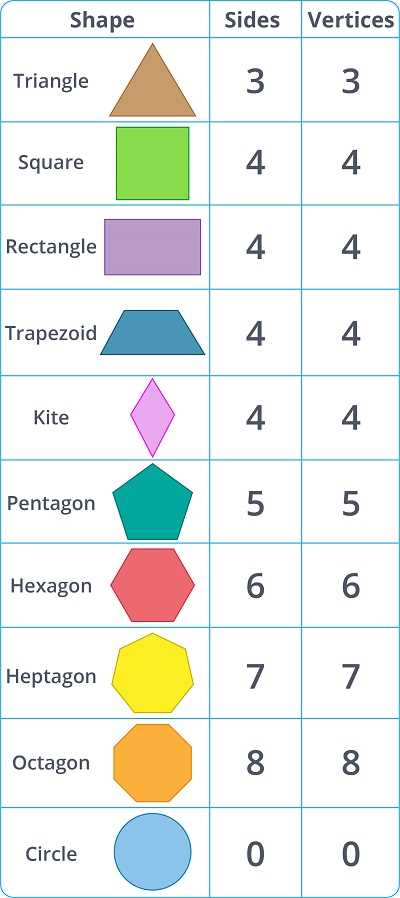
When it comes to shapes, we often think of the number of sides they have. The number of sides a shape has can tell us a lot about its properties and characteristics. In this article, we will be ranking different shapes from greatest to fewest number of sides.
Starting with the shape that has the greatest number of sides, we have the polygon. A polygon is a closed figure with straight sides. It can have any number of sides greater than or equal to three. Some examples of polygons include triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and so on. The more sides a polygon has, the more complex and intricate its shape becomes.
Next, we have the circle. Unlike the polygon, a circle does not have any sides. It is a closed curve that is perfectly round and symmetrical. The circle is unique because it has an infinite number of points on its circumference. This means that no matter how closely you look, you will never find any corners or edges. The circle’s lack of sides gives it a smooth and continuous appearance.
Finally, we have the line as the shape with the fewest number of sides. A line is a straight path that extends infinitely in both directions. It has no thickness or width, and therefore, no sides. A line is the simplest and most fundamental shape in geometry, representing the concept of length without any width or depth. It provides the basis for all other shapes and can be thought of as an infinite number of infinitely small points.
Ranking Shapes by Number of Sides
In geometry, shapes can be categorized based on the number of sides they have. This classification helps us understand the unique properties and characteristics of each shape. Let’s explore and rank some common shapes based on their number of sides.
Polygon: A polygon is a two-dimensional shape that is formed by straight lines. Polygons can have any number of sides, as long as they are all straight. For example, a triangle has three sides, a quadrilateral has four sides, and so on. So, in terms of the number of sides, polygons can be ranked from fewest to greatest.
Ranking Shapes:
- Triangle: With three sides, a triangle has the fewest number of sides among polygons. Triangles can further be classified into different types, such as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene, based on the lengths of their sides and angles.
- Quadrilateral: Next in line is the quadrilateral, which has four sides. Quadrilaterals can take various forms, such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, etc.
- Pentagon: Moving up the ranking, the pentagon has five sides. The name “pentagon” is derived from the Greek word “penta,” meaning five.
- Hexagon: Following the pentagon is the hexagon, which has six sides. The term “hexa” in hexagon comes from the Greek word for six.
- Heptagon: With the prefix “hepta” meaning seven, the heptagon consists of seven sides. It is also known as a septagon.
- Octagon: An octagon has eight sides, making it higher in the ranking. The word “octagon” is derived from the prefix “octa,” which signifies eight.
- Nonagon: Also known as an enneagon, a nonagon has nine sides. The prefix “nona” refers to the number nine in Greek.
- Decagon: Taking it a step further, the decagon has ten sides. The term “deca” in decagon represents the number ten.
This ranking provides a brief overview of some common shapes based on the number of sides they possess. Understanding the number of sides in a shape helps us distinguish and comprehend their unique properties and characteristics.
Polygon
A polygon is a two-dimensional shape that is formed by straight lines, known as sides, which are joined together to form a closed figure. The sides of a polygon do not intersect, and each side is connected to exactly two other sides. Polygons can have various numbers of sides, which gives them different names.
The number of sides in a polygon determines its name. For example, a polygon with three sides is called a triangle, while a polygon with four sides is called a quadrilateral. As the number of sides increases, the names of the polygons become more specific.
Here is a list of polygons ranked from greatest to fewest number of sides:
- Decagon: A polygon with ten sides.
- Nonagon: A polygon with nine sides.
- Octagon: A polygon with eight sides.
- Heptagon: A polygon with seven sides.
