
Human beings have always been a part of the Earth’s ecosystem, but in recent centuries, our impact on the environment has been significant and, in many cases, negative. The term “Anthropocene” was coined to describe this new geological epoch, in which human activity has become a dominant force shaping the planet. This article will explore some key ways in which human beings have impacted the environment and discuss the consequences of these actions.
One of the most apparent ways in which humans have influenced the environment is through deforestation. Forests cover about 30% of the Earth’s land surface, but they are being destroyed at an alarming rate. This deforestation is primarily driven by the demand for agricultural land, logging, and urbanization. The consequences of deforestation are far-reaching, including the loss of habitat for countless species, the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, and increased soil erosion and flooding.
Another major impact of human activity on the environment is the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Burning fossil fuels for energy and industrial processes has led to a significant increase in carbon dioxide levels, which is a major contributor to climate change. Additionally, other greenhouse gases, such as methane and nitrous oxide, are released through agricultural practices and waste management. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures, melting ice caps, and more extreme weather events.
Furthermore, human beings have also had a profound impact on the world’s water resources. Increasing demands for water, both for agricultural and industrial use, have led to overexploitation of rivers, lakes, and groundwater reserves. This has resulted in the depletion of freshwater sources, increased salinization of soils, and the loss of aquatic habitats. Additionally, pollution from industrial and agricultural activities has contaminated water bodies, making them unfit for consumption and endangering aquatic life.
In conclusion, the human impact on the environment is undeniable and has far-reaching consequences. Deforestation, the release of greenhouse gases, and the exploitation of water resources are key ways in which human activity has negatively affected the planet. It is crucial that we acknowledge these impacts and take action to mitigate them, as our future and the health of the Earth depend on it.
The Anthropocene Human Impact on the Environment Answer Key
The Anthropocene, a term coined by scientists to describe the current geological epoch we are living in, is defined by the significant impact humans have had on the environment. This impact has been unprecedented in scale and scope, leading to a number of environmental challenges that we now face.
One of the key human activities that has contributed to the Anthropocene is the burning of fossil fuels. This has resulted in an increase in greenhouse gas emissions, which has in turn led to climate change. The rapid rise in global temperatures is causing a range of effects, including melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events.
Another major human impact on the environment is deforestation. Trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, helping to regulate the Earth’s climate. However, widespread deforestation for agriculture, logging, and urbanization has resulted in the loss of millions of hectares of forest each year. This not only reduces the Earth’s carbon sinks, but also threatens the habitats of countless plant and animal species.
In addition, the Anthropocene has seen a significant increase in waste generation and pollution. The production and consumption of goods and services has resulted in the generation of vast amounts of waste, much of which ends up in landfills or pollutes our oceans and rivers. The pollution of air, water, and soil has detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems.
To mitigate the impact of the Anthropocene on the environment, it is crucial that we take action to reduce our carbon emissions, preserve forests and biodiversity, and implement sustainable waste management practices. This requires a global effort and a shift towards more sustainable and regenerative practices that prioritize the long-term health and well-being of our planet.
The Concept of Anthropocene
The concept of Anthropocene refers to the current geological epoch in which human activities have had a significant impact on the Earth’s ecosystems. The term was coined by Paul Crutzen, a Dutch Nobel laureate in atmospheric chemistry, in 2000. It is derived from the Greek words “anthropos,” meaning human, and “kainos,” meaning new or recent. The Anthropocene can be seen as a marker of the immense influence that humans have had on the planet, surpassing any previous geological epoch.
Human activities in the Anthropocene have brought about profound changes in the Earth’s environment, including deforestation, urbanization, pollution, and climate change. These impacts have led to biodiversity loss, the degradation of ecosystems, and the alteration of natural processes. One of the key aspects of the Anthropocene is the acceleration of these changes, with many of them occurring at a rate unprecedented in geological history.
In the Anthropocene, human actions have become a dominant force shaping the planet. The scale and magnitude of human impact are evident in various indicators, such as rising carbon dioxide levels, the extinction of species, and the alteration of the Earth’s climate. The concept of the Anthropocene highlights the urgency for humans to recognize their role in the changing environment and take proactive measures to mitigate the negative effects of their actions.
The Consequences of Deforestation
Deforestation is the deliberate clearing of forests or trees, primarily caused by human activity. It has numerous negative consequences on both the environment and human society.
Loss of Biodiversity: Deforestation destroys the habitats of countless plant and animal species, leading to a significant loss of biodiversity. The removal of trees disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to the extinction of many species and a decrease in overall ecosystem health.
