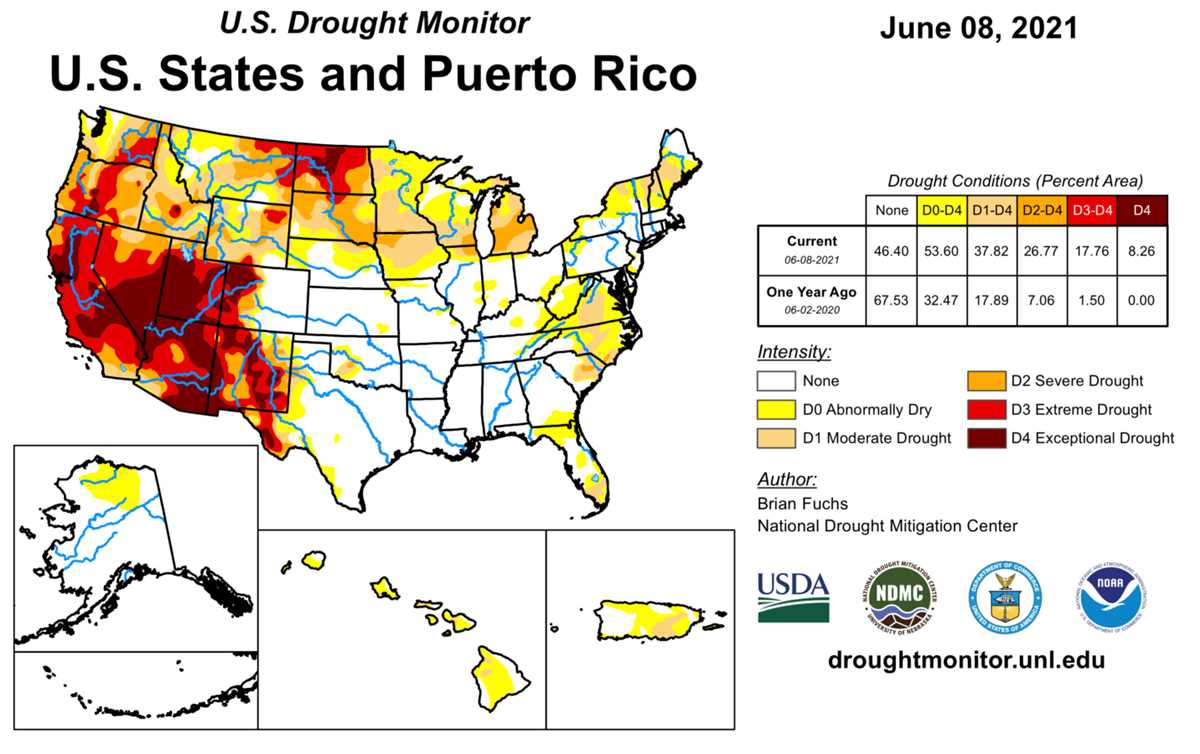
Climate change is a pressing issue that has been impacting our planet in various ways. One of the most noticeable effects is the increase in drought conditions around the world. Droughts have severe consequences on both the environment and human populations, leading to crop failures, water scarcity, and displacement of communities.
In this excerpt from the ‘On Drought Conditions’ answer key, we will explore some of the key factors contributing to droughts and their implications. It is vital to understand these factors to effectively address and mitigate the impacts of droughts.
One of the primary causes of drought conditions is the imbalance in the water cycle. With rising global temperatures, evaporation rates increase, leading to more water vapor in the atmosphere. However, this excess vapor does not always manifest as rainfall, creating dry conditions and exacerbating droughts.
Furthermore, deforestation and land degradation play a significant role in drought formation. Trees and vegetation act as natural water reservoirs, absorbing and retaining rainfall. When forests are cleared, these crucial water-holding structures disappear, leading to reduced water availability in the soil and contributing to droughts.
Understanding the causes and effects of drought conditions is essential for implementing effective strategies to mitigate their impacts. By addressing climate change, proper land management practices, and promoting water conservation, we can work towards safeguarding our planet and our future generations from the devastating effects of droughts.
