
When it comes to sexual health and reproduction, it’s important to have a good understanding of sperm and its role. Sperm, the male reproductive cells, play a crucial role in fertilization and conception. However, there are many questions and misconceptions surrounding sperm that need to be addressed. In this article, we will answer some of the most commonly asked questions about sperm.
One of the frequently asked questions is about the lifespan of sperm. How long can sperm survive inside the female reproductive system? The answer depends on various factors, including the quality of the sperm and the conditions within the reproductive tract. Generally, sperm can survive for up to five days, but the chances of fertilization decrease significantly after the first 24-48 hours.
Another common question is whether the quality of sperm can be improved. The answer is yes. Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances like tobacco and alcohol can positively impact sperm quality. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress levels, and avoiding excessive heat exposure can also contribute to better sperm quality.
Many individuals also wonder whether certain foods or supplements can enhance sperm production. While some studies suggest that certain nutrients like zinc, selenium, and vitamins C and E may have a positive impact on sperm health, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before making any dietary changes or starting any supplements.
Sperm Questions Answers
Welcome to our informative guide on sperm questions and answers. We understand that there may be many questions and concerns surrounding sperm, fertility, and reproductive health. In this guide, we have compiled some frequently asked questions about sperm and provided answers to help address any uncertainties or curiosities you may have.
1. What is sperm?
Sperm is the male reproductive cell or gamete that is involved in the fertilization of an egg to create a new life. Sperm cells are produced in the testicles and are released during ejaculation.
2. How long do sperm live?
Once ejaculated, sperm can live inside a woman’s reproductive system for up to five days. However, the majority of sperm will only survive for a few hours.
3. What can affect sperm quality?
Various factors can affect sperm quality, including age, lifestyle choices, certain medical conditions, and exposure to environmental toxins. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and certain medications can also impact sperm health.
4. Can lifestyle changes improve sperm quality?
Yes, making positive lifestyle changes can potentially improve sperm quality. Maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, managing stress levels, and exercising regularly can all contribute to better sperm quality and overall reproductive health.
5. Can fertility treatments help improve sperm count?
Fertility treatments can be helpful in cases where there are issues with sperm count or quality. Treatments such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) can help bypass certain sperm-related challenges and increase the chances of successful conception.
6. Can sperm be frozen and stored for future use?
Yes, sperm can be frozen and stored for future use. This process is known as sperm cryopreservation. It allows individuals or couples to preserve sperm for future fertility treatments, such as IVF, or in the case of individuals facing medical treatments that may affect their fertility.
7. Are there natural ways to increase sperm count?
While there is no guaranteed natural method to increase sperm count, certain lifestyle changes and dietary modifications may help support sperm production. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and avoiding excessive heat exposure to the testicles can all potentially contribute to a healthier sperm count.
8. Can certain foods or supplements enhance sperm quality?
Some studies suggest that certain foods and supplements may have a positive impact on sperm quality. These include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and zinc. However, it is always important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary supplements.
9. Can frequent ejaculation affect sperm count?
Frequent ejaculation does not significantly impact sperm count. In fact, regular ejaculation can be beneficial as it helps to prevent the build-up of stagnant sperm and promotes the production of fresh, healthy sperm.
10. Can certain medical conditions affect sperm production?
Yes, certain medical conditions can affect sperm production. Conditions such as varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum), hormonal imbalances, infections, genetic disorders, and certain chronic illnesses can all have an impact on sperm production and quality.
Remember, if you have specific concerns or questions about sperm, fertility, or reproductive health, it is always beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional or fertility specialist who can provide personalized advice and guidance.
What is Sperm?
Sperm is the male reproductive cell or gamete that is essential for sexual reproduction in many organisms, including humans. It is produced in the testicles within specialized structures called seminiferous tubules. Sperm cells are formed through a process called spermatogenesis, which involves the division and differentiation of germ cells.