- Hexagon: A polygon with six sides.
- Pentagon: A polygon with five sides.
- Quadrilateral: A polygon with four sides.
- Triangle: A polygon with three sides.
Polygons are widely studied in geometry and have many practical applications. They can be found in various objects, such as buildings, signs, and even the patterns on a soccer ball. Understanding the properties and names of polygons is important for differentiating and classifying them in mathematical and real-world contexts.
Circle
A circle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that is perfectly round. It is defined as the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed center point. The center point is often marked with a small dot and is also the point from which the radius is measured. The radius is the distance from the center point to any point on the circumference of the circle. The circumference of a circle is the distance around its outer edge.
Circles have several notable properties. One of the most important properties is that all points on the circumference of a circle are equidistant from the center point. This means that any line segment drawn from the center to the circumference will have the same length. Additionally, the circumference of a circle can be found using the formula C = 2πr, where C is the circumference and r is the radius. The area of a circle can be found using the formula A = πr^2, where A is the area and r is the radius.
Unlike other shapes, a circle does not have any sides or angles. It is a curved shape that is continuous and smooth. Circles are found in many natural and man-made objects, such as wheels, coins, plates, and even celestial bodies like the sun and the moon. In geometry, circles are often used in calculations and constructions due to their unique properties. They are also used in various fields like engineering, architecture, and physics.
Ellipse
An ellipse is a geometric shape that is characterized by a curved and closed path. It is often described as an elongated or stretched circle. The shape of an ellipse is symmetrical, with two distinct focal points called foci and a major and minor axis. It is also a conic section, which means it can be formed by cutting a cone at a certain angle.
The major axis of the ellipse is its longest diameter, while the minor axis is its shortest diameter. The foci of an ellipse are located on the major axis, and the sum of the distances from any point on the ellipse to the two foci is always constant. This property is known as the focal property of an ellipse.
Ellipses have many applications in various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, and engineering. In mathematics, ellipses are commonly used to represent solutions to mathematical equations and describe the orbits of celestial bodies such as planets and satellites. In architecture and design, ellipses are used to create aesthetically pleasing shapes and curves. Additionally, ellipses can be found in everyday objects, such as the shape of an egg or an oval-shaped plate.
Compared to other shapes, such as triangles, squares, and pentagons, ellipses have an infinite number of sides. This is because an ellipse is a continuous curve that does not have distinct sides like polygons. However, in terms of the complexity of its shape, an ellipse is considered less complex than shapes with a larger number of sides.
Triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. It is one of the simplest and most basic shapes in geometry. Triangles can be classified based on their side lengths and angle measures.
Types of Triangles:
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three equal sides and three equal angles, each measuring 60 degrees. It is a regular polygon.
- Isosceles Triangle: An isosceles triangle has two equal sides and two equal angles. The angles opposite the equal sides are congruent.
- Scalene Triangle: A scalene triangle has no equal sides or angles. Each angle and side length is different from the others.
- Right Triangle: A right triangle has one angle measuring 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
- Obtuse Triangle: An obtuse triangle has one angle measuring more than 90 degrees. The other two angles are acute, measuring less than 90 degrees.
- Acute Triangle: An acute triangle has all angles measuring less than 90 degrees.
Triangles have a variety of properties and formulas that are useful in solving geometry problems. They are widely used in different fields of science, engineering, and architecture. The study of triangles is fundamental in understanding more complex shapes and concepts in mathematics.
Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral is a polygon that has four sides. It is a four-sided shape with four vertices or corners. The word “quadrilateral” comes from the Latin words “quadri” meaning four, and “latus” meaning side. Quadrilaterals are classified based on their properties, such as the lengths of their sides and the angles between those sides.
There are different types of quadrilaterals, including rectangles, squares, parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids. Let’s explore some of these types in more detail:
Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It has opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length. The opposite sides of a rectangle are also perpendicular to each other. The area of a rectangle can be found by multiplying its length and width.
Square
A square is a special type of rectangle where all four sides are equal in length. It has four right angles just like a rectangle. The area of a square can be found by multiplying the length of one side by itself.
