Welcome to the Unit 5 test on relationships in triangles! In this test, we will be exploring the various relationships that exist within triangles, including angles, sides, and special types of triangles. This test is designed to assess your understanding of the concepts covered in Unit 5 and your ability to apply them to solve problems. It is important to read each question carefully and show all work to receive full credit for your answers. Let’s dive in and test your knowledge!
In this test, you will encounter questions that require you to identify and classify different types of triangles based on their angles and sides. You will also be asked to apply the properties of triangles to solve problems involving angles and sides. It is crucial to review the definitions and properties of different types of triangles, such as equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles, before attempting this test. Additionally, it is essential to understand the relationships between angles and sides in a triangle, such as the Triangle Sum Theorem and the Pythagorean Theorem.
To successfully complete this test, it is recommended that you have a good understanding of basic geometry concepts, such as angle measurement, congruence, and similarity. Familiarize yourself with the different properties and formulas related to triangles, as they will be vital in solving the problems presented in the test. Pay close attention to the given information and apply the appropriate theorem or property to arrive at the correct answers. Remember to present your work clearly and neatly, showing all necessary steps to receive full credit.
Understanding Relationships in Triangles: Unit 5 Test
Unit 5 Test on relationships in triangles is an important assessment that helps students evaluate their understanding and knowledge of various concepts related to triangles. In this unit, students learn about the different types of triangles, their properties, and the relationships between angles and sides in a triangle.
One key concept covered in this unit is the classification of triangles based on their angles and sides. Students learn about acute, obtuse, and right triangles, as well as equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles. They also learn how to identify these types of triangles based on their angles and sides.
- Acute triangle: a triangle with all angles less than 90 degrees.
- Obtuse triangle: a triangle with one angle greater than 90 degrees.
- Right triangle: a triangle with one angle of exactly 90 degrees.
- Equilateral triangle: a triangle with all three sides equal in length.
- Isosceles triangle: a triangle with two sides equal in length.
- Scalene triangle: a triangle with no sides equal in length.
Furthermore, students explore the relationships between angles and sides in a triangle, such as the sum of interior angles being equal to 180 degrees and the Pythagorean theorem, which relates the sides of a right triangle. They also learn about the triangle inequality theorem, which states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
The Unit 5 Test on relationships in triangles provides students with an opportunity to apply their understanding of these concepts through solving various problems and answering questions. It assesses their ability to identify different types of triangles, calculate missing angles and side lengths, and apply theorems and principles related to triangles. This test is crucial in evaluating students’ proficiency in this topic and guiding further instruction, if needed.
Exploring Triangle Relationships
In geometry, triangles are one of the fundamental shapes that we study. Triangles have unique properties and relationships that help us understand their geometric characteristics. Exploring these relationships allows us to solve problems related to triangles, such as finding missing angles or sides.
Angle Relationships: The sum of the three angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees. This relationship, known as the Triangle Sum Theorem, is a fundamental property of triangles. It can be used to find missing angles in a triangle if two angles are already known. Another important angle relationship is the Exterior Angle Theorem, which states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
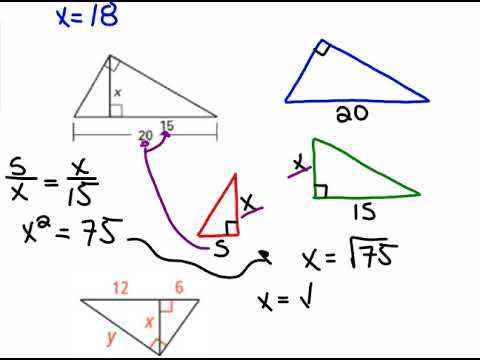
Side Relationships: Triangles have various side relationships that are crucial in understanding their properties. One of the most basic side relationships is the Pythagorean Theorem, which applies to right triangles. It states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Another important side relationship is the Triangle Inequality Theorem, which states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side. This theorem is useful in determining whether a given set of side lengths can form a triangle.
