Snowflakes are intricate formations of ice crystals that fall from the sky during cold weather, delighting both children and adults alike. Each snowflake is unique, with its own distinct pattern and shape. In order to better understand and classify these beautiful and delicate structures, scientists have developed a classification system known as the dichotomous key.
A dichotomous key is a tool used by scientists to help identify and classify organisms or objects based on their characteristics. It consists of a series of questions or statements that lead to further questions, ultimately leading to the identification of the organism or object in question. In the case of snowflakes, the dichotomous key helps us categorize them based on their structural features.
The classification dichotomous key of snowflakes consists of a set of questions that focus on various aspects of their structure, such as the number and shape of branches, the presence of elaborate details, and the overall symmetry of the snowflake. By answering these questions and following the predetermined pathway, we can identify the specific type of snowflake we are observing.
The answer key for the classification dichotomous key of snowflakes provides a guide to help identify and classify the different types of snowflakes. It lists the possible characteristics and features that snowflakes may exhibit and provides the corresponding classification. This allows scientists and enthusiasts alike to accurately identify and appreciate the unique beauty of each snowflake they encounter.
Classification dichotomous key of snowflakes: Answer Key
This answer key provides a comprehensive classification of snowflakes using a dichotomous key. The classification is based on the unique features and characteristics of each snowflake, allowing for easy identification and categorization.
Key:
- 1a: Snowflake has six branches
- 1b: Snowflake has more than six branches
- 2a: Snowflake branches are all equal in length
- 2b: Snowflake branches are not all equal in length
- 3a: Snowflake branches are all patterned with smaller branches
- 3b: Snowflake branches are not patterned with smaller branches
- 4a: Snowflake branches are symmetrical
- 4b: Snowflake branches are not symmetrical
| Snowflake Category | Snowflake Description |
|---|---|
| Category 1 | Snowflakes with six branches and all equal in length. |
| Category 2 | Snowflakes with more than six branches and not all equal in length. |
| Category 3 | Snowflakes with six branches, all equal in length, and patterned with smaller branches. |
| Category 4 | Snowflakes with more than six branches, not all equal in length, and patterned with smaller branches. |
| Category 5 | Snowflakes with six branches, all equal in length, patterned with smaller branches, and symmetrical. |
| Category 6 | Snowflakes with more than six branches, not all equal in length, patterned with smaller branches, and symmetrical. |
| Category 7 | Snowflakes with six branches, all equal in length, patterned with smaller branches, symmetrical, and with unique features or characteristics. |
| Category 8 | Snowflakes with more than six branches, not all equal in length, patterned with smaller branches, symmetrical, and with unique features or characteristics. |
This classification dichotomous key of snowflakes answer key allows for easy identification and categorization of snowflakes based on their distinct features. By following the series of choices in the key, one can determine the category and description of a snowflake, providing a deeper understanding of the variety and complexity of these beautiful ice crystals.
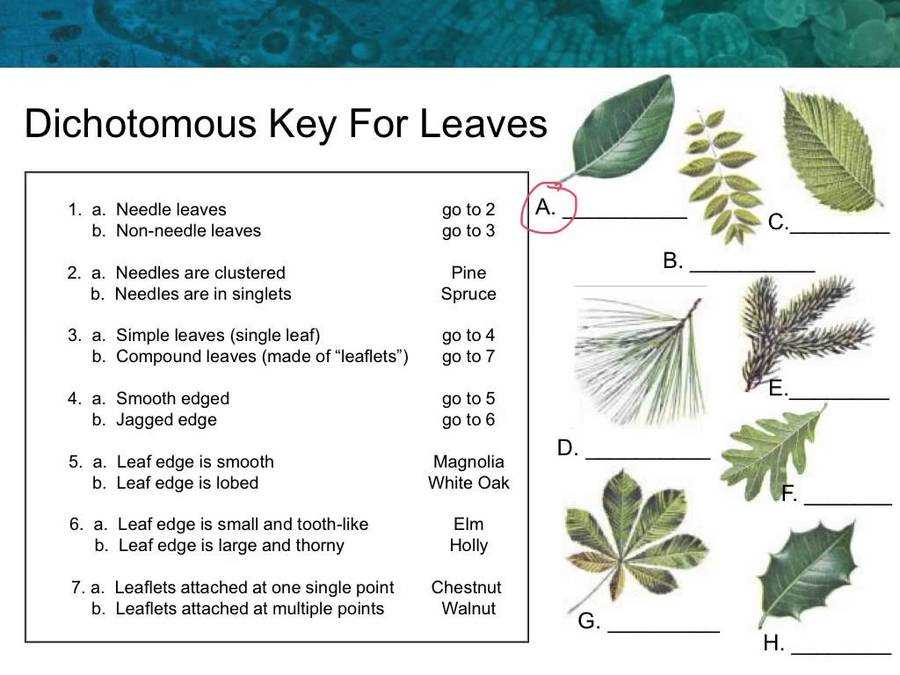
What is a Dichotomous Key?
