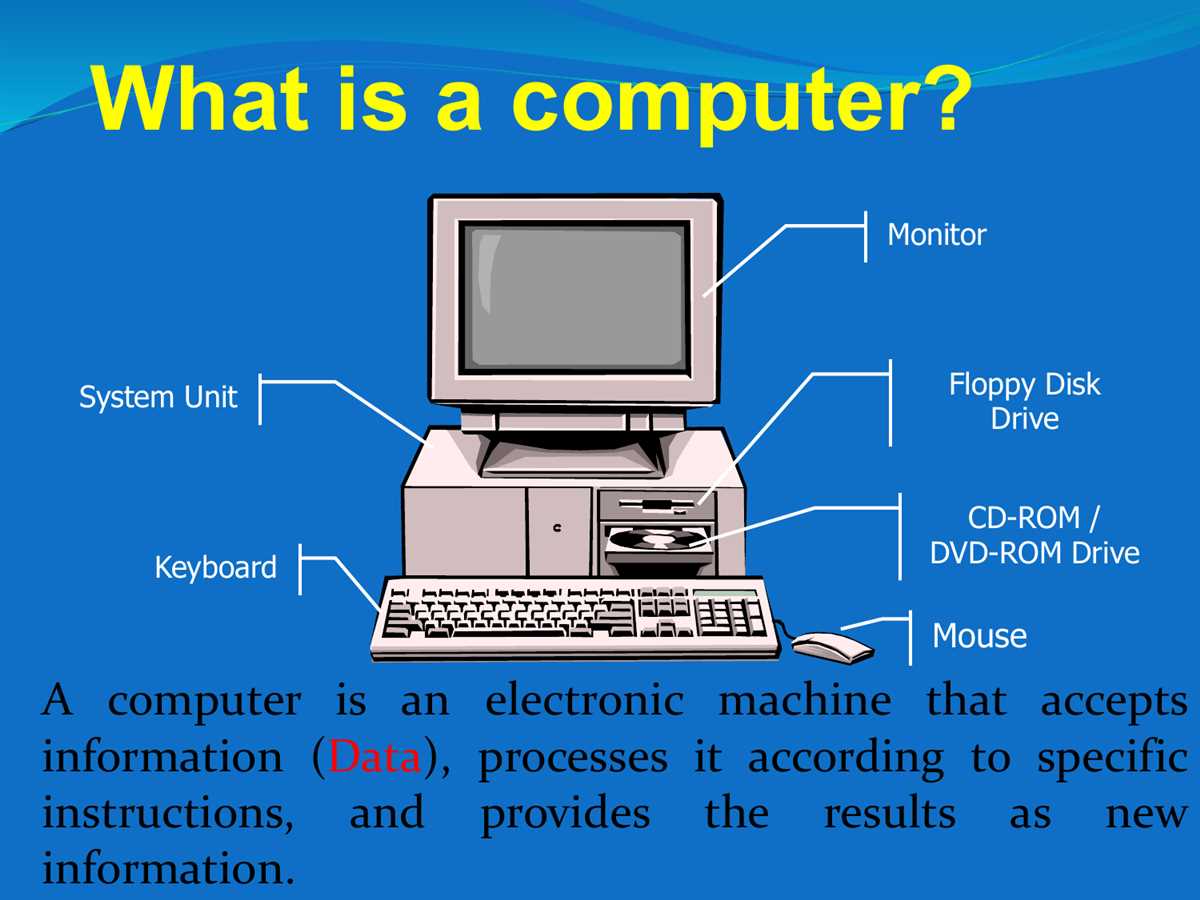
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer. It is also known as the logic board or system board. The motherboard connects and allows communication between various internal components, such as the CPU, memory, storage devices, and expansion cards.
Components:
- CPU Socket: The CPU socket is where the processor is installed. It provides a mechanical and electrical connection between the CPU and the motherboard.
- Memory Slots: The memory slots are where the RAM modules are inserted. The motherboard can have multiple memory slots, allowing for expansion of memory capacity.
- Expansion Slots: The expansion slots are used to install expansion cards, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards. These cards enhance the functionality of the computer.
- Storage Connectors: The motherboard has various connectors for storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives. These connectors include SATA ports and M.2 slots.
- Power Connectors: The power connectors on the motherboard provide power to the various components. These include the CPU power connector, ATX power connector, and auxiliary power connectors.
- BIOS Chip: The BIOS chip stores the basic input/output system, which contains the firmware that initializes the computer hardware during the boot process.
- Chipset: The chipset is a set of integrated circuits that provide communication between the CPU, memory, and peripheral devices. It includes the Northbridge and Southbridge chips.
The motherboard is an essential component of a computer and determines the compatibility and performance of other components. It plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and stability of the system.
Power Supply Unit (PSU)

A Power Supply Unit (PSU) is a crucial component of a computer that is responsible for converting the electrical power from an outlet into usable power for the internal components of the computer. It is often overlooked, but it plays a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning of a computer system.
The PSU connects directly to the motherboard and other internal components such as the hard drive, graphics card, and CPU. It supplies them with the necessary power to operate. A good PSU provides a steady and reliable flow of power, which is essential for the stability and performance of the computer.
Key Components of a PSU
- Transformer: The transformer in the PSU is responsible for converting the high voltage from the power outlet into lower voltages that are suitable for the internal components.
- Rectifier: The rectifier converts the alternating current (AC) from the power outlet into direct current (DC) that the computer components can use.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store electrical energy and help prevent voltage fluctuations, maintaining a steady supply of power.
- Fan: The PSU has a fan to regulate its temperature and prevent overheating. It ensures proper airflow to keep the PSU cool.
Conclusion
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is an essential component of a computer that converts electrical power from an outlet into usable power for the internal components. It ensures a stable and reliable supply of power, which is crucial for the proper functioning and performance of a computer system. Understanding the components of a PSU and their role can help diagnose and troubleshoot power-related issues in a computer.