Binomial distribution is a probability distribution that describes the number of successful outcomes in a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials. It is used to model situations where there are only two possible outcomes, such as success or failure, yes or no, heads or tails.
A binomial distribution worksheet provides a set of problems and exercises for students to practice and apply the concepts of binomial distribution. The worksheet contains a series of questions with different scenarios, where students are required to calculate the probabilities of certain outcomes using the binomial distribution formula.
The answers to the worksheet are provided in a PDF format, making it easy for students to check their answers and verify their calculations. This allows students to track their progress and identify any areas that may require further practice or review.
Working through a binomial distribution worksheet can help students develop their understanding of the concepts and applications of binomial distribution. It also provides an opportunity for students to improve their problem-solving skills and gain confidence in their ability to calculate probabilities using the binomial distribution formula.
Understanding the Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution is a probability distribution that models the number of successes in a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials. It is widely used in statistics and probability theory to analyze and understand various real-world phenomena.
The key concept in the binomial distribution is the Bernoulli trial, which represents a single experiment with two possible outcomes: success or failure. Each trial is independent and has the same probability of success, denoted by p. The binomial distribution then calculates the probability of obtaining a specific number of successes in a given number of trials.
To better understand the binomial distribution, let’s consider an example: flipping a fair coin. In this case, each coin flip is a Bernoulli trial, with success defined as getting heads and failure as getting tails. If we wanted to find the probability of getting exactly 3 heads in 5 coin flips, we can use the binomial distribution formula.
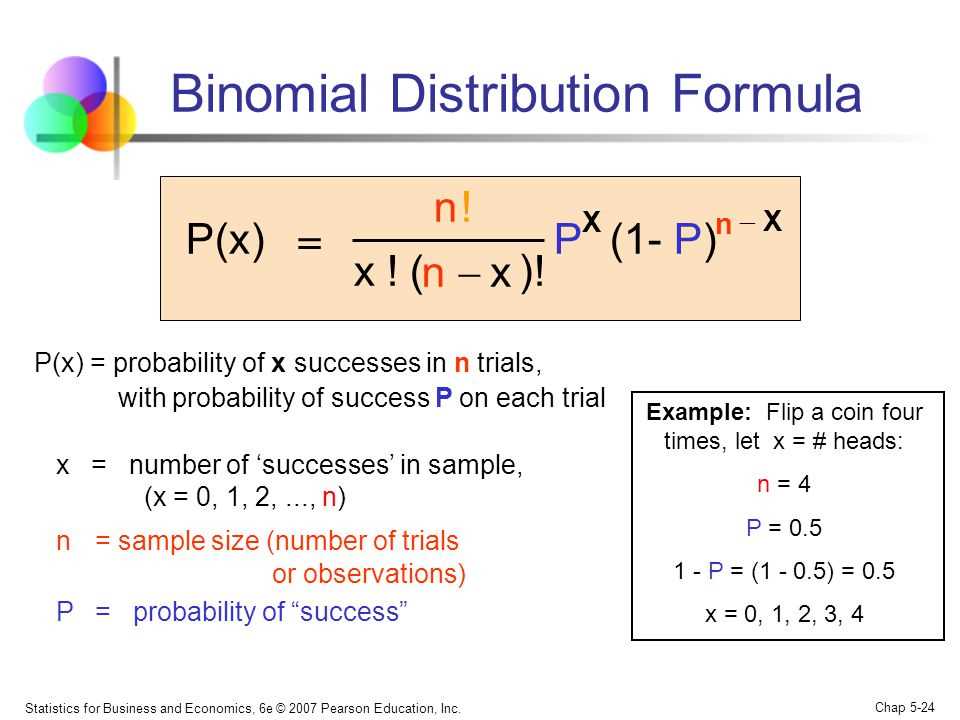
The formula for the binomial distribution is:
P(X = k) = C(n, k) * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k)
Where P(X = k) is the probability of getting exactly k successes in n trials, C(n, k) is the combination formula (n choose k), p is the probability of success in a single trial, and (1-p) is the probability of failure in a single trial.