Climate Change: Trees play a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate by trapping carbon dioxide (CO2) through photosynthesis. Deforestation disrupts this process, releasing large amounts of stored carbon back into the atmosphere. As a result, deforestation contributes to the greenhouse effect and global warming, further exacerbating climate change.
Soil Erosion and Loss: Trees act as a natural barrier against soil erosion, their roots holding the soil in place. When forests are cleared, the soil becomes vulnerable to erosion caused by wind and water. This leads to desertification, decreased soil fertility, and increased sedimentation in rivers and streams, which negatively impacts both agricultural productivity and water quality.
Loss of Indigenous Cultures: Many indigenous communities rely on forests for their livelihoods and cultural practices. Deforestation directly threatens their way of life, as it diminishes their access to traditional resources such as food, medicine, and housing materials. Furthermore, the loss of forests can contribute to social and economic challenges for these communities.
Loss of Economic Opportunities: While deforestation may provide short-term economic gain through logging, mining, and agricultural expansion, the long-term consequences are detrimental. Deforestation reduces the availability of natural resources, limits ecotourism potential, and degrades overall environmental services, leading to decreased economic opportunities in the long run.
In summary, deforestation has far-reaching consequences that affect not only the environment but also society as a whole. It is crucial to recognize the importance of preserving forests and implementing sustainable practices to mitigate the negative impacts of deforestation.
Industrialization and Pollution
Industrialization, the process of developing industries in a country or region on a large scale, has had a profound impact on the environment. The rapid growth of industries during the past two centuries has resulted in significant pollution and degradation of natural resources. Industrial activities generate various types of pollution, including air pollution, water pollution, and soil contamination.
Air pollution is one of the most serious consequences of industrialization. Industries release large amounts of toxic gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere, leading to smog, acid rain, and an increase in respiratory diseases. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, for energy production and transportation is a major contributor to air pollution. Sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide are among the pollutants emitted by industrial processes.
Water pollution is another consequence of industrialization. Industries release wastewater, containing harmful chemicals, heavy metals, and other pollutants, into rivers, lakes, and oceans. This pollution has devastating effects on aquatic ecosystems and poses significant risks to human health. Industrial activities, such as mining and manufacturing, also contribute to the contamination of groundwater, which is a critical source of drinking water for many communities.
Furthermore, industrial activities have led to soil contamination. Chemical spills, improper waste disposal, and the use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture have resulted in the accumulation of toxic substances in the soil. This contamination affects soil fertility, damages ecosystems, and can enter the food chain, posing risks to human health. Industrialization has also led to deforestation and habitat destruction, further exacerbating the negative impact on the environment.
- Industrialization has resulted in air pollution due to the release of toxic gases and particulate matter.
- Water pollution is another consequence of industrial activities, with harmful chemicals and pollutants being discharged into water bodies.
- Soil contamination has occurred as a result of industrial practices, including chemical spills and improper waste disposal.
- Deforestation and habitat destruction have also been influenced by industrialization.
Climate Change and Global Warming
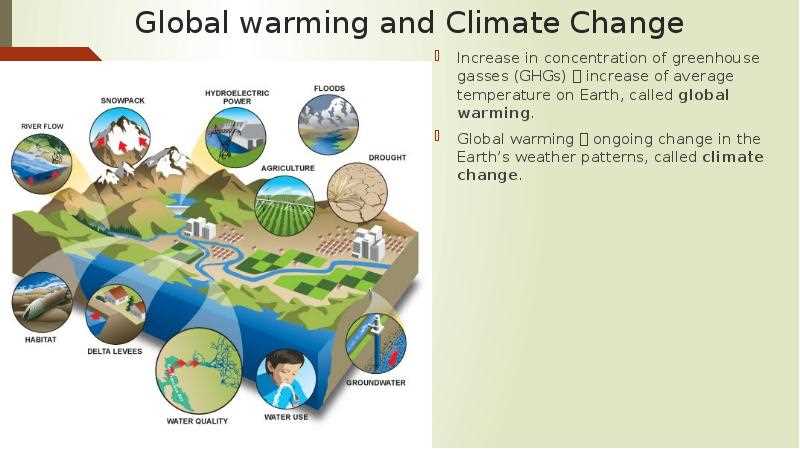
Climate change and global warming are two interconnected phenomena that pose significant threats to the planet and its inhabitants. The Earth’s climate has always been subject to natural variations, but human activities in the Anthropocene era have accelerated these changes to unprecedented levels. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes, and agricultural practices have released large amounts of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun, leading to a rise in global temperatures and disrupting the Earth’s climate system.
