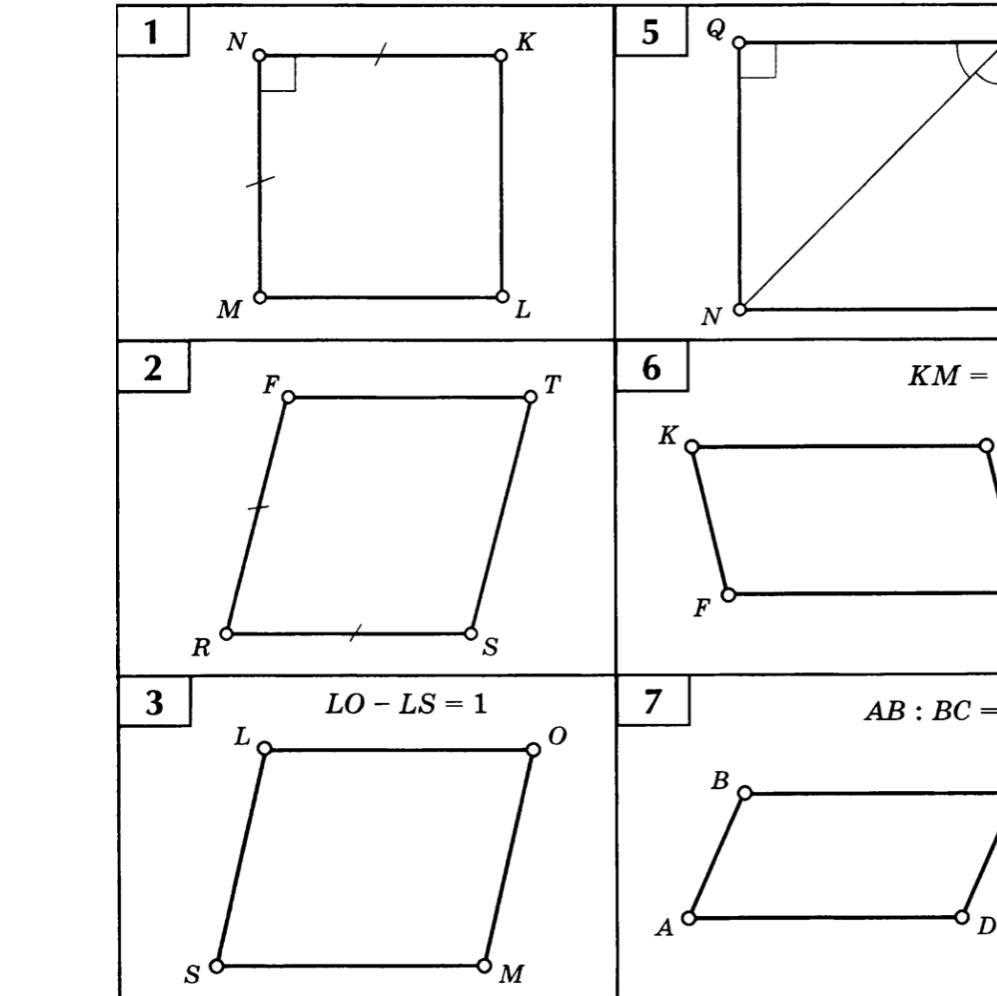
A parallelogram is a two-dimensional figure with four sides, where opposite sides are parallel and congruent. It is a special type of quadrilateral that has unique properties and characteristics. Understanding the properties of parallelograms is important in geometry as it helps in solving various mathematical problems.
One way to practice and enhance your understanding of parallelograms is by using worksheets. Parallelogram worksheets provide a variety of exercises and problems that involve different aspects of parallelograms, including identifying their properties, finding missing angles or sides, and determining area and perimeter.
These worksheets often come with answer keys, which help students check their work and ensure they are on the right track. The answer keys provide step-by-step explanations and solutions to the problems, making it easier for students to understand the concepts and learn from their mistakes.
By using parallelogram worksheets and their corresponding answer keys, students can develop their problem-solving skills, strengthen their geometry knowledge, and become more familiar with the properties and characteristics of parallelograms. These worksheets serve as a valuable resource for both students and teachers in their geometry studies.