By using this formula and plugging in the values for our example (n = 5, k = 3, p = 0.5), we can calculate the probability of getting exactly 3 heads in 5 coin flips. This probability allows us to analyze the likelihood of certain outcomes and make informed decisions based on the binomial distribution.
What is the Binomial Distribution?
The Binomial Distribution is a probability distribution that models the number of successes in a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials. It is used to calculate the probabilities of different outcomes in situations where there are only two possible outcomes, often referred to as success or failure.
The distribution is characterized by two parameters: the number of trials (n) and the probability of success in each trial (p). The probability mass function of the Binomial Distribution gives the probability of getting exactly k successes in n trials. The formula for calculating the probability is:
P(X=k) = C(n,k) * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k)
Where P(X=k) is the probability of getting exactly k successes, C(n,k) is the binomial coefficient, p is the probability of success, and (1-p) is the probability of failure.
The Binomial Distribution has several applications in various fields such as genetics, economics, and quality control. It can be used to model the likelihood of a certain number of successes in a series of independent events. For example, it can be used to calculate the probability of flipping a coin and getting heads a certain number of times in a given number of flips.
The properties of the Binomial Distribution include a mean of n * p and a standard deviation of sqrt(n * p * (1-p)). These properties make it a useful tool for analyzing and predicting the outcomes of discrete events with two possible outcomes.
Properties of the Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution is a probability distribution that describes the number of successes in a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials, where each trial has the same probability of success. It is characterized by the parameters n and p, where n is the number of trials and p is the probability of success in each trial. The binomial distribution has several properties that make it a useful tool in probability and statistics.
1. Fixed number of trials: The binomial distribution is defined for a fixed number of trials, which means that the number of trials must be specified in advance. This makes it suitable for situations where we are interested in the number of successes or failures in a specific number of trials, such as the number of correct answers on a multiple-choice test.
2. Independent trials: Each trial in the binomial distribution is assumed to be independent, meaning that the outcome of one trial does not affect the outcomes of the other trials. This assumption allows us to model a wide range of real-world phenomena, such as flipping a coin or rolling a dice multiple times.
- 3. Bernoulli trials: The binomial distribution is based on the concept of Bernoulli trials, which are experiments that have two possible outcomes (usually labeled success and failure) and a fixed probability of success. Each trial in the binomial distribution is a Bernoulli trial, where the probability of success (p) is the same for all trials.
- 4. Probability mass function: The binomial distribution is described by its probability mass function (PMF), which gives the probability of observing a specific number of successes in the fixed number of trials. The PMF can be calculated using the formula P(X=k) = (n choose k) * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k), where X is the random variable representing the number of successes, k is the number of successes, n is the number of trials, p is the probability of success, and (n choose k) is the binomial coefficient.
- 5. Mean and variance: The mean (expected value) of the binomial distribution is given by μ = np, where μ represents the average number of successes in the fixed number of trials. The variance of the binomial distribution is given by σ^2 = np(1-p). These formulas allow us to quantify the central tendency and variability of the binomial distribution.
Overall, the binomial distribution provides a powerful framework for modeling and analyzing discrete random variables that arise from repeated independent trials with a fixed probability of success. Its properties make it a valuable tool in various fields, including statistics, probability theory, and experimental design.
Calculating Probabilities Using the Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution is a probability distribution that represents the number of successes in a fixed number of trials. It is widely used in various fields, including statistics, genetics, and quality control.
In order to calculate probabilities using the binomial distribution, certain parameters must be known. These include the number of trials (n), the probability of success on each trial (p), and the number of desired successes (k). The formula for calculating the probability of k successes in n trials is:
P(k) = (n choose k) * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k)
Here, (n choose k) represents the number of ways to choose k successes out of n trials, p^k represents the probability of k successes, and (1-p)^(n-k) represents the probability of (n-k) failures.
