
Optics is a branch of physics that focuses on the behavior and properties of light. It is a field that has fascinated scientists and philosophers for centuries, as the study of light has helped unlock the secrets of the universe. From understanding the behavior of light in different mediums to explaining how it interacts with matter, optics plays a crucial role in various scientific disciplines.
One of the fundamental concepts in optics is the nature of light itself. Is light a particle or a wave? This question has puzzled scientists for centuries, and it was not until the 19th century that both theories were reconciled. The wave-particle duality of light is now one of the cornerstones of modern physics and provides a framework for understanding the behavior of light in different circumstances.
Optics also encompasses the study of how light interacts with matter. This includes phenomena such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference. Understanding these interactions is essential in fields such as photography, medicine, and telecommunications. For example, the development of lenses and mirrors based on the principles of optics has revolutionized the world of optics, enabling us to capture images, correct vision, and transmit information over long distances.
In this answer key, we will explore some of the key concepts in optics. We will examine the principles of reflection and refraction, delve into the phenomenon of color, and discuss the different types of lenses and their uses. Whether you are a student studying physics or someone with a general interest in the nature of light, this answer key is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the field of optics.
What is Optics?
Optics is the scientific study of light and its behavior and properties. It focuses on understanding how light interacts with matter and how it is transmitted, refracted, reflected, absorbed, and diffused. Optics plays a crucial role in various fields such as physics, engineering, astronomy, and medicine, and it has a wide range of applications in everyday life.
One of the fundamental concepts in optics is the nature of light itself. Light is an electromagnetic wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. It travels in straight lines, at a constant speed in a vacuum, and exhibits wave-like properties such as interference and diffraction. Understanding the nature and behavior of light is essential in many practical applications, such as designing optical systems, developing imaging technologies, and studying the universe.
Key Terms and Concepts:
- Refraction: The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, caused by a change in its speed.
- Reflection: The bouncing back of light when it hits a surface, without passing through it.
- Absorption: The process by which light is taken in and converted into other forms of energy by matter.
- Diffusion: The spreading out of light in different directions when it encounters an uneven or rough surface.
- Optical systems: Devices or arrangements of lenses, mirrors, and other optical components that manipulate the behavior and properties of light.
- Visible spectrum: The range of wavelengths of light that are visible to the human eye, from approximately 400 to 700 nanometers.
In summary, optics is the study of light and its interactions with matter. It encompasses various phenomena and concepts related to the behavior, properties, and manipulation of light, and it has numerous practical applications in different scientific and technological fields.
Key Concepts in Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior and properties of light. It explores how light interacts with matter and how it can be manipulated and controlled. Understanding the key concepts in optics is essential in various fields, including engineering, astronomy, and telecommunications.
Wave-particle duality: One of the fundamental concepts in optics is the wave-particle duality of light. Light can behave both as a wave and as a particle, known as a photon. This duality is described by the wave-particle theory, which explains phenomena such as interference and diffraction.
Reflection and refraction: Reflection is the bouncing back of light when it hits a surface, while refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. These optical phenomena play a crucial role in everyday life, from the reflection of light in a mirror to the refraction of light in lenses.
Optical instruments: Optics is closely associated with the design and use of various optical instruments. These include microscopes, telescopes, cameras, and lasers. Each instrument utilizes different optical principles to enhance our ability to observe and measure objects and phenomena.
Color theory: Optics also explores the science of color and how it is perceived by the human eye. The study of color involves understanding the properties of light, such as wavelength and intensity, and how they affect the perception of different colors.
Optical phenomena: Optics encompasses a wide range of fascinating phenomena, such as polarization, diffraction, and scattering. Each of these phenomena involves the behavior of light and its interaction with various materials and structures, providing valuable insights into the nature of light.
Overall, the key concepts in optics form the foundation of our understanding of light and its properties. By studying and applying these concepts, scientists and engineers can develop new technologies and improve existing ones in fields like imaging, communications, and energy. Optics continues to be a thriving area of research, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge and enabling new discoveries.