Special Triangles: There are several types of special triangles that have unique relationships. The most well-known special triangles are the equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles. Equilateral triangles have three congruent sides and three congruent angles. Isosceles triangles have two congruent sides and two congruent angles. Right triangles have one right angle (90 degrees) and follow the Pythagorean Theorem. These special triangles have specific properties and formulas that make them useful in solving triangle problems.
Types of Triangles and Their Properties
In geometry, a triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. Triangles can be classified based on their side lengths and angle measurements. Understanding the properties of different types of triangles is essential for solving problems involving triangles and their relationships.
1. Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle with all three sides of equal length. In addition, all three angles of an equilateral triangle are equal, measuring 60 degrees. The equilateral triangle has the highest degree of symmetry among all types of triangles.
2. Isosceles Triangle
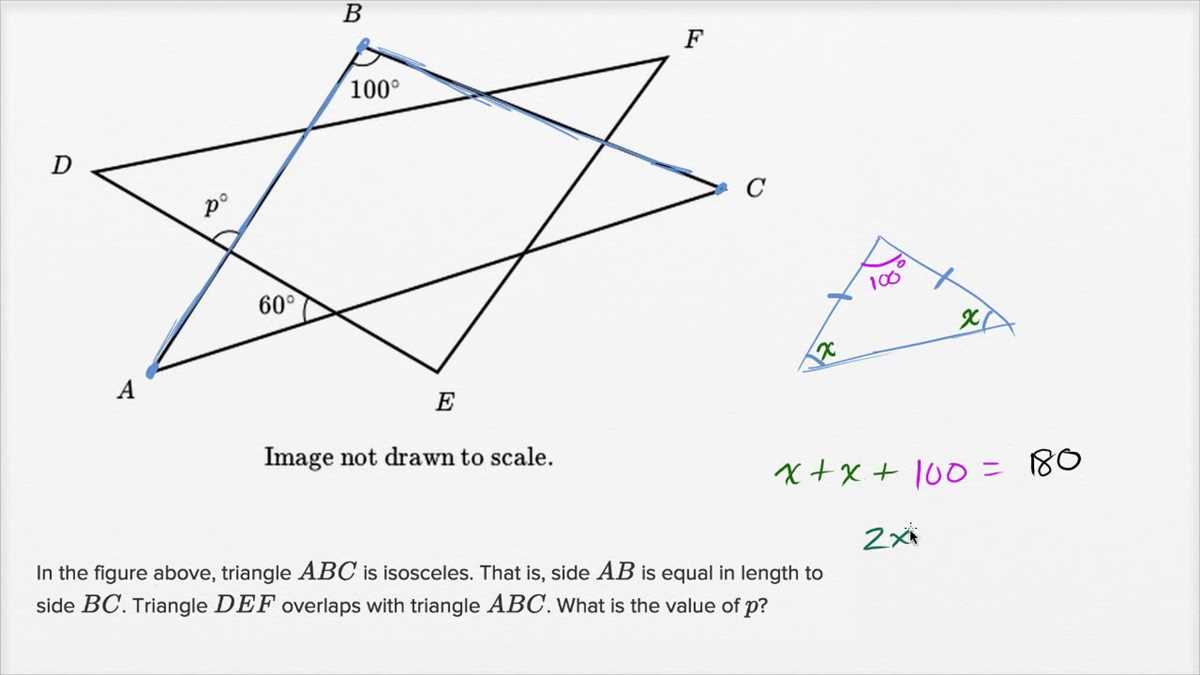
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two sides of equal length. The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal. The third side, called the base, can be of a different length. The angles opposite the base are equal. The sum of the angles in an isosceles triangle is always 180 degrees.
3. Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle is a triangle with all three sides of different lengths. As a result, all three angles of a scalene triangle are also different. The sum of the angles in a scalene triangle is always 180 degrees.
4. Right Triangle
A right triangle is a triangle with one angle measuring 90 degrees, called the right angle. The side opposite the right angle, called the hypotenuse, is the longest side in a right triangle. The other two sides are called legs.