Global warming refers specifically to the increase in the Earth’s average surface temperature, primarily due to the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by human activities. The consequences of global warming are far-reaching and include rising sea levels, more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, and extreme weather events such as hurricanes and floods. These changes not only affect the natural environment but also have profound implications for human societies, including food security, water resources, and public health.
One of the key challenges in addressing climate change and global warming is the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This involves transitioning to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, such as renewable energy, and implementing energy-efficient practices in all sectors of society. Additionally, efforts to adapt to the changing climate and mitigate its impacts are crucial. This includes implementing strategies to protect vulnerable communities, enhancing coastal defenses, and promoting sustainable land and water management.
In conclusion, climate change and global warming are urgent issues that require immediate attention and action from individuals, governments, and the international community. By understanding the causes and consequences of these phenomena and taking proactive measures to reduce emissions and adapt to the changing climate, we can strive towards a more sustainable and resilient future for both the planet and its inhabitants.
Loss of Biodiversity

Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including all organisms found in different ecosystems. It is a crucial component of the planet’s health and is essential for the functioning of ecosystems and the provision of ecosystem services. However, human activities have led to a significant loss of biodiversity worldwide.
One major cause of biodiversity loss is habitat destruction. Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture have resulted in the destruction and fragmentation of natural habitats. This has led to the loss of species and the disruption of ecological processes. Many species are unable to adapt to the changes in their habitat, leading to their decline or extinction.
Another contributing factor to biodiversity loss is pollution. Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and human waste has contaminated ecosystems, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic species. Pollutants can accumulate in the environment, causing long-term harm to species and disrupting their reproductive processes. Marine ecosystems, in particular, are at risk due to pollution from plastic waste, oil spills, and chemical runoff.
Overexploitation of natural resources is also a significant driver of biodiversity loss. Hunting, fishing, and illegal wildlife trade have led to the depletion of many species populations. In many cases, these activities are unsustainable and threaten the survival of various plants and animals. The loss of keystone species can have cascading effects on entire ecosystems, leading to imbalances and reduced biodiversity.
If immediate action is not taken to address the loss of biodiversity, the consequences could be severe. The loss of essential species can disrupt the stability of ecosystems and compromise their ability to provide valuable services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation. It is essential for individuals, governments, and organizations to work together to conserve and protect biodiversity through sustainable practices, habitat conservation, and the establishment of protected areas.
Sustainable Solutions for the Future
In conclusion, the anthropocene human impact on the environment is undeniable and has led to significant challenges for the planet. However, there are sustainable solutions that can help mitigate these issues and ensure a better future for all.
1. Renewable Energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can significantly reduce carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. Investing in and supporting the development of renewable energy technologies is crucial for a sustainable future.
2. Sustainable Agriculture: Adopting practices such as organic farming, agroforestry, and precision agriculture can help reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. Implementing sustainable farming techniques can preserve soil health, protect biodiversity, and minimize the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
3. Circular Economy: Moving towards a circular economy model, where resources are reused, recycled, and repurposed, can help reduce waste generation and the extraction of raw materials. Emphasizing product design for recyclability and implementing effective waste management systems are essential steps towards achieving a circular economy.
4. Conservation and Restoration: Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and coral reefs, is crucial for biodiversity conservation and climate change mitigation. Supporting initiatives that focus on conservation and restoration efforts can help mitigate the negative impacts of human activities on the environment.
5. Sustainable Urban Planning: Creating sustainable cities that prioritize efficient public transportation, green spaces, and energy-efficient buildings can reduce carbon emissions, promote active lifestyles, and improve the quality of life for urban residents. Integrating sustainable urban planning principles into city development is essential for sustainable growth.
- Investing in research and innovation: Continued investment in research and innovation is necessary to develop new sustainable technologies, solutions, and practices. This includes advancements in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, waste management, and more.
- Education and awareness: Educating individuals and raising awareness about the anthropocene human impact on the environment is crucial for cultivating sustainable behaviors and lifestyles. Promoting environmental education in schools, communities, and through media platforms can foster a sense of responsibility towards the planet.
- Policy and regulation: Governments and international organizations play a crucial role in implementing policies and regulations that promote sustainable practices and hold industries accountable for their environmental impact. Strong environmental policies can incentivize businesses and individuals to adopt sustainable behaviors.
In conclusion, addressing the anthropocene human impact on the environment requires a multi-faceted approach that involves collaboration between governments, industries, communities, and individuals. By implementing sustainable solutions and making conscious choices, we can work towards a more resilient and harmonious relationship with our planet.