The Definition of Drought
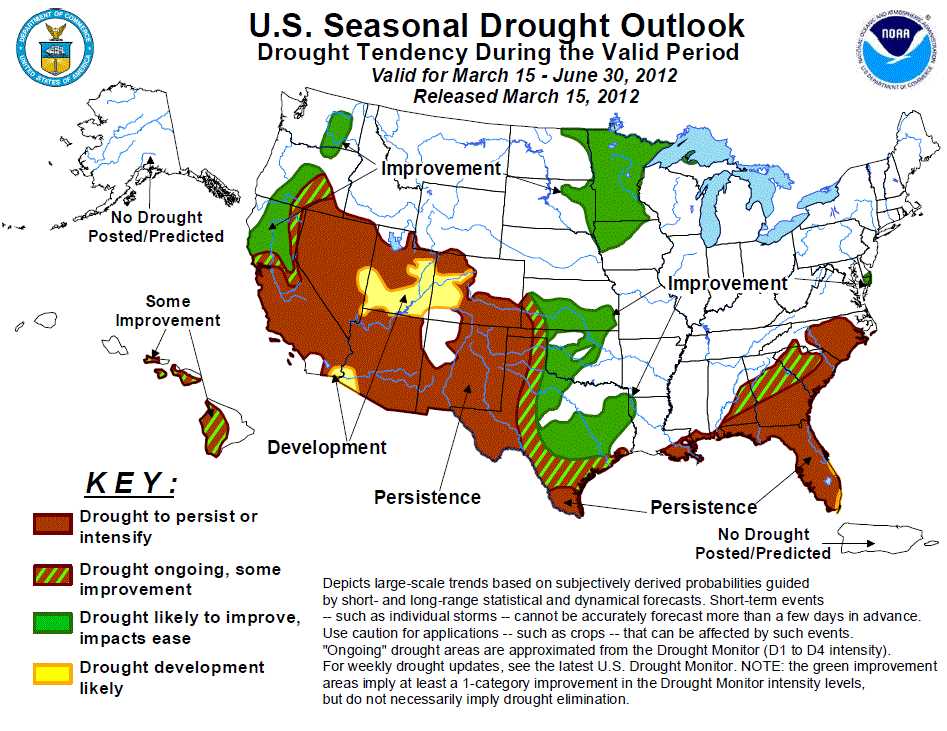
Drought is a natural disaster that occurs when there is a prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall in a particular region, resulting in a shortage of water supply for human, animal, and plant life. It is characterized by a lack of precipitation, which leads to a depletion of water resources and an imbalance in the water cycle. Droughts can have significant impacts on agriculture, ecosystems, and overall socio-economic stability.
There are various types of drought, each with its own characteristics and impacts. Meteorological drought refers to a deficit in precipitation over a certain period of time, while agricultural drought focuses on the lack of moisture in the soil and its effect on crop production. Hydrological drought relates to the reduced levels of water in rivers, lakes, and groundwater, while socio-economic drought refers to the impact of water scarcity on communities and economies.
The severity of a drought is measured by its duration, intensity, and spatial extent. It can range from mild, short-term droughts that have minimal effects to severe and prolonged droughts that cause extensive damage to ecosystems and human activities. Droughts can occur in any part of the world, but they are particularly common in arid and semi-arid regions where water resources are already limited. Climate change is also exacerbating drought conditions in many areas, as rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns contribute to water scarcity.
Mitigating the effects of drought requires proactive measures such as water conservation, implementing drought-resistant agricultural practices, and developing infrastructure for water storage and distribution. Early warning systems and effective drought management strategies are essential for minimizing the impacts on communities and ecosystems. Additionally, raising awareness about the importance of water conservation and sustainable water management is crucial in preventing future drought crises.
In conclusion, drought is a natural hazard that poses significant challenges to human societies and ecosystems. Understanding its definition, causes, and impacts is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its effects and ensure the resilience of water resources in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Causes of Drought

Drought is a natural disaster that occurs when there is a prolonged period of below-average precipitation in a particular region. Droughts can have devastating effects on agriculture, water supply, and the environment. Understanding the causes of drought is crucial for effective mitigation and management strategies.
