
Photosynthesis is one of the fundamental processes that occur in plants, enabling them to convert sunlight into energy. It is a complex process that involves several steps, including the absorption of light, the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, and the production of glucose.
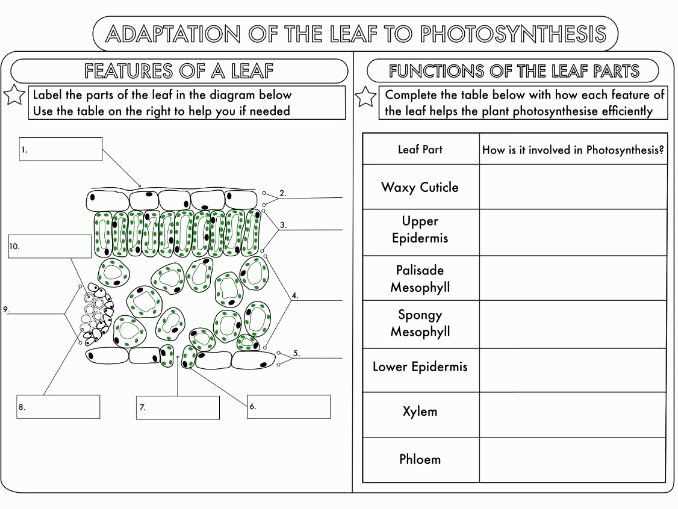
To understand photosynthesis better, students often use color by number activities, where they color different parts of a diagram or image according to a key. This type of activity not only helps students visually represent the different components of photosynthesis but also reinforces their understanding of the process.
The color by number photosynthesis answer key provides students with a guide to coloring the different components of the process. It typically includes labels for the different parts of a plant cell, such as the chloroplasts, mitochondria, and nucleus. It also includes labels for the key molecules involved in photosynthesis, such as water, carbon dioxide, glucose, and oxygen. By following the color by number key, students can accurately color in the different parts of the diagram, creating a visual representation of photosynthesis.
Understanding Photosynthesis and its Importance

Photosynthesis is a vital biological process that occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria. It is an intricate chemical reaction that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. This process takes place in chloroplasts, the specialized structures within plant cells responsible for capturing light energy.
The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two stages:
- Light-dependent reactions: This stage occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. Light energy is absorbed by pigments, such as chlorophyll, and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. Water is also split, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle): This stage occurs in the stroma of the chloroplasts. The ATP and NADPH produced in the previous stage are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of chemical reactions.
Photosynthesis is crucial for the survival of life on Earth. It is responsible for the production of oxygen, which is essential for aerobic respiration in organisms. Additionally, photosynthesis is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems, as it provides the necessary building blocks for the synthesis of organic compounds.
The importance of photosynthesis can be summarized as follows:
- It is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms, either directly or indirectly.
- It drives the carbon cycle by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converting it into organic matter.
- It plays a key role in maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- It is the basis of the food chain, as plants are the primary producers and form the foundation of most ecosystems.
- It contributes to the preservation of biodiversity by providing habitats and food sources for a wide range of organisms.
In conclusion, photosynthesis is an intricate process that utilizes sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it is essential for the survival of life on Earth and plays a fundamental role in maintaining ecosystem balance.
What is Photosynthesis and Why is it Important?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen. It takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in the green pigment called chlorophyll. This complex chemical process is crucial for the survival of life on Earth as it is the primary source of oxygen and plays a vital role in the carbon cycle.
During photosynthesis, plants capture energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This glucose serves as the main source of energy for plants to grow, reproduce, and carry out metabolic processes. Additionally, plants store excess glucose in the form of starch for later use.
Not only is photosynthesis important for the growth and survival of plants, but it also has a significant impact on the environment. Through the process of photosynthesis, oxygen is released into the atmosphere, which is essential for the respiration of animals and other organisms. This oxygen also helps maintain the balance of atmospheric gases and supports life on Earth.
Photosynthesis is also responsible for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming. By absorbing this carbon dioxide, plants act as natural carbon sinks and help mitigate the effects of climate change. Additionally, the process of photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain, as plants are the primary producers that provide energy and nutrients for other organisms, including humans.