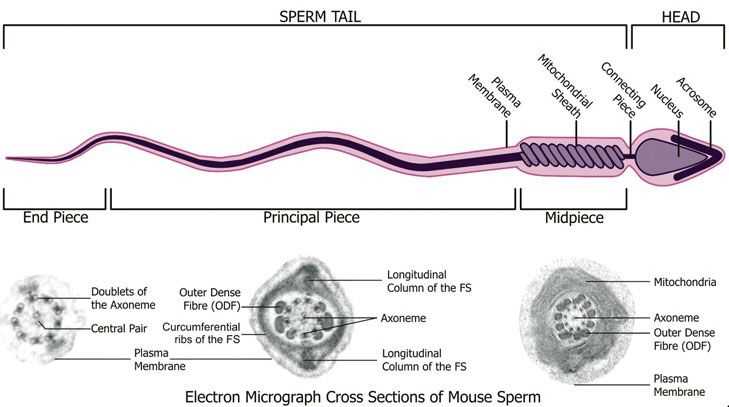
Sperm cells are typically small and have a unique shape that allows them to swim towards the female reproductive tract. They are microscopic in size, measuring about 0.05 millimeters in length. Each sperm cell consists of a head, midpiece, and tail. The head contains the genetic material, including a haploid set of chromosomes that will combine with the female egg during fertilization. The midpiece contains mitochondria, which provide energy for the sperm’s movement, while the tail, also known as the flagellum, propels the sperm forward.
The production of sperm begins at puberty and continues throughout a man’s life, with millions of sperm being produced each day. Sperm cells have a limited lifespan and can survive for a few days to several days inside the female reproductive tract, depending on various factors such as the acidity of the environment and the presence of cervical mucus that supports their survival.
Sperm cells play a crucial role in sexual reproduction, as they are responsible for fertilizing the female egg to initiate the development of a new organism. The journey of sperm cells through the female reproductive tract is a complex process that involves navigating through the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes to reach the egg. Only one sperm cell out of the millions that are ejaculated during sexual intercourse can successfully fertilize the egg, leading to the formation of a zygote and ultimately the development of a fetus.
In addition to their role in reproduction, sperm cells have also been studied for their potential use in scientific research and medical applications. They have unique characteristics, such as their ability to penetrate the protective layer surrounding the egg, which make them valuable for various studies and techniques, including fertility treatments and genetic engineering.
How is Sperm Produced?
Sperm production, also known as spermatogenesis, is a complex and intricate process that occurs in the male reproductive system. It is a continuous process that typically begins during puberty and continues throughout a man’s lifetime. Sperm production takes place in the testicles, specifically in the seminiferous tubules, which are small, coiled structures.
The process of sperm production involves several stages. It starts with the spermatogonia, which are the stem cells that are present in the walls of the seminiferous tubules. These stem cells undergo a process called mitosis, where they divide and produce more stem cells. Some of these stem cells develop into spermatocytes, which are the primary cells of spermatogenesis. The spermatocytes then undergo a series of divisions called meiosis, which ultimately results in the formation of spermatids.
During the final stage of sperm production, the spermatids undergo a process called spermiogenesis, where they mature and develop into spermatozoa or sperm cells. This transformation involves the formation of a head, a midpiece, and a tail. The head contains the genetic material, the midpiece contains mitochondria for energy production, and the tail functions as a flagellum to help the sperm move.
In summary, sperm production is a complex and highly regulated process that occurs in the testicles. It involves the development and maturation of spermatogonia into spermatozoa through a series of stages, including mitosis, meiosis, and spermiogenesis. This process ensures the continuous production of sperm throughout a man’s life, allowing for the possibility of fertilization and reproduction.
What is Sperm Made of?
Sperm is the reproductive cell or gamete produced by males of many species, including humans. It is the key component in sexual reproduction and is responsible for fertilizing the female egg. Sperm is composed of various components that enable it to successfully reach and penetrate the egg, leading to the formation of a zygote.
Sperm Head: The head of a sperm is the most important part and contains the genetic information necessary for fertilization. It is covered by a cap-like structure called the acrosome, which contains enzymes that help the sperm penetrate the outer layers of the egg.