A dichotomous key is a tool used by scientists to identify and classify organisms or objects based on their characteristics. It is a methodical and systematic approach that relies on a series of paired statements or questions, each with two possible answers, to narrow down the possibilities and determine the correct identification.
The key begins with a broad, general question or statement that applies to the entire group being classified. As the key progresses, subsequent questions or statements become more specific, allowing the user to eliminate certain options and move closer to the correct identification. Each answer leads to another set of paired statements until a final identification is achieved.
In the context of the classification dichotomous key of snowflakes, the key would present a series of statements or questions related to the physical characteristics of the snowflakes. These characteristics could include the shape of the snowflake, the number and arrangement of branches, the presence or absence of facets, and other distinct features. By answering the questions or statements, users would be able to classify the snowflakes into different categories or species.
A well-constructed dichotomous key provides clear and unambiguous choices, ensuring that users can accurately identify the object in question. It also allows for flexibility and accommodation of unique or rare variations within a group. Furthermore, dichotomous keys are often presented in a tabular or branching format, making them easy to follow and navigate.
Overall, a dichotomous key is a valuable tool in scientific classification and identification, helping researchers and enthusiasts alike to better understand and appreciate the diversity and complexity of the natural world.
The Importance of Classification in Snowflakes
The classification of snowflakes is of great importance in the field of meteorology and atmospheric science. By identifying and categorizing different types of snowflakes, scientists can better understand the conditions under which they form and the processes that affect their growth and development.
Classification allows scientists to create a standardized system for describing and comparing snowflake shapes and structures. This systematic approach is essential for communication and research purposes. It enables scientists to share data, compare findings, and collaborate on experiments, ultimately advancing our knowledge of snowflake formation and the factors that influence it.
Through classification, scientists can determine the influence of temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors on snowflake morphology. By observing and analyzing the characteristics of different types of snowflakes, researchers can gain insights into the intricate processes that occur within clouds and during the freezing of water vapor.
Classification also plays a crucial role in forecasting and predicting weather conditions associated with snowfall. By examining the shapes and sizes of snowflakes in different regions, meteorologists can infer the temperature and moisture profiles of the atmosphere at different altitudes. This valuable information helps in determining the likelihood and intensity of snowfall, aiding in the preparation and response to winter weather events.
Furthermore, studying the classification of snowflakes contributes to our understanding of climate change and its potential impact on snowfall patterns. By collecting data on snowflake structures over time, scientists can identify trends and anomalies that may be linked to broader climatic patterns. This knowledge can contribute to the development of more accurate climate models and predictions.
In conclusion,
the classification of snowflakes plays a crucial role in the fields of meteorology and atmospheric science. It enables scientists to better understand snowflake formation, predict weather conditions, and study climate change. By organizing and categorizing snowflakes, scientists can unlock valuable insights into the processes that shape our winter weather.
Characteristics Used in the Classification Dichotomous Key
The classification dichotomous key is a tool used to categorize and identify snowflakes based on their characteristics. These characteristics are used to create a series of choices or questions, each with two possible answers, that ultimately lead to the correct identification of a snowflake.
1. Shape: One of the main characteristics used in the classification dichotomous key is the shape of the snowflake. Snowflakes can have various shapes, such as dendrite, needle, plate, column, or irregular. The shape can be determined by examining the symmetry and structure of the snowflake.
2. Size: Another important characteristic used in the classification dichotomous key is the size of the snowflake. Snowflakes can range in size from tiny crystals to large flakes. The size can be measured by comparing the diameter of the snowflake to known standards.
3. Branching pattern: The branching pattern of the snowflake’s arms is also considered in the classification dichotomous key. This characteristic refers to the arrangement and structure of the branches that extend from the main arms of the snowflake. The branching pattern can be classified as simple, complex, or dendritic.