Parallelogram Worksheet Answers
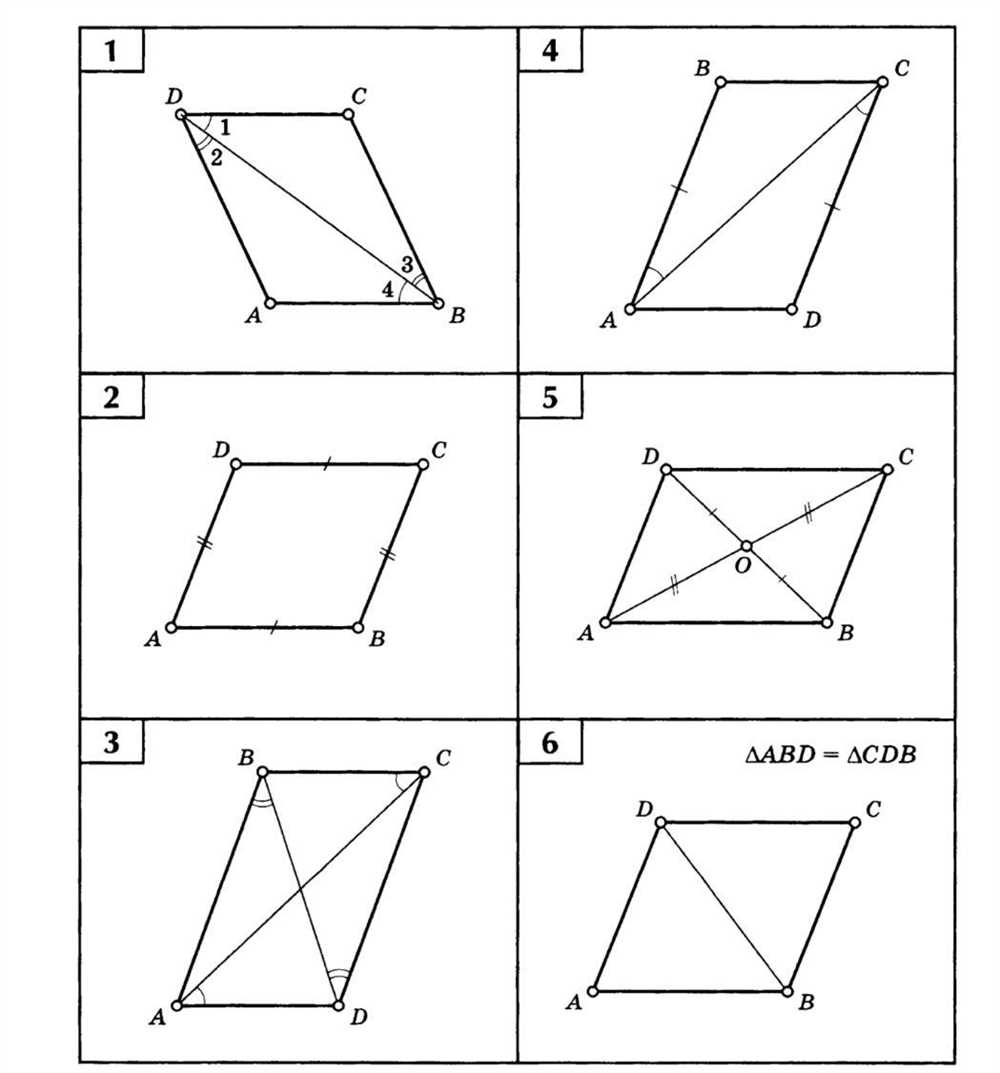
When studying geometry, one of the key concepts that students need to understand is the parallelogram. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length. To help students practice their skills with parallelograms, teachers often assign worksheet exercises that require them to solve problems and find the missing angles or measurements.
These parallelogram worksheet exercises cover a wide range of topics, such as finding the area and perimeter of a parallelogram, determining the measures of angles within a parallelogram, and solving real-world problems using the properties of parallelograms. While solving these worksheets, students will need to apply their knowledge of the properties of parallelograms, such as opposite sides being congruent, opposite angles being congruent, and consecutive angles being supplementary.
Here are some sample answers to a parallelogram worksheet:
- Question 1: Find the area of a parallelogram with a base of 10 cm and a height of 5 cm.
Answer: The area of the parallelogram is 50 square cm.
- Question 2: Find the missing angle in the parallelogram below.
Answer: The missing angle is 60 degrees, as opposite angles in a parallelogram are congruent.
- Question 3: A parallelogram has a base of 8 cm and a height of 6 cm. Find the perimeter of the parallelogram.
Answer: The perimeter of the parallelogram is 28 cm, as each side is equal in length and there are four sides in total.