1. Climate Variability: Climate variability plays a significant role in causing droughts. Natural climate patterns such as El Niño and La Niña can lead to changes in precipitation patterns, leading to drought conditions. The interaction between the atmosphere and ocean currents affects rainfall distribution and can result in prolonged dry spells.
2. High Pressure Systems: High pressure systems can cause drought by preventing the formation of clouds and inhibiting rainfall. When a high-pressure system stagnates over an area for an extended period, it can block moisture-laden air from reaching the region, resulting in dry conditions.
3. Land and Vegetation Changes: Human activities such as deforestation and overgrazing can alter the natural landscape and vegetation cover, leading to increased evaporation and reduced moisture retention in the soil. These changes can exacerbate drought conditions and make the region more susceptible to water scarcity.
4. Climate Change: The warming of the Earth’s climate due to human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, can contribute to the occurrence and severity of droughts. Climate change can alter precipitation patterns, increase evaporation rates, and lead to more frequent and intense heatwaves, all of which can exacerbate drought conditions.
5. Water Mismanagement: Inefficient water management practices, including over-extraction of groundwater and unsustainable irrigation techniques, can deplete water sources and accelerate the onset of drought. Poor water resource management can exacerbate the impacts of natural climate variability and diminish the region’s resilience to drought conditions.
To effectively combat drought, it is essential to address these underlying causes and adopt sustainable water management practices. Strategies such as water conservation, improved irrigation techniques, reforestation, and climate change mitigation efforts can play a crucial role in mitigating the impacts of drought and ensuring long-term water security.
Effects of Drought
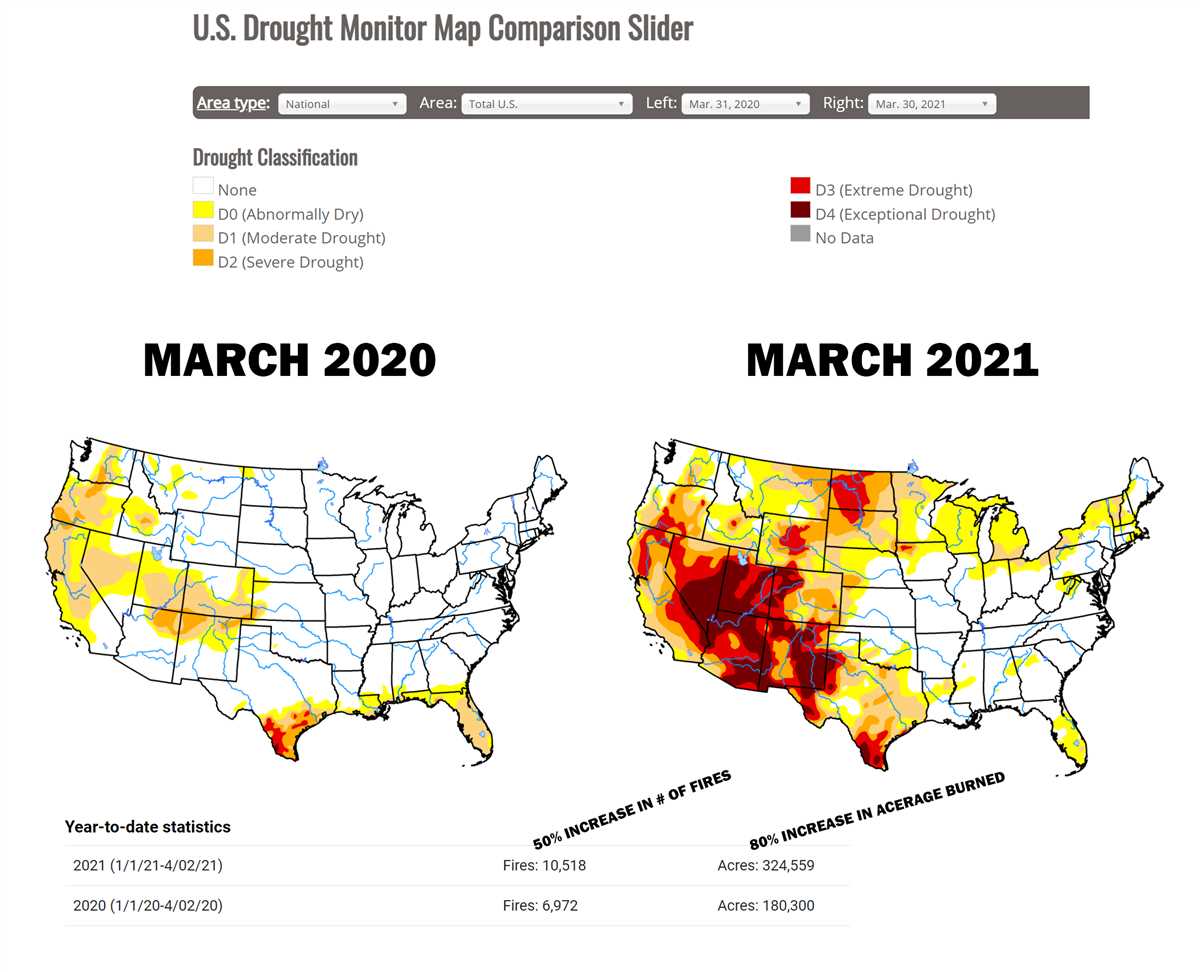
The effects of drought can be far-reaching and have significant impacts on various aspects of ecosystems and human lives. In ecosystems, drought can lead to reduced plant productivity, increased plant mortality, and changes in species composition. Drought can also disrupt the balance of predator-prey relationships and alter the overall biodiversity of an area. Additionally, the lack of water can cause water bodies to dry up, leading to the loss of aquatic habitats and affecting the survival of aquatic organisms.
Furthermore, drought can have severe consequences for agriculture and food production. Without sufficient water, crops may fail or yield significantly less, leading to reduced food availability and rising food prices. Livestock may also suffer from lack of water and forage, resulting in decreased productivity and potential loss of animals. In areas heavily reliant on agriculture, drought can lead to economic hardships and food insecurity for local communities.
