
In Unit 1, Session 7 of the LETRS (Language Essentials for Teachers of Reading and Spelling) professional development program, participants delve into the topic of word recognition and fluency. This session focuses on helping educators understand how to teach students to recognize and read words accurately and fluently, which is crucial for building strong reading skills.
During this session, participants explore various strategies and techniques to support word recognition and fluency. They learn about the importance of teaching phonics and phonemic awareness, as these skills are fundamental for proficient reading. Through interactive activities and discussions, educators also discover ways to develop students’ reading fluency through repeated reading, modeling, and guided practice.
The Letrs Unit 1 Session 7 Answers article provides a comprehensive overview of the key concepts covered in this session. It highlights the main strategies and techniques discussed and offers insights into how educators can apply these practices in their classrooms. By implementing the strategies and techniques presented in this session, teachers can help students become skilled and fluent readers.
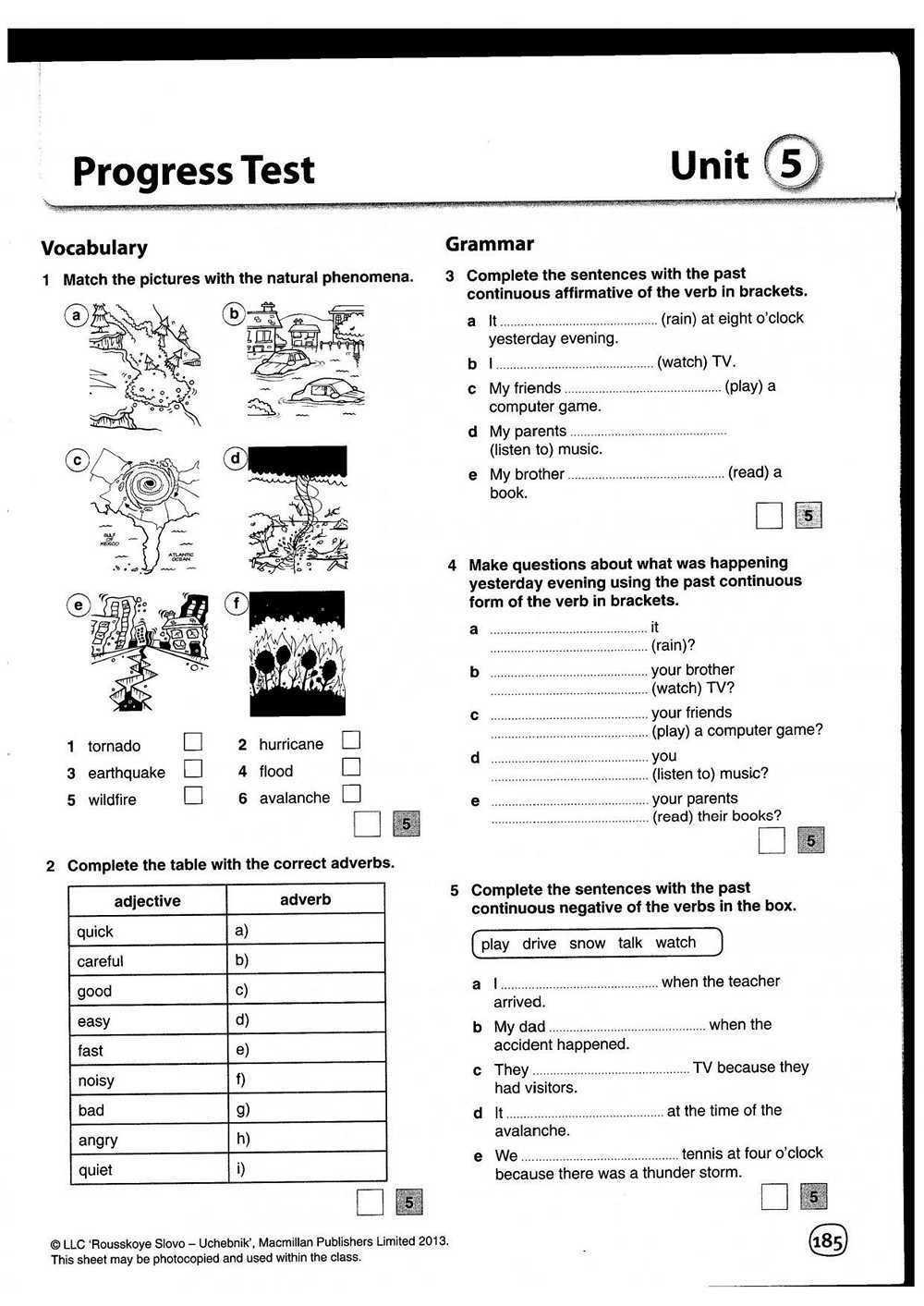
What are the Answers to Letrs Unit 1 Session 7?