By practicing these worksheet exercises and checking the answers, students can strengthen their understanding of parallelograms and improve their problem-solving skills in geometry.
Definition of a Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon that has two pairs of parallel sides. In other words, opposite sides of a parallelogram are always parallel and equal in length. This fundamental property distinguishes a parallelogram from other types of quadrilaterals.
One key characteristic of a parallelogram is that its opposite angles are congruent. This means that if you have two angles formed by intersecting lines within a parallelogram, the measure of one angle will always be equal to the measure of its opposite angle. This property is known as the “parallelogram angle theorem” and is a crucial factor in determining the properties and relationships within a parallelogram.
A parallelogram can also be classified based on its angles. If all angles of a parallelogram are right angles (90 degrees), then the parallelogram is considered a rectangle. If only one pair of angles is right angles, the parallelogram is a rhombus. If all sides and angles are equal, it is called a square.
Understanding the definition of a parallelogram is essential in geometry and other related fields. It serves as the foundation for studying more complex concepts, such as the properties of different types of parallelograms, theorems related to parallelograms, and their applications in various mathematical and real-world scenarios.
Properties of Parallelograms
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon with opposite sides that are parallel and congruent. It is a special type of quadrilateral that has several unique properties.
Property 1: Opposite sides are parallel.
In a parallelogram, the opposite sides are parallel. This means that if two sides of a quadrilateral are parallel, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. The opposite sides are also congruent, which means they have the same length.
Property 2: Opposite angles are congruent.
The opposite angles in a parallelogram are congruent. This means that if two angles are opposite each other in a quadrilateral and they have the same measure, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a parallelogram is always 360 degrees.
Property 3: Diagonals bisect each other.
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. This means that the point where the diagonals intersect divides each diagonal into two congruent segments. The diagonals also create four congruent triangles within the parallelogram.
Property 4: Consecutive angles are supplementary.
The consecutive angles in a parallelogram are supplementary. This means that the measure of one angle plus the measure of the angle next to it adds up to 180 degrees. The sum of the measures of the consecutive angles in a parallelogram is always 360 degrees.
These properties help us identify and work with parallelograms in geometry. They provide a foundation for understanding the relationships between the sides and angles of a parallelogram, and they are essential in proving theorems and solving problems involving parallelograms.
Formulas for Finding the Area of a Parallelogram
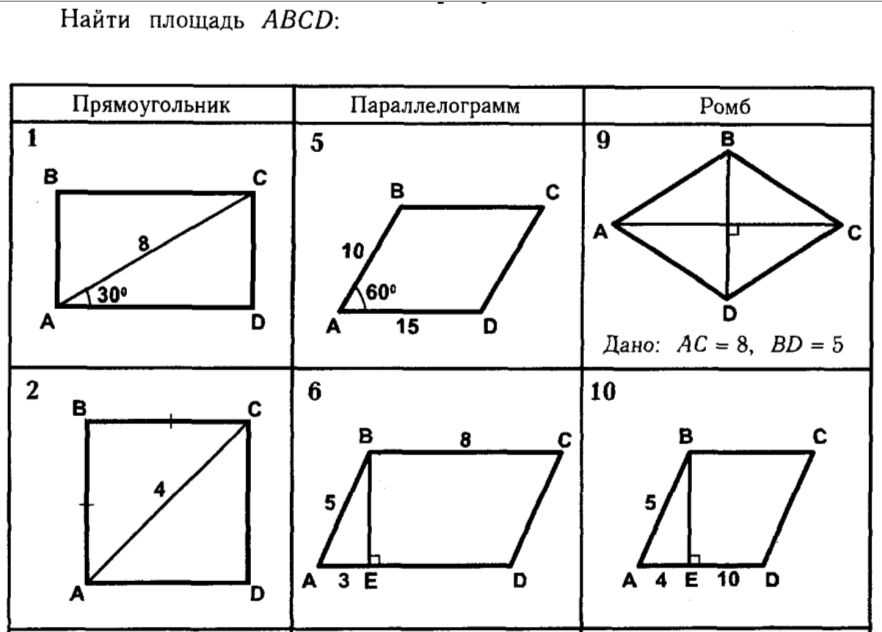
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon with opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length. Finding the area of a parallelogram is an important skill in geometry, as it allows us to calculate the amount of space enclosed by this shape. There are different formulas we can use to find the area, depending on the information given.