In addition to environmental and agricultural impacts, drought can also have social and economic consequences. Water scarcity can disrupt daily life, with rationing and restrictions on water use becoming necessary. This can affect people’s ability to carry out basic activities such as cooking, cleaning, and personal hygiene. Moreover, drought can lead to unemployment and migration as industries that rely on water, such as manufacturing and tourism, are affected. Overall, drought can have wide-ranging effects on ecosystems, agriculture, and societies, highlighting the importance of proactively addressing and mitigating its impacts.
Measures to Prevent Drought
Given the devastating impacts that drought can have on communities, agriculture, and the environment, it is crucial to implement proactive measures to prevent drought conditions from occurring or mitigate their effects. Here are some key strategies that can be employed:
- Water Conservation: One of the most effective ways to prevent drought is by implementing water conservation measures. This includes promoting water-saving practices such as using efficient irrigation systems, fixing leaks, and encouraging individuals and industries to reduce their water consumption.
- Water Recycling: Another important measure is to invest in water recycling infrastructure. By treating and reusing wastewater for non-potable purposes such as irrigation or industrial processes, communities can reduce their reliance on freshwater sources, thus preserving scarce water resources.
- Improved Agricultural Practices: Agriculture is a major consumer of water resources, so implementing sustainable farming techniques can help prevent drought. This includes promoting precision agriculture, which optimizes water usage through advanced technologies, and adopting drought-resistant crops that require less water to grow.
- Forest Management: Managing and preserving forests is crucial for preventing drought. Healthy forests act as natural water reservoirs, absorbing rainfall and releasing it slowly over time. Implementing forest conservation practices, such as preventing deforestation and promoting reforestation, can help maintain healthy ecosystems and prevent drought conditions.
- Water Infrastructure Development: Investing in robust water infrastructure is essential for managing water resources effectively. This includes building dams, reservoirs, and water storage facilities to capture and store water during periods of abundant rainfall for use during dry spells. It also involves improving the efficiency of water distribution systems to minimize losses due to leaks.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting education and awareness about the importance of water conservation and drought prevention is crucial. This can be done through public campaigns, school programs, and community engagement initiatives to encourage individuals, businesses, and policymakers to take action and make informed decisions regarding water usage.