Letrs Unit 1 Session 7 covers the topic of phonemic awareness and its importance in learning to read and spell. Phonemic awareness refers to the ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds in spoken words. It is a crucial skill that helps children develop strong reading and spelling abilities.
In this session, educators are introduced to various instructional strategies and activities that can be used to develop phonemic awareness in students. These include segmentation and blending of sounds, phoneme isolation, and phoneme categorization. These activities are designed to help students become more aware of the individual phonemes in words and develop their ability to manipulate them.
An important concept discussed in this session is the difference between phonemic awareness and phonics. While phonemic awareness focuses on the individual sounds in spoken words, phonics involves the relationship between sounds and written letters. Phonemic awareness is a prerequisite to phonics instruction, as students need to be able to hear and identify sounds before they can associate them with letters.
Some of the answers to the activities in Letrs Unit 1 Session 7 include:
- Activity 1: The answer to the first activity may vary depending on the specific sounds and words given, but it typically involves identifying the individual sounds in spoken words.
- Activity 2: The answer to this activity may involve blending or segmenting sounds to create new words. For example, if the given sound is /b/, students could blend it with /at/ to create the word “bat.”
- Activity 3: This activity may involve categorizing words based on their initial or final sounds. For example, students could categorize words that begin with the /s/ sound and words that end with the /t/ sound.
By completing these activities and understanding the importance of phonemic awareness, educators can effectively support their students’ development in reading and spelling skills.
Understanding the Importance of Phonemic Awareness
Phonemic awareness is a crucial component of early literacy development. It refers to the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate individual sounds, or phonemes, in spoken words. This skill is vital for children to become successful readers and writers.
Research has shown that phonemic awareness is a strong predictor of reading success. Children who have a solid foundation in phonemic awareness are more likely to excel in decoding words, spelling, and comprehension. They are also better equipped to understand the relationship between sounds and letters, which is essential for phonics instruction.
Phonemic awareness activities can be incorporated into daily instruction to support students in developing this critical skill. These activities include segmenting words into individual sounds, blending sounds to form words, manipulating sounds, and rhyming. Teachers can use various resources, such as flashcards, manipulatives, and games, to engage students in interactive phonemic awareness practice.
It is important to note that phonemic awareness is distinct from phonics. While phonemic awareness is focused on the individual sounds in spoken words, phonics emphasizes the relationship between sounds and letters. Phonemic awareness serves as a foundation for phonics instruction, as children need to understand and manipulate sounds before they can match them to letters.
Overall, phonemic awareness plays a crucial role in developing strong literacy skills. By fostering this skill, educators can support students in becoming proficient readers and writers. It is essential to provide explicit and systematic instruction in phonemic awareness to build a strong foundation for future literacy success.