For example, let’s say we have a fair coin and we want to calculate the probability of getting exactly 3 heads in 5 tosses. In this case, n = 5 (number of trials), p = 0.5 (probability of heads), and k = 3 (number of desired successes).
Using the formula, we can plug in these values and calculate the probability:
- (5 choose 3) * (0.5)^3 * (1-0.5)^(5-3)
- = 10 * 0.125 * 0.25
- = 0.3125
Therefore, the probability of getting exactly 3 heads in 5 coin tosses is 0.3125.
Binomial Distribution Worksheet: Practice Questions
Are you looking to practice your understanding of the binomial distribution? This worksheet provides a set of practice questions to help you test your knowledge and skills. Each question is designed to assess your understanding of the binomial distribution, its parameters, and how to calculate probabilities using this distribution.
Question 1:
You are flipping a fair coin 10 times. What is the probability of getting exactly 7 heads?
Possible answers:
- 0.1176
- 0.401
- 0.117
- 0.125
Question 2:
You are conducting a survey and each respondent has a 20% chance of answering “yes” to a particular question. If you survey 30 people, what is the probability that at least 5 of them will answer “yes”?
Possible answers:
- 0.6539
- 0.3774
- 0.9948
- 0.0224
Question 3:
In a multiple-choice test with 10 questions, each with 4 possible answers, what is the probability of answering at least 8 questions correctly by guessing?
Possible answers:
- 0.0016
- 0.3385
- 0.5765
- 0.0256
These practice questions will not only help you review the concepts of the binomial distribution but also improve your problem-solving skills. Check your answers against the given options and refer to the accompanying answer key for detailed explanations. Good luck with your practice!
Answers to the Binomial Distribution Worksheet
Below are the answers to the questions on the binomial distribution worksheet:
1. In a fair coin toss, what is the probability of getting heads?
The probability of getting heads in a fair coin toss is 0.5 or 50%.
2. In a biased coin toss, the probability of getting heads is 0.6. If the coin is flipped 10 times, what is the probability of getting exactly 7 heads?
To calculate the probability of getting exactly 7 heads, we can use the binomial distribution formula: P(X=k) = (n choose k) * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k). Plugging in the values, we get:
P(X=7) = (10 choose 7) * 0.6^7 * (1-0.6)^(10-7)
= 120 * 0.6^7 * 0.4^3
= 0.214990848
So, the probability of getting exactly 7 heads is approximately 0.215 or 21.5%.
3. In a game of chance, the probability of winning is 0.3. If the game is played 5 times, what is the probability of winning more than 3 times?
To calculate the probability of winning more than 3 times, we need to find the sum of the probabilities of winning 4 times and winning 5 times.
P(X>3) = P(X=4) + P(X=5)
= (5 choose 4) * 0.3^4 * (1-0.3)^(5-4) + (5 choose 5) * 0.3^5 * (1-0.3)^(5-5)
= 5 * 0.3^4 * 0.7 + 0.3^5
= 0.302355 + 0.00243
= 0.304785
So, the probability of winning more than 3 times is approximately 0.305 or 30.5%.
4. In a survey, 80% of people prefer chocolate ice cream over vanilla ice cream. If 200 people are surveyed, what is the probability that more than 180 people prefer chocolate ice cream?
To calculate the probability that more than 180 people prefer chocolate ice cream, we need to find the sum of the probabilities of 181 people, 182 people, …, and 200 people.
P(X>180) = P(X=181) + P(X=182) + … + P(X=200)
= (200 choose 181) * 0.8^181 * (1-0.8)^(200-181) + (200 choose 182) * 0.8^182 * (1-0.8)^(200-182) + … + (200 choose 200) * 0.8^200 * (1-0.8)^(200-200)
Calculating each individual probability and summing them up will give us the final answer.
Overall, the binomial distribution is a useful tool for calculating probabilities in situations where there are only two possible outcomes and each outcome has a fixed probability of occurring. By applying the binomial distribution formula, we can find the probabilities of various events and make informed decisions based on the likelihood of those events happening.