4. Surface texture: The surface texture of the snowflake is another characteristic used in the classification dichotomous key. This refers to the patterns and textures that are present on the surface of the snowflake. It can be smooth, rough, or have specific indentations or protrusions.
5. Transparency: The transparency of the snowflake is also considered in the classification dichotomous key. This refers to the ability of light to pass through the snowflake. Snowflakes can be transparent, translucent, or opaque, depending on the structure and density of the ice crystals.
6. Melting point: The melting point of the snowflake is a characteristic used in the classification dichotomous key when considering temperature and meteorological factors. Different types of snowflakes have different melting points, and this can be determined by observing how quickly the snowflake melts when exposed to heat sources.
Overall, these characteristics provide a systematic approach to classify and identify different types of snowflakes using a classification dichotomous key. By considering the shape, size, branching pattern, surface texture, transparency, and melting point of a snowflake, scientists and enthusiasts can accurately identify and categorize the beautiful and unique world of snowflakes.
Steps to Identify Snowflakes Using the Classification Dichotomous Key
Snowflakes are unique and complex crystalline structures that form when water vapor freezes in the atmosphere. Each snowflake has its own intricate pattern and shape, making them fascinating to observe and study. To identify different types of snowflakes, scientists and enthusiasts use a classification dichotomous key. This key is a tool that helps in the identification process by asking a series of yes or no questions about the characteristics of the snowflake.
Step 1: Observe the Snowflake
The first step in using the classification dichotomous key is to carefully observe the snowflake. Pay attention to its overall shape, the number of branches, and the presence of any distinct patterns or features. These initial observations will help in determining which set of questions to start with in the key.
Step 2: Start with the Appropriate Question Set
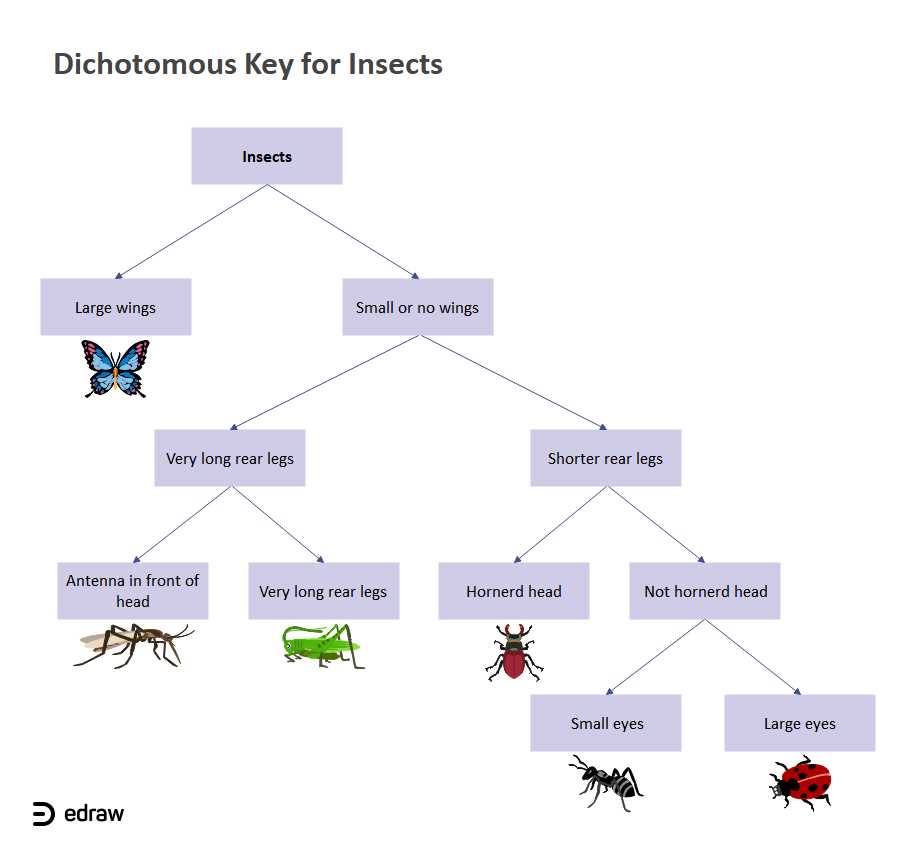
Based on the observations from step 1, determine the appropriate question set to start with in the dichotomous key. The key typically has different branches that correspond to specific characteristics of the snowflake. For example, one branch may focus on the presence or absence of a central core, while another may focus on the number of branches.