Understanding the Behavior of Light Waves
Light waves are a fundamental aspect of the study of optics. Understanding the behavior of light waves is crucial in various fields, such as physics, astronomy, and telecommunications. Light waves are electromagnetic waves that travel at a constant speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second in a vacuum.
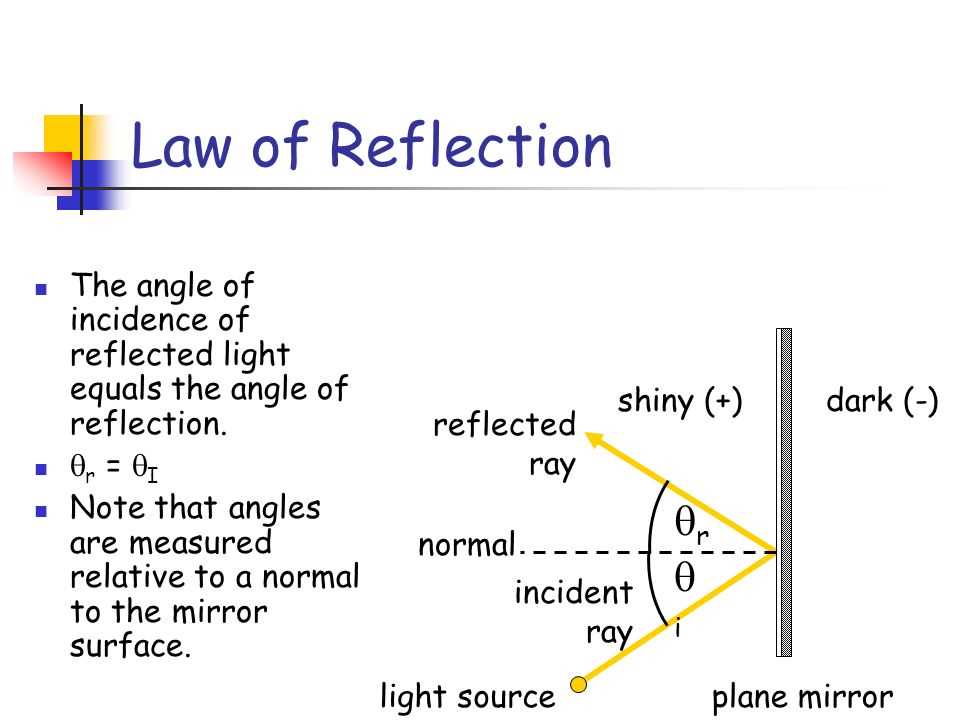
Reflection: One behavior of light waves is reflection, where light bounces off a surface. The angle of incidence, which is the angle at which the light ray strikes the surface, is equal to the angle of reflection, which is the angle at which the light ray reflects off the surface. This behavior is the basis for understanding how mirrors work and how we see objects.
Refraction: Another behavior of light waves is refraction, where light bends as it passes from one medium to another, such as from air to water or from water to glass. The speed of light changes as it enters a different medium, causing the light to change direction. This behavior is utilized in lenses for correcting vision and in the design of optical fibers for transmitting data at high speeds.
Interference: Light waves also exhibit interference, which is the interaction between two or more waves. When waves interact constructively, they add up and create regions of high intensity. When waves interact destructively, they cancel each other out and create regions of low or zero intensity. This behavior is used in various applications, such as interferometry for precise measurements and in some types of light filters.
Diffraction: Diffraction is another behavior of light waves, where light bends around obstacles or spreads out after passing through a small opening. This behavior is why we can hear sounds around corners and why we see a bright spot in the center of a shadow. Diffraction plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of light in different situations.
Overall, understanding the behavior of light waves is essential for researchers, scientists, and engineers to develop new technologies, improve existing systems, and unravel the mysteries of the universe.
The Role of Optics in Science and Technology

Optics, the study of light and its properties, plays a crucial role in various fields of science and technology. The understanding of optics has revolutionized numerous industries and continues to drive innovation and development in areas such as telecommunications, imaging, and materials science.