The Importance of Photosynthesis:
- Produces oxygen, necessary for the respiration of animals and the balance of atmospheric gases.
- Removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Provides energy and nutrients for other organisms in the food chain.
- Allows plants to grow, reproduce, and carry out metabolic processes.
- Serves as the foundation for the carbon cycle.
The Process of Photosynthesis

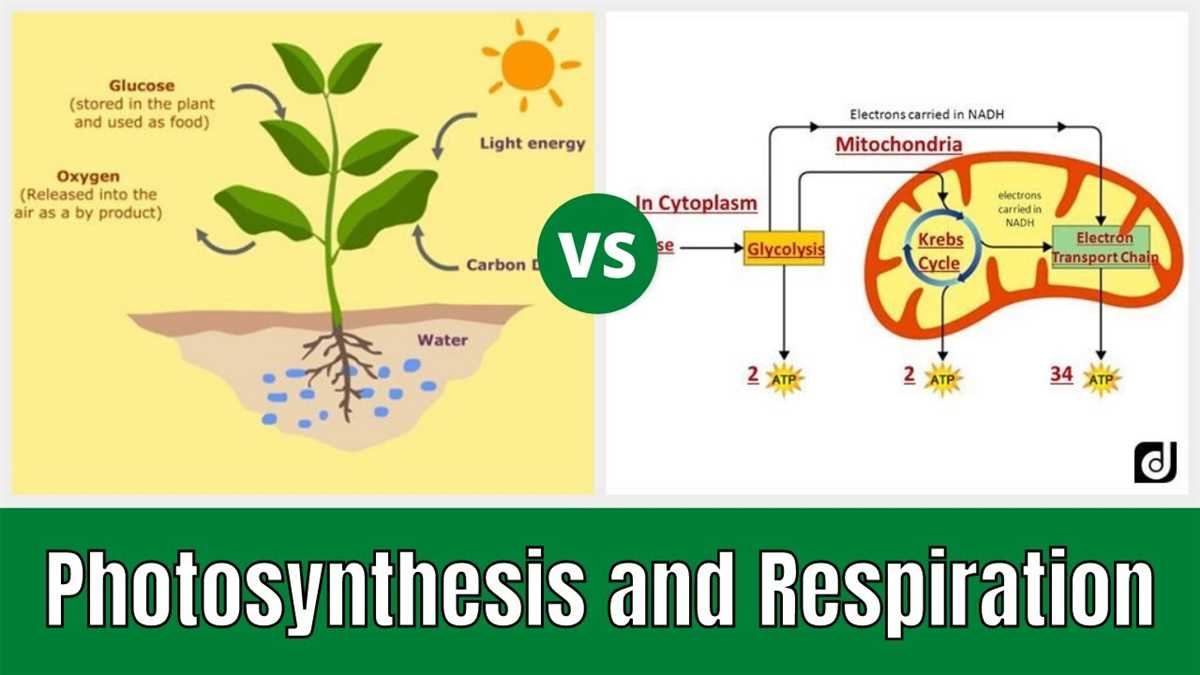
The process of photosynthesis is the means by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll. This biochemical process converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen, which is then released into the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells. These organelles contain chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs sunlight. When light hits a chlorophyll molecule, the energy is transferred to an electron. This energized electron passes through a series of chemical reactions known as the light-dependent reactions, where it is used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
The ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions are used in the second phase of photosynthesis, called the light-independent reactions or the Calvin cycle. In this cycle, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere enters the plant through tiny openings called stomata. The carbon dioxide is combined with the ATP and NADPH to produce glucose. This glucose can be used immediately by the plant for energy, or it can be stored as starch for later use.
Photosynthesis is an essential process for life on Earth. It is responsible for the oxygen in the atmosphere, as well as the food supply for all organisms that rely on plants. Without photosynthesis, life as we know it would not be possible.
Key terms:
- Photosynthesis: The process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize food.
- Chlorophyll: A pigment that absorbs sunlight and is responsible for the green color of plants.