Formula 1: Base times Height
One of the simplest ways to find the area of a parallelogram is to multiply the length of the base (or one of the parallel sides) by the perpendicular height, or distance between the base and the opposite parallel side. The formula for finding the area using the base and height is:
Area = Base × Height
Formula 2: Opposite Sides times Sine of Angle between them
In cases where we have information about the lengths of both pairs of opposite sides and the angle between them, we can use the trigonometric function sine to find the area. The formula for finding the area using the lengths of the opposite sides and the angle is:
Area = Length of Side 1 × Length of Side 2 × Sin(Angle)
Formula 3: Diagonal Lengths
If we know the lengths of the two diagonals of the parallelogram, we can use them to find the area. The formula for finding the area using the lengths of the diagonals is:
Area = (Length of Diagonal 1 × Length of Diagonal 2) / 2
These formulas provide different ways to calculate the area of a parallelogram depending on the given information. By applying these formulas correctly, we can accurately determine the area of any parallelogram.
Calculating the Perimeter of a Parallelogram
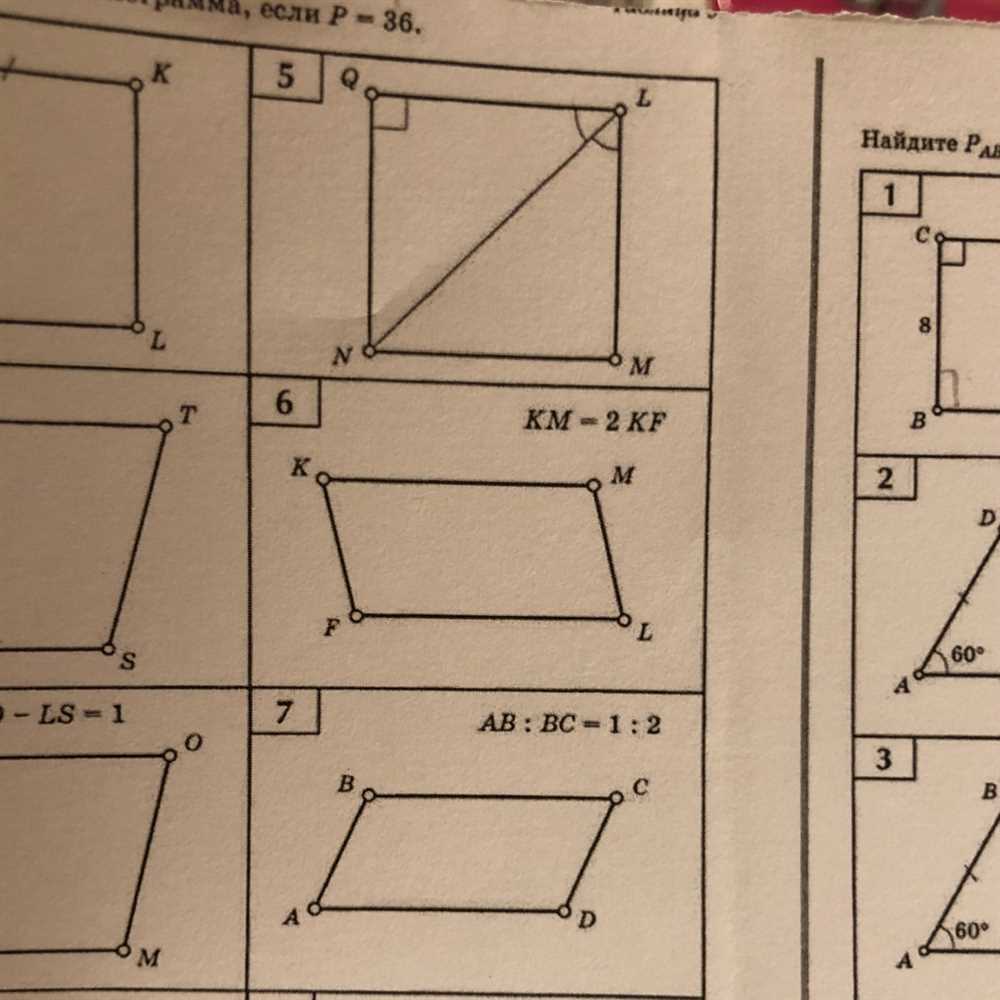
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel. The perimeter of a parallelogram is the total length of its sides. In order to calculate the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of all four sides.