5. Obtuse Triangle
An obtuse triangle is a triangle with one angle greater than 90 degrees. The other two angles are acute angles, measuring less than 90 degrees. The longest side in an obtuse triangle is opposite the obtuse angle.
6. Acute Triangle
An acute triangle is a triangle with all three angles measuring less than 90 degrees. In an acute triangle, all three sides are shorter than the hypotenuse of a right triangle with the same angles.
Understanding the properties and characteristics of different types of triangles allows us to calculate their measurements, identify relationships between triangles, and solve various geometry problems.
Special Right Triangles
In geometry, a right triangle is a triangle with one angle measuring 90 degrees. Special right triangles are a specific type of right triangles that have special relationships between their sides and angles.
There are two types of special right triangles: the 45-45-90 triangle and the 30-60-90 triangle. The 45-45-90 triangle has two congruent legs and a hypotenuse that is equal to the length of the leg multiplied by the square root of 2. The angles in a 45-45-90 triangle are always 45 degrees, 45 degrees, and 90 degrees.
The 30-60-90 triangle has angles that measure 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees. The ratio of the lengths of the sides in a 30-60-90 triangle is 1:√3:2. The shorter leg is always half the length of the hypotenuse, and the longer leg is equal to the length of the shorter leg multiplied by the square root of 3.
Special right triangles are useful because their side lengths and angles can be easily calculated using simple ratios. This makes them helpful in many geometry problems and applications, such as finding the lengths of sides in triangles or determining the angles of elevation or depression.
Knowing the properties of special right triangles allows us to solve problems more efficiently and accurately. By recognizing these triangles and applying the appropriate formulas, we can simplify calculations and find solutions more easily.
- In summary, special right triangles have specific relationships between their angles and sides.
- The 45-45-90 triangle has two congruent legs and a hypotenuse that is equal to the length of the leg multiplied by the square root of 2.
- The 30-60-90 triangle has angles that measure 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees, and the ratio of the lengths of its sides is 1:√3:2.
Congruence and Similarity of Triangles
In geometry, congruence and similarity are two important concepts when it comes to triangles. Congruence refers to when two figures have the exact same shape and size, while similarity refers to when two figures have the same shape but different sizes.
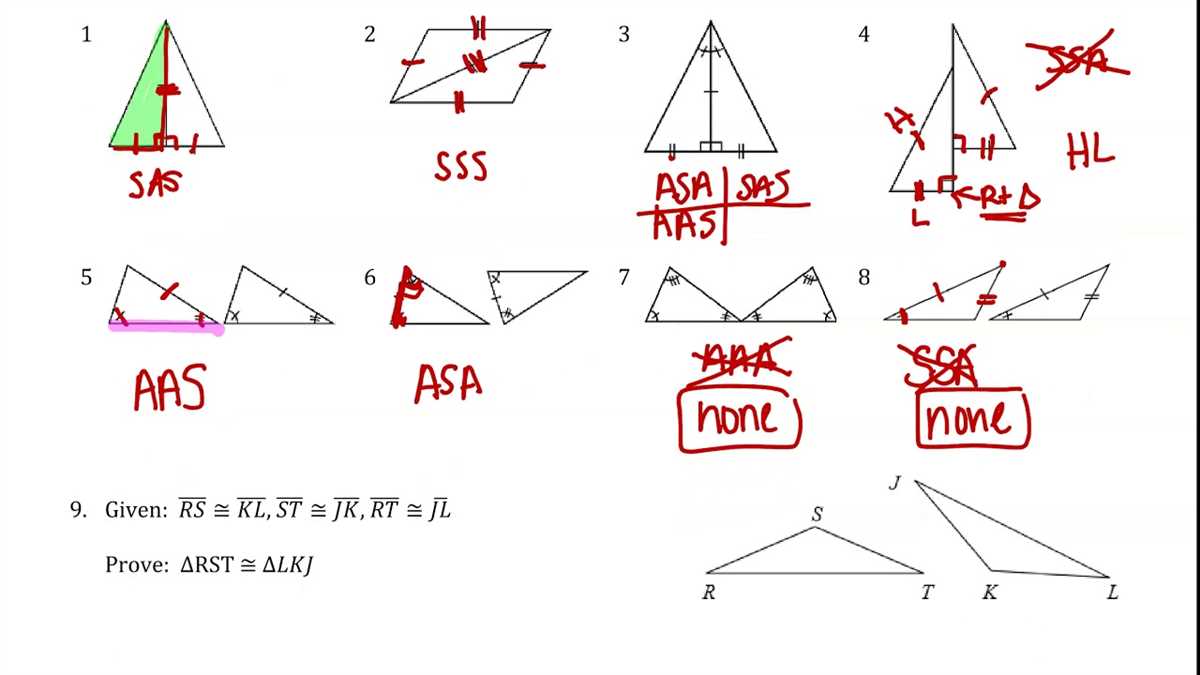
When it comes to triangles, congruence is determined by the congruence of their corresponding sides and angles. If all three sides and all three angles of two triangles are congruent, then the triangles are congruent. We can denote congruent triangles by using the symbol ≅.