- ATP: Adenosine triphosphate, a molecule that stores and releases energy.
- NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, a molecule that carries high-energy electrons.
- Calvin cycle: The second phase of photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide is converted into glucose.
- Stomata: Tiny openings in plant leaves that allow for the exchange of gases.
Overall, photosynthesis is an intricate process that plays a crucial role in the Earth’s ecosystems and sustains life on our planet.
The Role of Chlorophyll in Photosynthesis
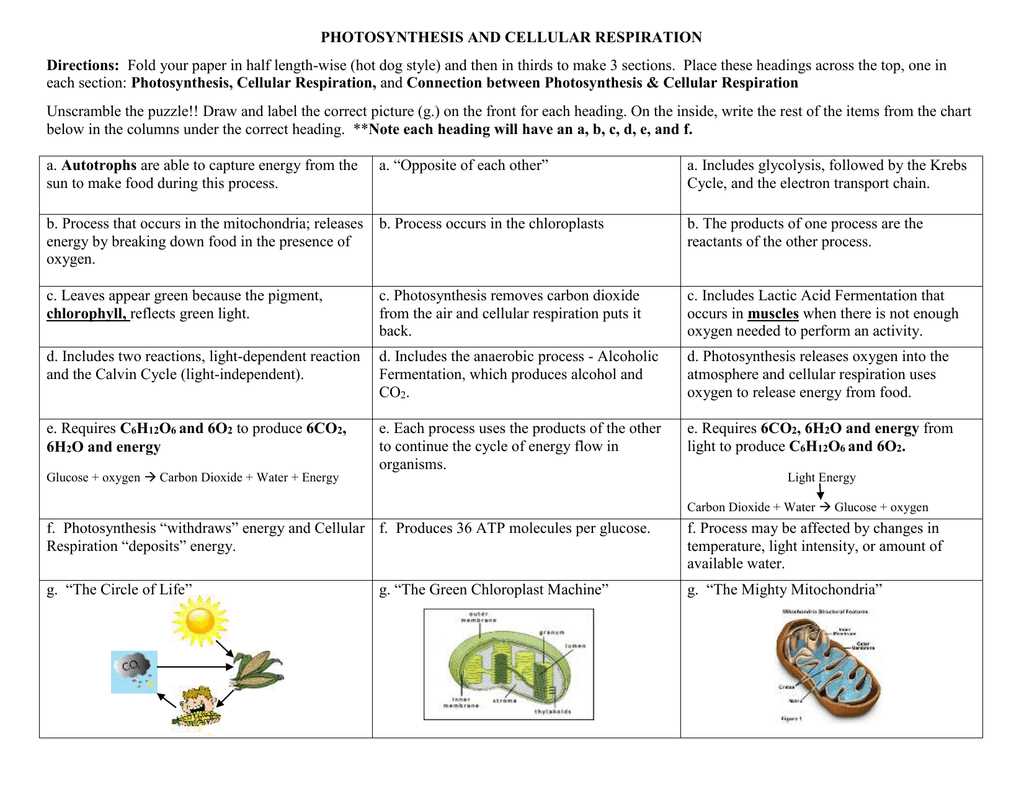
Chlorophyll is a crucial pigment found in plants and algae that plays a central role in the process of photosynthesis. It is responsible for capturing sunlight energy and converting it into chemical energy that can be used by the plant for growth and development.
Structure and Function: Chlorophyll molecules are located within specialized structures called chloroplasts, which are found in the cells of plant leaves. These pigment molecules have a distinct structure consisting of a porphyrin ring with a magnesium ion at its center. This structure allows chlorophyll to absorb light energy across a wide range of wavelengths, but it is most efficient at capturing red and blue light.
Light Absorption: When chlorophyll molecules absorb photons of light, the energy is transferred to the electrons in the porphyrin ring. This excites the electrons and initiates a series of biochemical reactions within the chloroplasts, leading to the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
- ATP: ATP is a molecule that stores and transports chemical energy within cells. It is used as a source of energy for various metabolic processes in the plant, including the synthesis of sugars and other organic compounds.