Telecommunications: Optics forms the backbone of modern telecommunications systems, enabling the transmission of information over long distances at high speeds. Fiber optics, which utilize strands of hair-thin glass fibers to transmit light, are widely used for data transfer in telephone networks, internet connections, and cable television. The ability of light to carry vast amounts of information and travel long distances with minimal loss has made fiber optics an essential technology in modern communication.
Imaging: Optics plays a fundamental role in imaging technologies, such as cameras, microscopes, and telescopes. The study of optics allows for the design and construction of lenses that can focus and manipulate light, enabling the capture and analysis of images at a wide range of scales. Microscopes, for example, utilize lenses and other optical components to magnify and illuminate microscopic objects, allowing scientists and researchers to study the smallest details of biological samples and materials. Similarly, telescopes rely on optics to collect and concentrate light from distant celestial objects, enabling astronomers to observe and study the universe.
Materials Science: Optics also plays a vital role in materials science, the study of the properties and behavior of materials. Optical techniques, such as spectroscopy and microscopy, provide powerful tools for characterizing and analyzing materials at the atomic and molecular level. Spectroscopy, for instance, allows scientists to study the interaction of light with matter, providing valuable information about the composition, structure, and properties of materials. These optical techniques are essential in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and materials engineering, enabling the development of new materials and technologies.
In conclusion, optics is a foundational discipline that underpins numerous scientific and technological advancements. Its applications in telecommunications, imaging, and materials science have revolutionized these fields and continue to drive further innovation and progress. The study of optics has not only enhanced our understanding of light but also transformed the way we communicate, observe the world, and develop new materials and technologies.
Applications of Optics in Medicine and Imaging
Optics plays a crucial role in medicine and imaging, enabling scientists and doctors to visualize and understand the human body in different ways. One important application is in the field of diagnostic imaging, where optics-based techniques are used to capture detailed images of internal organs and tissues. For example, optical coherence tomography (OCT) uses light waves to create high-resolution cross-sectional images of tissues, allowing for early detection and diagnosis of diseases such as cancer.
Another application of optics in medicine is in the field of ophthalmology. Optics is used to study and correct vision problems, such as nearsightedness and farsightedness, through the use of corrective lenses. Additionally, advanced optical imaging techniques, such as confocal microscopy, are used to examine the structures of the eye and detect abnormalities, helping to diagnose and monitor eye diseases.
Furthermore, optics is integral to the field of surgery. Laser technology, for instance, is widely used in various surgical procedures, offering precise incisions and minimal tissue damage. Laser ablation techniques are used in procedures such as eye surgery and skin resurfacing. Additionally, optical fibers are utilized in endoscopic procedures to provide real-time imaging and guidance during minimally invasive surgeries.
In the field of medical imaging, optics-based imaging modalities are used extensively. Fluorescence imaging, for example, utilizes fluorescent dyes and light to visualize specific molecules or cells in tissues. This imaging technique is particularly useful for cancer research and diagnosis, as it can help identify and track cancer cells. Optics-based imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), are also used to visualize metabolic activities and molecular structures in the body, aiding in the detection and management of various diseases.
In conclusion, optics plays a crucial role in medicine and imaging, enabling scientists and doctors to diagnose and treat various diseases. From diagnostic imaging to ophthalmology and surgical procedures, optics-based techniques provide valuable insights into the human body and contribute to advancements in medical science.
Optical Instruments and Devices
Optical instruments and devices play a crucial role in various fields, including physics, astronomy, medicine, and telecommunications. These instruments are designed to manipulate and measure light, allowing us to study and understand its properties and behavior.
One of the most common optical instruments is the microscope. Microscopes use lenses to magnify small objects and allow us to see details that are not visible to the naked eye. They are widely used in scientific research, medical diagnostics, and quality control in manufacturing. Microscopes have contributed significantly to advancements in various fields, such as biology, medicine, and materials science.
Telescopes are another essential optical device used in astronomy to observe celestial objects. They collect and focus light from distant objects, allowing us to study stars, planets, galaxies, and other astronomical phenomena. Telescopes come in different types and sizes, ranging from small portable instruments used by amateur astronomers to large-scale observatory telescopes.