Example:
- If the snowflake has a central core, proceed to question set A.
- If the snowflake does not have a central core, proceed to question set B.
Step 3: Answer the Questions
Read each question in the selected question set and answer it based on the characteristics observed in the snowflake. Each question will have two possible answers, usually represented as “yes” or “no.” Make a note of the chosen answer and proceed to the next question in the set.
Step 4: Follow the Key’s Path

As you proceed through the question sets, continue following the key’s path based on your answers. Each question set will lead to the next set of questions, narrowing down the possible options for the snowflake’s classification.
Step 5: Reach a Classification
After answering all the questions in the dichotomous key, you will eventually reach a classification for the snowflake based on your answers. The classification will identify the specific type of snowflake, considering its shape, symmetry, and other distinguishing features.
Using a classification dichotomous key is an effective way to identify different types of snowflakes. It provides a systematic and organized approach, allowing for accurate and consistent identification. By following these steps and carefully observing the characteristics of the snowflake, anyone can become proficient in identifying these beautiful natural formations.
Common Types of Snowflakes Based on Classification
Snowflakes are intricate and beautiful ice crystals that form in the clouds when water vapor freezes. Despite their delicate appearance, snowflakes can actually be classified into different types based on their shape and structure. Understanding the different types of snowflakes can help us appreciate the diversity and uniqueness of each snowfall.
1. Stellar Dendrites: Stellar dendrites are the most common and recognizable type of snowflake. They have a classic six-fold symmetry, with intricate branches extending in different directions. Stellar dendrites are flat and often have a feathery or fern-like appearance. Due to their broad branches, they can accumulate easily and create fluffy, powdery snow.
2. Plate or Fern-Like Snowflakes: Plate or fern-like snowflakes are flat and thin, with branching arms extending from a central point. They can have a hexagonal or irregular shape, and their arms can be simple or complex. These snowflakes are often associated with colder temperatures and can form when there is high humidity.
3. Needles or Column Snowflakes: Needles or column snowflakes are long and cylindrical in shape. They can be thin or thick and may have a hexagonal or prismatic structure. Column snowflakes are often found in dry, cool conditions, and they can form in high concentrations, creating a powdery snowfall.
4. Bullet or Columnar Plates: Bullet or columnar plates are similar to column snowflakes but have a flatter, plate-like shape. They can have regular or irregular edges and are often associated with colder temperatures. Bullet snowflakes can stack upon each other and form compact, dense snow.
5. Irregular Snowflakes: Irregular snowflakes are a catch-all category for snowflakes that do not fit into any specific shape. They can have a variety of forms and structures, often resulting from complex atmospheric conditions. These snowflakes can be jagged, asymmetrical, or have multiple branches.
Overall, the classification of snowflakes provides a framework for studying and appreciating the different shapes and structures that snow can take. Each snowflake is unique and offers a glimpse into the wondrous complexity of nature’s frozen art.
Applications of Snowflake Classification
The classification of snowflakes plays a vital role in various fields and industries. It provides useful information for meteorologists, scientists, and even artists. Here are some of the applications of snowflake classification:
- Weather Forecasting: Understanding the structure and shape of snowflakes helps meteorologists in predicting and studying weather patterns. Different snowflake types may indicate specific atmospheric conditions, such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the formation of snow.
- Winter Sports and Recreation: Snowflake classification can be applied in winter sports and recreation activities. For example, ski resorts can use the information to determine the quality of snow for skiing or snowboarding. Different types of snowflakes may result in varying snow textures, which can influence the overall experience for outdoor enthusiasts.
- Climate Research: The classification of snowflakes provides valuable data for climate researchers. By analyzing the composition and structure of snowflakes, scientists can gain insights into long-term climate changes and study the impact of global warming on snowfall patterns. This information contributes to a better understanding of our changing environment.
- Art and Photography: Snowflake classification also has artistic applications. Photographers, artists, and enthusiasts capture and showcase the intricate beauty of snowflakes. By understanding the different types of snowflakes, artists can depict their unique shapes and structures, creating captivating visual representations of wintertime.
In conclusion, the classification of snowflakes serves as a valuable tool in various fields. From weather forecasting to climate research and artistic endeavors, understanding the different types of snowflakes allows us to appreciate their beauty, predict weather patterns, and gain insights into our changing climate.