Similarity, on the other hand, is determined by the proportionality of the corresponding sides of two triangles. If the ratios of the lengths of the corresponding sides of two triangles are equal, then the triangles are similar. We can denote similar triangles by using the symbol ~.
When working with congruent or similar triangles, we can use various properties and theorems to solve problems. Some of the key theorems include the Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Congruence Theorem, the Angle-Angle (AA) Similarity Theorem, and the Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarity Theorem.
In summary, congruence and similarity of triangles are important concepts in geometry. Understanding the properties and theorems related to congruent and similar triangles can help us solve various problems involving triangles.
Angle Measures and Side Lengths in Similar Triangles
In the study of triangles, an important concept to understand is that of similar triangles. Similar triangles have the same shape but different sizes, and their corresponding angles are congruent. This means that the angle measures in similar triangles are equal, even though the side lengths may be different.
Knowing the angle measures in similar triangles allows us to determine the relationships between the side lengths. By using the properties of similar triangles, we can set up proportions to find missing side lengths. For example, if triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF, and we know that angle A is congruent to angle D, angle B is congruent to angle E, and angle C is congruent to angle F, we can set up the proportion AB/DE = BC/EF = AC/DF to find the ratios between the corresponding side lengths.
In addition to determining side lengths, the angle measures in similar triangles can also be used to find other angles. For example, if we know that two triangles are similar and we are given one angle measure in each triangle, we can use the fact that the corresponding angles are congruent to find the measure of another angle.
In summary, angle measures and side lengths in similar triangles are closely related. The angle measures determine the ratios between the side lengths, and by using the properties of similar triangles, we can find missing side lengths and angles. Understanding these relationships is essential in solving problems involving similar triangles and applying them to real-world situations in areas such as geometry and engineering.
Applying Triangle Relationships in Real-World Problems
In this article, we have explored various triangle relationships and their applications in real-world problems. By understanding these relationships, we can solve practical problems that involve triangles and their measurements.
We started by discussing the properties of congruent triangles and how they can be used to determine missing side lengths or angles in a triangle. Congruent triangles have corresponding sides and angles that are equal, allowing us to solve for unknown values using a variety of methods such as side-side-side (SSS), side-angle-side (SAS), and angle-angle-side (AAS) congruence criteria.
We then delved into the concept of similar triangles and how they can be used to solve problems involving proportions. Similar triangles have corresponding angles that are equal, but their corresponding sides are proportional. This allows us to set up ratios and solve for missing side lengths or distances.
Furthermore, we explored the relationships between the angles and side lengths in right triangles. We discussed the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This theorem is fundamental in solving for missing side lengths in right triangles.
Finally, we applied these triangle relationships to real-world problems, such as determining the height of a tall object using similar triangles, finding the distance between two objects using trigonometry, or calculating the length of a side in a triangle using the Pythagorean theorem.
By understanding and applying these triangle relationships, we can solve a wide range of problems in various fields such as engineering, architecture, surveying, and physics. These relationships help us make accurate measurements, solve practical problems, and understand the geometry of triangles in real-world contexts.