Parallelogram
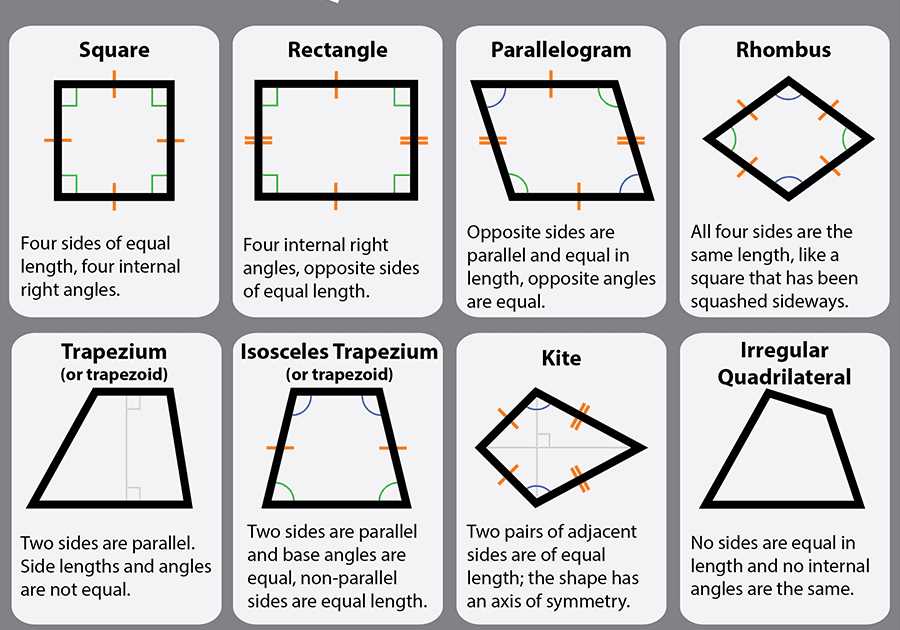
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length. The opposite angles of a parallelogram are also equal. The area of a parallelogram can be found by multiplying the length of a base by the height perpendicular to that base.
Rhombus
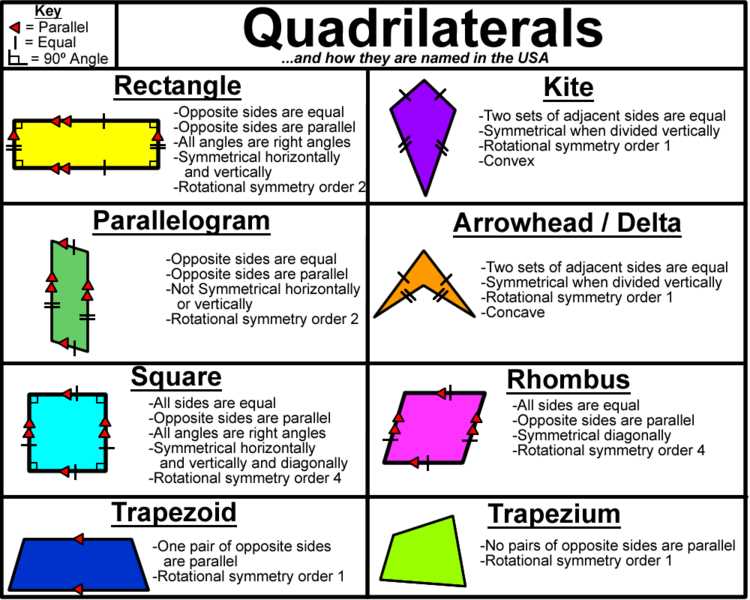
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length. It also has opposite sides that are parallel and opposite angles that are equal. The area of a rhombus can be found by multiplying the lengths of its diagonals and dividing by 2.
Trapezoid
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. It does not have any equal angles or sides. The area of a trapezoid can be found by multiplying the sum of the lengths of its parallel sides by the height perpendicular to those sides and dividing by 2.
- A quadrilateral has four sides and four vertices.
- Quadrilaterals can be classified into different types based on their properties.
- Examples of quadrilaterals include rectangles, squares, parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids.
- Each type of quadrilateral has unique properties, such as the lengths of its sides and the angles between those sides.
- The area of a quadrilateral can be found using different formulas depending on its type.
Pentagon
A pentagon is a polygon with five sides. It is a closed shape, meaning all of its sides are connected, and it has five angles.
Here are some key facts about the pentagon:
- The word “pentagon” comes from the Greek words “pente” meaning five and “gonia” meaning angle.
- All five sides of a pentagon are the same length.
- Each interior angle of a regular pentagon measures 108 degrees.
- A regular pentagon has five lines of symmetry.
- Pentagons can be found in nature, such as in certain starfish and flowers.
The pentagon is unique among the shapes we have ranked so far. It has fewer sides than the hexagon and the heptagon, but more sides than the triangle, square, and octagon. Therefore, we can rank the pentagon as follows:
- Hexagon (six sides)
- Heptagon (seven sides)
- Pentagon (five sides)
- Square (four sides)
- Octagon (eight sides)
- Triangle (three sides)
In conclusion, the pentagon is a fascinating shape with its distinct five sides. It holds a unique position in our ranking, showcasing the diversity of polygonal shapes.