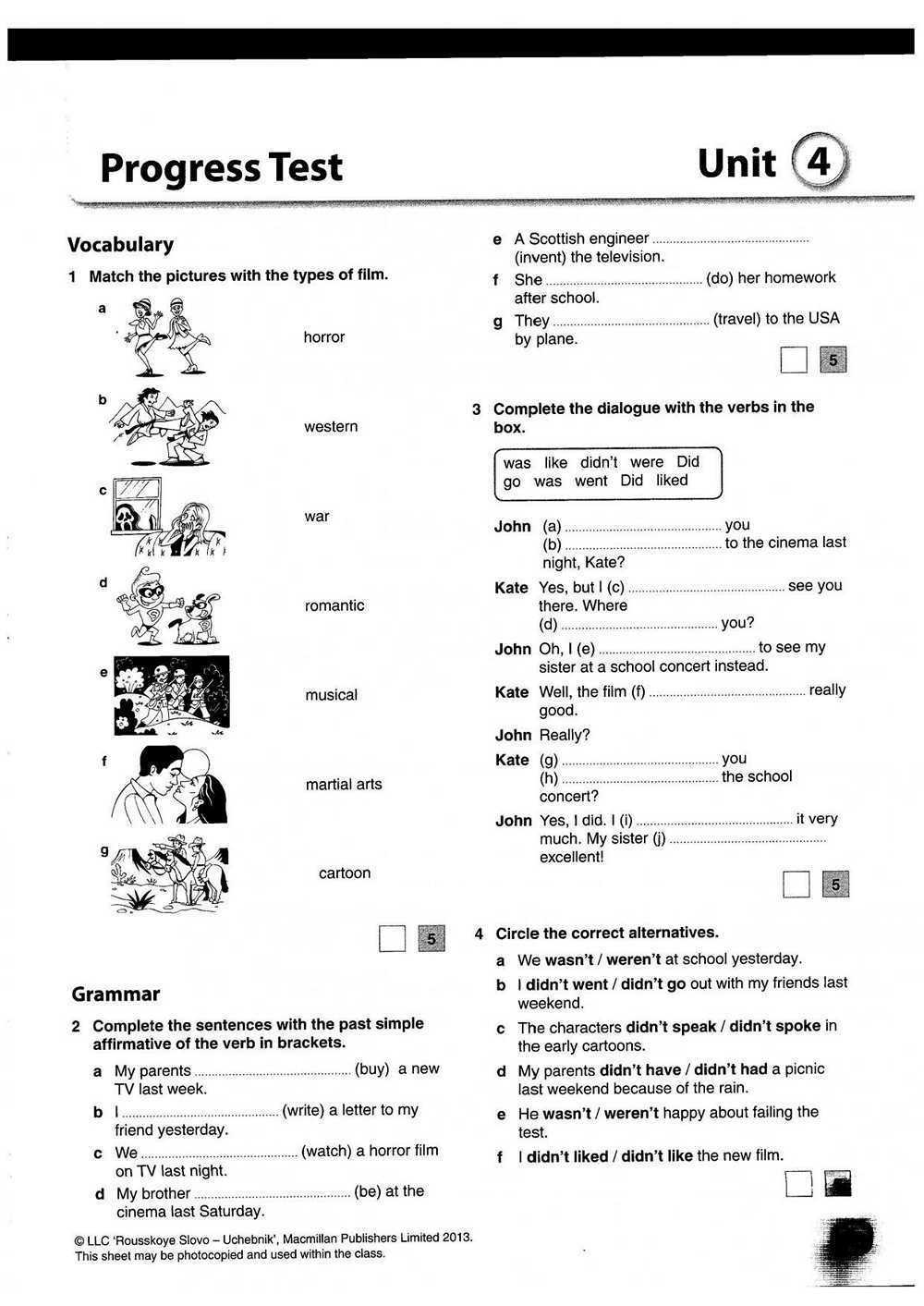
Exploring Strategies for Developing Phonemic Awareness
Phonemic awareness is a crucial skill in the early development of reading and literacy. It refers to the ability to hear and manipulate individual phonemes, which are the smallest units of sound in a language. Developing phonemic awareness lays the foundation for understanding the relationships between letters and sounds, and is an essential prerequisite for successful reading and spelling.
There are several effective strategies that educators can implement to support the development of phonemic awareness in young learners. One strategy is phoneme isolation, where students are asked to identify individual sounds in spoken words. For example, the teacher might say “cat” and ask the students to isolate the /k/ sound. This helps students to focus on the individual sounds within words and develop their ability to hear and identify phonemes.
- Phoneme segmentation is another useful strategy that involves breaking words down into their individual sounds. Students might be asked to say the sounds in the word “bat” (/b/-/a/-/t/) or to use manipulatives, such as letter tiles, to physically separate the sounds.