In addition to microscopes and telescopes, there are many other optical instruments and devices. Optical fibers, for example, are used in telecommunication systems to transmit information through the rapid propagation of light. Spectrometers are used to measure the properties of light, such as its wavelength and intensity, and are widely used in laboratories for chemical analysis and research. Laser devices are used for various purposes, including precision cutting, welding, and medical procedures.
Overall, optical instruments and devices have revolutionized our understanding of light and its applications in various fields. They continue to evolve and advance, enabling us to explore the frontiers of science and technology.
Exploring the World of Microscopes and Telescopes
The study of optics, the branch of physics that deals with the properties and behavior of light, has opened up an incredible world of discovery. By harnessing the power of microscopes and telescopes, scientists have been able to explore the smallest and largest objects in our universe. These remarkable instruments have revolutionized our understanding of the world around us.
Microscopes serve as our window into the microscopic world. By using lenses to magnify tiny objects, they allow us to observe cells, bacteria, and other tiny organisms that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. With the advent of electron microscopes, which use beams of electrons instead of light, we can even examine objects at the atomic level. The world of microscopes has paved the way for major advancements in medicine, biology, and materials science.
Microscopes:
- Revealing the invisible
- Advancements in medicine, biology, and materials science
- Observing cells, bacteria, and atomic-level structures
On the other end of the scale, telescopes expand our view of the cosmos. By collecting and focusing light, telescopes enable us to observe distant stars, galaxies, and even other planets in our solar system. The Hubble Space Telescope, for example, has captured breathtaking images of deep space, revealing new insights into the formation and evolution of our universe. Telescopes have allowed astronomers to study celestial objects, unravel the mysteries of the universe, and make groundbreaking discoveries.
Telescopes:
- Unlocking the secrets of the universe
- Observing distant stars, galaxies, and planets
- Making groundbreaking discoveries
The world of microscopes and telescopes highlights the power and beauty of optics. Whether it’s peering into the microscopic world or gazing at the wonders of the universe, these instruments have expanded the boundaries of human knowledge and continue to inspire new generations of scientists and explorers.
Advancements in Optics
The study of optics has played a crucial role in our understanding of light and its applications. Over the years, there have been significant advancements in this field, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and technological innovations. These advancements have revolutionized various industries and have had a profound impact on our daily lives.
1. Development of Optical Fibers
One of the key advancements in optics is the development of optical fibers. These thin, flexible strands of glass or plastic have the ability to transmit light over long distances with minimal loss of signal. Optical fibers have revolutionized the telecommunications industry, enabling high-speed internet connections, long-distance phone calls, and cable television.
2. Advances in Imaging Technology
Advancements in optics have greatly improved imaging technology, allowing us to capture and visualize light in new and exciting ways. From microscopes that can see into the nanoscale world to cameras that can capture stunning high-resolution images, these advancements have expanded our understanding of the world around us and have paved the way for new discoveries in various scientific disciplines.
3. Breakthroughs in Laser Technology
Laser technology is another area where optics has made significant advancements. Lasers have found applications in diverse fields, including medicine, telecommunications, manufacturing, and entertainment. They are used in surgeries for precision cutting and cauterization, in optical communication systems for high-speed data transmission, in manufacturing processes for precise etching and cutting, and in entertainment for light shows and display technologies.
4. Exploration of Quantum Optics

Quantum optics is a relatively new field that combines quantum mechanics and optics to explore the behavior of light at the quantum level. This field has led to fascinating discoveries, such as quantum entanglement and quantum teleportation, which have the potential to revolutionize fields such as cryptography and computing.
Conclusion
The advancements in optics have transformed the way we perceive and utilize light. From the development of optical fibers for high-speed communication to the breakthroughs in laser technology and quantum optics, these advancements have opened up new possibilities in various fields. As we continue to explore the fundamental properties of light and push the boundaries of optics, we can expect even more exciting discoveries and innovations in the future.