- NADPH: NADPH is a coenzyme that acts as a reducing agent in photosynthesis. It provides the necessary electrons and hydrogen ions for the synthesis of glucose and other organic molecules.
Carbon Dioxide Fixation: In addition to capturing light energy, chlorophyll also plays a crucial role in the process of carbon dioxide fixation. During this process, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is converted into glucose through a series of chemical reactions known as the Calvin cycle. Chlorophyll acts as a catalyst in these reactions, facilitating the conversion of carbon dioxide into a usable form of energy.
In conclusion, chlorophyll is an essential pigment in photosynthesis, as it is responsible for capturing sunlight energy and converting it into chemical energy. It plays a vital role in the synthesis of ATP, NADPH, and the fixation of carbon dioxide. Without chlorophyll, plants would not be able to carry out photosynthesis and sustain themselves.
Color by Number Activity to Learn Photosynthesis
Learning about photosynthesis can be a complex topic, but it is an essential process that occurs in plants and algae. To make the learning process more interesting and engaging, a color by number activity can be used. This activity combines the fun of coloring with the educational aspect of learning about photosynthesis.
The color by number activity consists of an image related to photosynthesis that is divided into different sections. Each section is assigned a number and corresponds to a specific color. Students are provided with a key that indicates which number corresponds to which color. By following the key, they can color the sections accordingly.
As students color the image, they will not only be engaged in a creative activity, but they will also be reinforcing their understanding of photosynthesis. They will be able to visually see how different components of photosynthesis, such as sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, come together to produce glucose and oxygen.
This hands-on activity helps students to remember the different stages and components of photosynthesis. It also allows them to actively participate in the learning process, rather than simply reading or listening to information. Additionally, the color by number activity can be used as an assessment tool or as a review activity to test students’ understanding of photosynthesis.
In conclusion, the color by number activity is an effective and engaging way to teach and reinforce the concept of photosynthesis. By combining coloring with learning, students can have a more interactive and enjoyable experience while gaining knowledge about this important biological process.
Answer Key for the Color by Number Activity
In the Color by Number activity on photosynthesis, students were given a picture of a plant cell and were asked to color the different organelles according to their functions in the process of photosynthesis. This activity was designed to help students visually understand the different parts of a plant cell and how they contribute to photosynthesis.
Below is the answer key for the Color by Number activity:
- Chloroplasts: Color these organelles green. They are responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- Mitochondria: Color these organelles orange. They are responsible for converting the chemical energy produced during photosynthesis into ATP, which is used by the cell for various functions.
- Nucleus: Color this organelle purple. It contains the plant cell’s genetic material and controls the cell’s activities, including photosynthesis.
- Cell Membrane: Color this structure blue. It surrounds and protects the plant cell, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell during photosynthesis.
- Cell Wall: Color this structure brown. It provides rigidity and support to the plant cell, helping it maintain its shape during photosynthesis.
- Vacuole: Color this organelle pink. It stores water, nutrients, and waste materials in the plant cell, playing a role in maintaining turgor pressure during photosynthesis.
By correctly coloring the different organelles and structures in the plant cell, students can visualize how each part contributes to the overall process of photosynthesis. This activity helps reinforce their understanding of photosynthesis and the importance of each organelle in the plant cell. It also encourages them to think critically and make connections between the structure and function of the cell.
Q&A:
Q: How can I get the answer key for the Color by Number activity?
A: You can request the answer key for the Color by Number activity from your teacher or instructor.
Q: Can I find the answer key online?
A: It depends on the specific Color by Number activity. Some answer keys may be available online, but it is best to check with your teacher or instructor for the most accurate answer key.
Q: What should I do if I can’t find the answer key for the Color by Number activity?
A: If you are unable to find the answer key, you can ask your teacher or instructor for assistance. They may be able to provide you with the correct answers or further guidance on how to complete the activity.
Q: How can I use the answer key for the Color by Number activity?
A: The answer key for the Color by Number activity can be used to check your answers and ensure that you have completed the activity correctly. It can also help you identify any mistakes and learn from them.