- Blending phonemes is another important skill that can be developed through strategies like phoneme manipulation. Students are asked to blend individual sounds together to form words. For example, the teacher might say the sounds /b/-/a/-/t/ and the students have to blend them to say “bat”. This helps students to understand the relationship between individual sounds and the formation of words.
- Rhyming and alliteration activities are also effective in developing phonemic awareness. By focusing on the similarities and differences in sound patterns, students become more aware of phonemes in words. For example, the teacher might ask students to identify words that rhyme with “cat” or to come up with a list of words that all start with the same sound.
By incorporating these strategies into daily instruction, educators can help students develop phonemic awareness and build a strong foundation for future reading and literacy skills.
Why Phonological Awareness is Essential for Reading and Writing
Phonological awareness is a crucial skill that plays a fundamental role in developing proficient reading and writing abilities. It refers to the ability to identify and manipulate the sounds in spoken language, including recognizing syllables, rhymes, and individual phonemes. Mastering phonological awareness enables individuals to understand the structure of words and accurately decode and encode them, leading to better reading comprehension and writing skills.
One reason why phonological awareness is essential for reading and writing is that it serves as a foundation for phonics instruction. Phonics involves the relationship between sounds and letters, and phonological awareness is a prerequisite for successful phonics learning. By recognizing and manipulating individual phonemes, students can make connections between sounds and letters, leading to improved decoding skills and the ability to accurately spell words.
Additionally, phonological awareness is closely linked to vocabulary development. Through activities like rhyming and segmenting words into syllables, students not only enhance their understanding of the sounds of language but also expand their vocabulary. This increased vocabulary knowledge directly contributes to improved reading comprehension and writing skills, as students are better able to comprehend and express themselves through a wider range of words.
Furthermore, phonological awareness plays a vital role in fluency and comprehension. By developing an awareness of the sounds in language, students can more easily recognize and analyze words, leading to smoother and more accurate reading. Through activities like phonemic segmentation and blending, students gain a deeper understanding of the structure of words and can more efficiently decode and understand text. This improved fluency and comprehension further supports their overall reading and writing abilities.
To sum up, phonological awareness is a critical skill that lays the foundation for successful reading and writing. From phonics instruction to vocabulary development and fluency and comprehension, phonological awareness plays a pivotal role in developing proficient literacy skills. By fostering phonological awareness, educators and parents can set students on a path towards becoming strong readers and writers.
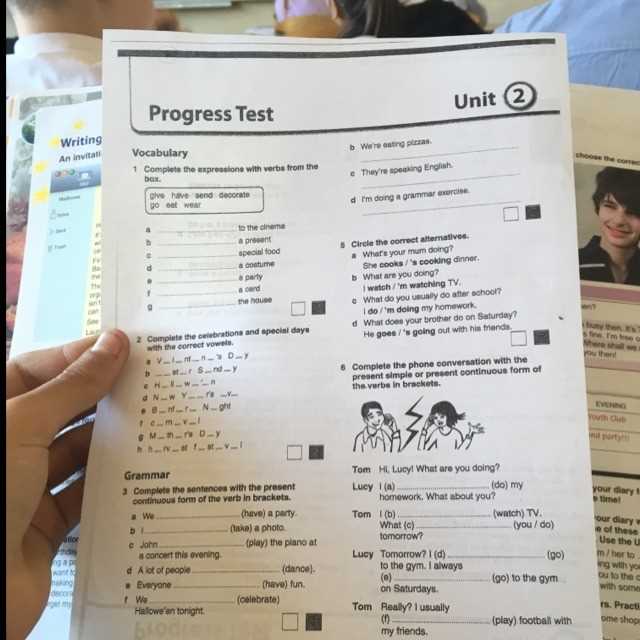
The Role of Phonics in Building Reading Skills
Phonics plays a crucial role in building reading skills as it helps children develop the fundamental understanding of the relationship between letters and sounds. Learning phonics allows children to decode written words by recognizing the letter-sound patterns, which is an essential skill for reading fluency and comprehension.