Sperm Midpiece: The midpiece of a sperm contains mitochondria, which provide the energy needed for the sperm to swim. Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that fuels sperm movement.
Sperm Tail: The tail, or flagellum, of a sperm is responsible for its characteristic swimming motion. It consists of a long, whip-like structure made up of microtubules. The tail propels the sperm forward towards the egg.
In addition to these main components, sperm also contains other substances such as proteins, enzymes, and fluids that provide structural support and nourishment. These components help protect the sperm during its journey through the female reproductive tract and increase its chances of reaching and fertilizing the egg.
In conclusion, sperm is made up of a head, midpiece, and tail. The head contains genetic information, the midpiece provides energy, and the tail enables movement. Together, these components work together to ensure successful fertilization and the continuation of the species.
How Long do Sperm Live?
Sperm, also known as spermatozoa, are the reproductive cells found in semen that are responsible for fertilizing an egg to create a pregnancy. The lifespan of sperm varies depending on the conditions they are exposed to, but on average, sperm can live inside a woman’s body for up to five days.
After ejaculation, sperm travel through the cervix and into the uterus, where they can survive for about 24-48 hours. If an egg is released during this time and fertilization occurs, pregnancy can result. However, if fertilization does not occur, the sperm will eventually die and be flushed out of the body.
Factors that can affect the lifespan of sperm include:
- Cervical mucus: The consistency of cervical mucus can either support or hinder the survival of sperm. Thin, watery mucus can help sperm swim more easily, while thicker mucus can make it more difficult for them to reach the egg.
- Ovulation: Sperm have a higher chance of survival if they are present in the reproductive tract prior to ovulation, as this is the ideal time for fertilization to occur.
- Temperature: Sperm thrive in a slightly cooler environment, so excessive heat can decrease their lifespan. This is why the testicles are located outside of the body.
- Lifestyle factors: Certain lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use, can negatively impact sperm health and reduce their lifespan.
Understanding how long sperm can live is important for couples trying to conceive, as it can help determine the best time to engage in sexual intercourse for a higher chance of pregnancy. It is also important for individuals practicing contraception to be aware of sperm lifespan in order to make informed decisions about preventing pregnancy.
Can Sperm Survive Outside the Body?
Sperm survival outside the body is a topic of interest and importance for many individuals. Whether it’s for fertility purposes, contraception, or research, understanding the lifespan of sperm once it leaves the body is crucial.
How long can sperm survive outside the body?
Sperm has the ability to survive outside the body for a certain period of time, but its lifespan is relatively short compared to other bodily fluids. In optimal conditions, such as inside a woman’s reproductive tract, sperm can live for up to five days. However, once outside the body, their lifespan significantly decreases.
Factors affecting sperm survival outside the body:
- Temperature: Sperm cells are highly sensitive to temperature changes. Exposure to extreme heat or cold can quickly degrade their viability. It is essential to keep sperm cells in a controlled environment to maximize their chances of survival.
- Moisture: Sperm cells require a moist environment to survive. When exposed to air or dry conditions, they can quickly lose their ability to fertilize an egg.
- Exposure to chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as those found in lubricants or cleaning agents, can be detrimental to sperm health. It is important to avoid exposing sperm to potentially harmful substances.
Methods to preserve sperm outside the body:
In certain situations, such as fertility treatments or sperm banking, preserving sperm outside the body becomes necessary. There are several methods that can help prolong the lifespan of sperm:
- Cryopreservation: Sperm can be frozen and stored at very low temperatures, usually in liquid nitrogen. This method allows sperm to be stored for an extended period without significant degradation in quality.
- Specialized storage media: Sperm can also be stored in specialized media that provide optimal conditions for their survival. These media typically maintain a controlled temperature and moisture level.
In conclusion, sperm can survive outside the body for a limited time, depending on various factors such as temperature, moisture, and exposure to chemicals. Understanding these factors and employing suitable preservation techniques can help maximize the lifespan and quality of sperm cells when their storage or transportation is necessary.