By implementing these measures and adopting a holistic approach to drought prevention, communities can significantly reduce the risk and impact of drought conditions, ensuring the availability of sufficient water resources for both current and future generations.
Adapting to Drought Conditions
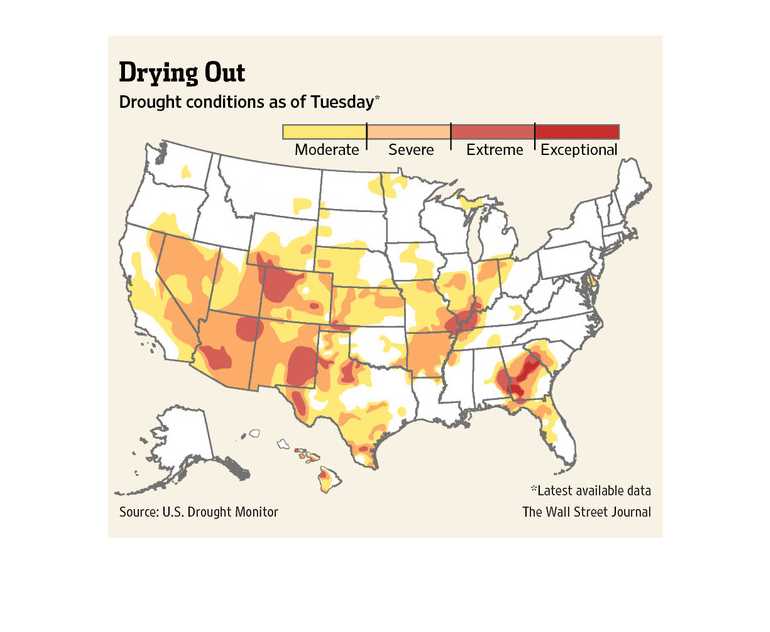
The growing threat of drought conditions around the world has forced communities, farmers, and policymakers to find innovative ways to adapt and mitigate the impacts of these water shortages. With the increasing frequency and severity of droughts, it has become crucial to develop strategies that promote water conservation, efficient water management, and sustainable agricultural practices.
Conserving water
- Implementing water-saving technologies such as low-flow faucets and toilets can significantly reduce household water consumption.
- Encouraging the use of rainwater harvesting systems and greywater recycling can help reduce dependence on freshwater sources.
- Promoting water-efficient landscaping practices, such as drip irrigation and native plantings, can minimize water waste.
- Establishing water conservation programs that educate the public on the importance of water conservation and provide incentives for water-saving behaviors.
Improving water management
- Developing comprehensive water management plans that consider the needs of various sectors, including agriculture, industry, and urban areas.
- Investing in infrastructure projects that improve water storage, distribution, and treatment systems.
- Implementing effective water pricing mechanisms that encourage responsible water use and discourage wasteful practices.
- Encouraging the use of water-efficient technologies in industries and promoting water audits to identify areas of improvement.
Sustainable agricultural practices
- Promoting the use of drought-resistant crop varieties and cultivars that require less water.
- Implementing precision irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and controlled-release systems, to reduce water waste in agriculture.
- Adopting soil conservation practices, such as mulching and conservation tillage, to improve water retention and prevent soil erosion.
- Encouraging farmers to diversify their crops and adopt agroforestry practices, which can help create microclimates and reduce water stress.
By implementing these strategies and initiatives, communities and individuals can adapt to drought conditions, reduce water consumption, and ensure the long-term sustainability of water resources. It is crucial for governments, businesses, and individuals to work together to address the challenges posed by drought and secure a future with adequate water supplies.