Phonics instruction involves teaching children the sounds that individual letters and letter combinations make. By mastering phonics, children can confidently sound out and blend words, which ultimately leads to improved reading abilities. It enables them to decode unfamiliar words and build their vocabulary, giving them the tools to read independently.
Phonics instruction emphasizes the importance of phonemic awareness, which is the ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds in spoken words. It helps children understand that words are made up of smaller units of sound, or phonemes. By becoming aware of these phonemes, children can then apply their knowledge of phonics to connect the corresponding letters and sounds.
Systematic and explicit phonics instruction ensures that children are taught the different letter-sound correspondences in a structured manner. This sequential approach helps children build a solid foundation in phonics, gradually introducing more complex letter-sound patterns and skills. It allows children to develop their reading skills incrementally, building upon previously learned phonics rules.
Additionally, phonics instruction provides children with strategies for reading and spelling irregular words that do not follow the typical letter-sound patterns. By understanding phonics principles, children can apply their knowledge to decipher and spell words accurately, even if they encounter unfamiliar or irregular spellings.
The use of phonics in building reading skills is supported by research and has proven to be effective in improving reading abilities in children. By teaching children the foundational skills of phonics, educators can empower them with the necessary tools to become fluent and confident readers.
Understanding the Impact of Oral Language and Vocabulary Development
Oral language and vocabulary development play a crucial role in a child’s overall academic success. Strong oral language skills enable children to express themselves clearly, understand instructions and explanations, and engage in meaningful conversations with peers and adults. Additionally, a rich vocabulary enhances a child’s reading comprehension, writing ability, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. Therefore, it is essential for educators and parents to understand the impact of oral language and vocabulary development and actively support their growth.
One way to support oral language development is by creating a language-rich environment. This can be achieved by engaging children in conversations, storytelling, and discussions that encourage active participation and thoughtful responses. Additionally, providing opportunities for children to engage with a variety of texts, such as books, poems, and songs, exposes them to new words, sentence structures, and ideas. Incorporating vocabulary-building activities, such as word games, word walls, and vocabulary journals, further enhances their language skills.
In conclusion, oral language and vocabulary development are essential for a child’s overall academic success. Providing a language-rich environment and engaging children in meaningful conversations and activities can greatly support their growth in these areas. By actively promoting oral language and vocabulary development, educators and parents can empower children with the necessary skills to excel academically and beyond.
Assessing Phonemic Awareness and Planning for Instruction

Phonemic awareness is a critical skill for students to develop in order to become proficient readers and spellers. In this unit, we have explored the importance of phonemic awareness and how it can be assessed and planned for instruction.
Assessing phonemic awareness involves administering various tasks and activities that measure a student’s ability to manipulate and identify individual sounds in words. These assessments can help educators determine the specific areas of phonemic awareness that a student may struggle with and guide their instructional planning.
During the assessment process, it is important to consider the different aspects of phonemic awareness, such as phoneme isolation, phoneme identity, phoneme categorization, phoneme blending, and phoneme segmentation. By using a variety of assessment tasks, educators can gain a comprehensive understanding of a student’s phonemic awareness skills and tailor instruction accordingly.
Once phonemic awareness has been assessed, educators can use the results to plan targeted instruction. This may involve implementing specific activities and lessons that focus on the areas of weakness identified during the assessment. It is important to provide explicit and systematic instruction that includes modeling, guided practice, and independent practice to help students develop their phonemic awareness skills.
Additionally, educators can incorporate phonemic awareness activities into their daily instruction across various subject areas. This integration of phonemic awareness into different content areas can help reinforce skills and provide additional practice opportunities for students.
To support students’ phonemic awareness development, educators should also provide ongoing monitoring and assessment to track progress and adjust instruction as needed. This continuous assessment and instructional planning cycle ensures that students receive the support they need to become proficient readers and spellers.
- In conclusion, assessing phonemic awareness and planning for instruction is crucial for promoting reading and spelling success in students. By understanding a student’s phonemic awareness abilities and tailoring instruction based on their needs, educators can support their growth and development in becoming proficient readers and spellers.