To find the perimeter of a parallelogram, you can use the formula: P = 2a + 2b, where “a” and “b” are the lengths of the adjacent sides. This formula works because opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length.
In some cases, you may be given the length of one side and the lengths of adjacent angles. In this case, you can use trigonometry to find the lengths of the other sides. For example, if you know the length of one side and the adjacent angles, you can use the law of cosines to find the lengths of the other two sides.
Once you have found the lengths of all four sides, you can simply add them up to find the perimeter of the parallelogram. Make sure to double the lengths of the adjacent sides, as the formula requires it.
In summary, to calculate the perimeter of a parallelogram, you need to know the lengths of all four sides. Use the formula P = 2a + 2b, where “a” and “b” are the lengths of the adjacent sides. In some cases, you may need to use trigonometry to find the lengths of the sides. Once you have all the side lengths, add them up to find the total perimeter.
Determining the Length of the Sides of a Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon in which opposite sides are parallel and congruent. To determine the length of the sides of a parallelogram, you need to know the measurements of the angles or other side lengths.
One way to determine the length of the sides of a parallelogram is by using the properties of parallelograms. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, so if you know the length of one side, you can find the length of the opposite side. You can also use the properties of parallel lines and transversals to find the lengths of the sides.
To find the length of the sides of a parallelogram, you can also use the Pythagorean theorem if the parallelogram is a rectangle or a rhombus. In a rectangle, the opposite sides are equal in length and the adjacent sides are perpendicular to each other. By applying the Pythagorean theorem, you can find the length of the sides. In a rhombus, all four sides are equal in length, so you can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of one side and then apply it to all four sides.
Another method to determine the length of the sides of a parallelogram is by using trigonometry. If you know the lengths of two sides and the measure of the included angle, you can use the cosine rule or sine rule to find the length of the third side. This can be useful when dealing with more complex shapes or if the measurements of the angles and other side lengths are given.
In conclusion, there are various methods to determine the length of the sides of a parallelogram, depending on the given information and the properties of the parallelogram. Whether it’s using the properties of parallelograms, applying the Pythagorean theorem, or utilizing trigonometry, these methods can help you solve for the unknown side lengths and accurately describe the shape of the parallelogram.
Solving Problems Involving Parallelograms
Parallelograms are quadrilaterals whose opposite sides are parallel and equal in length. They have several properties that can be used to solve problems related to their angles, sides, and diagonals.
One of the main properties of parallelograms is that the opposite angles are equal. This means that if we know the measure of one angle, we can easily find the measure of the other using the corresponding angle property. Additionally, the sum of the interior angles of a parallelogram is always 360 degrees.
Another important property of parallelograms is that the opposite sides are congruent. This means that if we know the length of one side, we can easily find the length of the other using the corresponding side property. Moreover, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, meaning they divide each other into two equal parts.
When solving problems involving parallelograms, it is important to identify the given information and determine which properties can be used to find the solution. It may be necessary to use multiple properties in combination to solve complex problems. Additionally, drawing a diagram of the parallelogram can help visualize the problem and make it easier to apply the properties. By applying these properties and using algebraic techniques when necessary, we can successfully solve problems involving parallelograms.
Key Concepts:
- Opposite angles: The opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
- Sum of interior angles: The sum of the interior angles of a parallelogram is 360 degrees.
- Opposite sides: The opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Applying Parallelogram Theorems
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal in length. It has several interesting properties and theorems that can be applied to solve problems involving parallelograms.
One of the most basic theorems is the Parallelogram Opposite Sides Theorem, which states that opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. This means that if one pair of opposite sides is known to be congruent, the other pair of opposite sides will also be congruent.
Another important theorem is the Parallelogram Opposite Angles Theorem. This theorem states that opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent. This means that if one pair of opposite angles is known to be congruent, the other pair of opposite angles will also be congruent.
The Diagonals of a parallelogram also have interesting properties. Theorem: In a parallelogram, the diagonals bisect each other. This means that the point where the diagonals intersect divides each diagonal into two equal parts.
These theorems can be used to solve various problems involving parallelograms. For example, if the lengths of one pair of opposite sides are known, the theorems can be used to find the lengths of the other pair of opposite sides. Similarly, if the measures of one pair of opposite angles are known, the theorems can be used to find the measures of the other pair of opposite angles.
Overall, the Parallelogram Theorems are useful tools for solving problems involving parallelograms. By understanding and applying these theorems, we can gain a better understanding of the properties and characteristics of parallelograms.