The Importance of Drought Preparedness
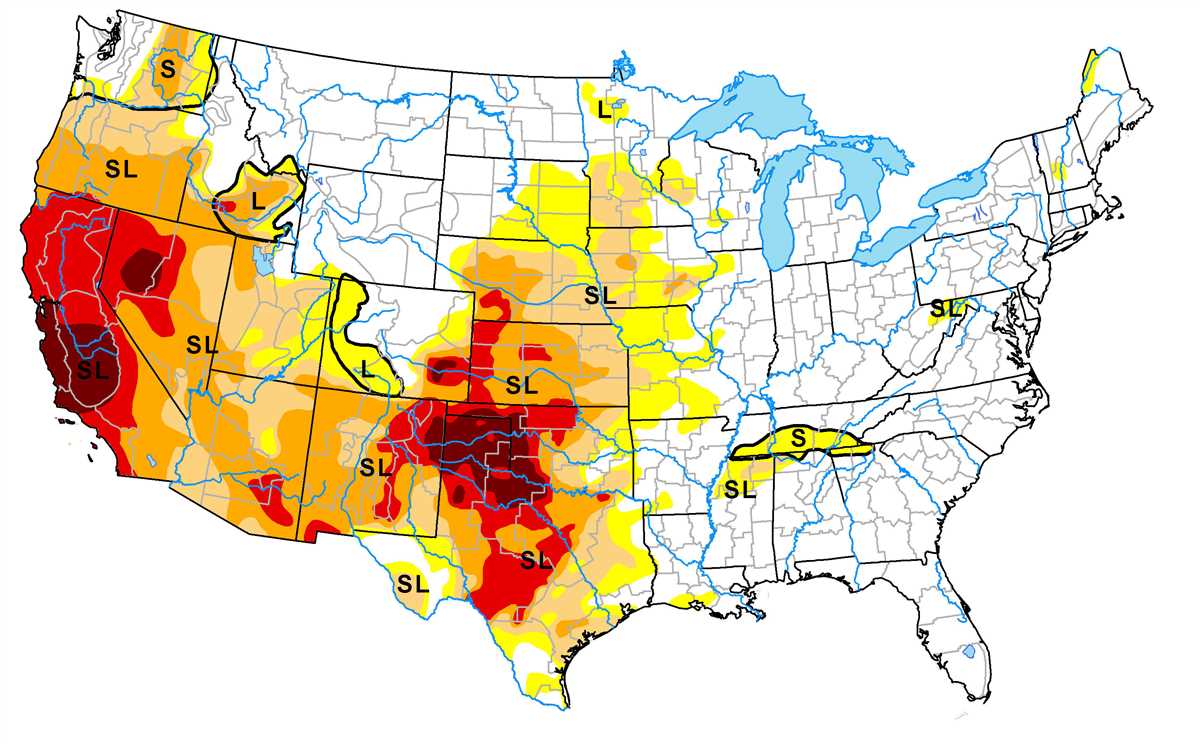
Droughts have become increasingly common in many regions around the world, and their impact on communities and ecosystems cannot be underestimated. It is crucial for individuals, communities, and governments to prioritize drought preparedness in order to mitigate the negative effects and ensure the well-being of both human and natural systems.
Drought preparedness involves implementing strategies and measures that aim to reduce vulnerability to drought and minimize its impacts. These measures can include:
- Developing and implementing water conservation plans
- Investing in water storage and infrastructure
- Implementing efficient irrigation systems and technologies
- Educating the public on water-saving practices
- Promoting the use of drought-resistant crops
- Improving early warning systems and drought monitoring
By prioritizing drought preparedness, communities and individuals can:
- Minimize water shortages and ensure access to clean water
- Protect agriculture and food security
- Reduce the risk of wildfires and forest degradation
- Mitigate the negative impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity
- Strengthen resilience to climate change and future drought events
Drought preparedness is a multifaceted approach that requires collaboration between different stakeholders, including governments, communities, and individuals. By working together and implementing proactive measures, we can build resilience and minimize the social, economic, and environmental impacts of droughts.
| Drought Preparedness Benefits | Actions to Achieve Them |
|---|---|
| Water conservation | Implementing water-saving practices |
| Food security | Promoting drought-resistant crops |
| Ecosystem preservation | Improving early warning systems and monitoring |
| Climate change resilience | Investing in water storage and efficient irrigation |
In conclusion, drought preparedness is crucial in the face of increasing drought conditions. By prioritizing and implementing strategies to mitigate the impacts of droughts, we can protect communities, ecosystems, and ensure water and food security for future generations.