Bigfoot, also known as Sasquatch, is one of the most well-known creatures in cryptozoology. For decades, people have reported sightings and shared stories of encounters with this elusive creature. However, many skeptics dismiss these claims as mere myths or hoaxes. In order to determine the truth behind the existence of Bigfoot, it is important to apply the scientific method.
The scientific method is a systematic approach used by scientists to investigate and understand phenomena. It involves making observations, formulating hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing data to draw conclusions. Applying the scientific method to the study of Bigfoot can help separate fact from fiction and provide a more objective analysis of the available evidence.
One of the first steps in applying the scientific method to the study of Bigfoot is collecting and analyzing eyewitness testimonies. These accounts can provide valuable information about the creature’s physical appearance, behavior, and habitat. However, it is important to note that eyewitness testimonies can be subjective and influenced by various factors such as memory biases and cultural beliefs. Therefore, it is crucial to approach these testimonies with a critical and objective mindset.
In addition to eyewitness testimonies, physical evidence is another important aspect of the scientific method in studying Bigfoot. Footprints, hair samples, and photographs can all be analyzed using scientific techniques to determine their authenticity and establish the presence of an unknown creature. DNA analysis, for example, can help identify the source of hair samples and determine if they belong to a known animal species or something entirely new.
What is Bigfoot?
Bigfoot, also known as Sasquatch, is a legendary creature that is said to inhabit forests, mountains, and other remote areas, primarily in North America. Described as a tall, ape-like creature, Bigfoot is said to stand between 7 and 10 feet tall and weigh around 500 pounds. It is often reported to have thick, dark fur, a large, muscular build, and distinctive footprints that resemble those of a human, but much larger.
The existence of Bigfoot has been the subject of much debate and controversy. While many people believe in the existence of Bigfoot based on personal sightings and anecdotal evidence, the scientific community largely remains skeptical. Scientists argue that the lack of physical evidence, such as bones or DNA samples, makes it difficult to prove the existence of such a creature. They also question the credibility of the anecdotal evidence, as it often relies on eyewitness accounts, which can be unreliable.
Despite the skepticism of the scientific community, the search for Bigfoot continues to captivate the public’s imagination. Researchers and enthusiasts alike conduct expeditions, analyze footprint casts, and listen for vocalizations in an effort to gather evidence of Bigfoot’s existence. Some even claim to have captured photographs and videos of the creature, although these have often been debunked as hoaxes.
Understanding the scientific method

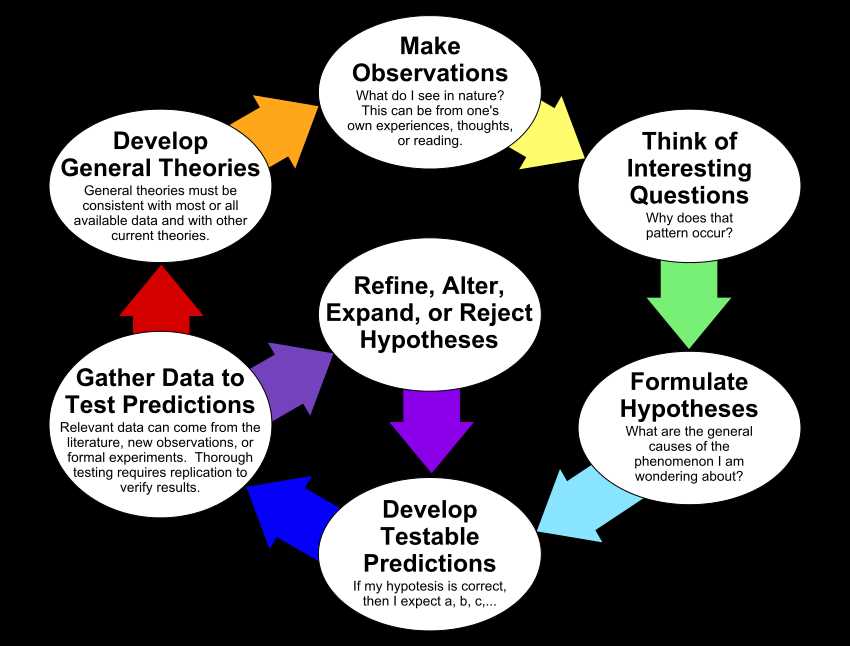
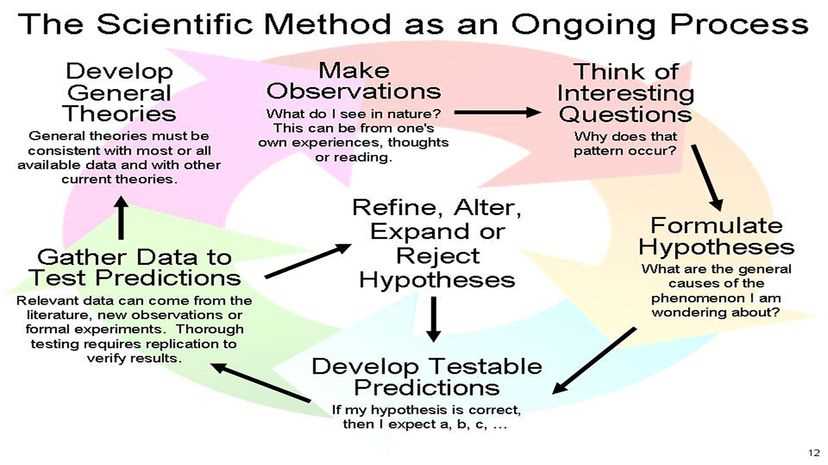
The scientific method is a systematic approach used by scientists to investigate and understand the natural world. It is a process that involves observation, hypothesis formation, experimentation, and analysis of results. By following the scientific method, scientists are able to make objective and evidence-based conclusions.
The first step in the scientific method is observation. Scientists use their senses to gather information about a particular phenomenon or problem. They may also review existing knowledge and literature to gain a better understanding of the topic. Once a scientist has made thorough observations, they can formulate a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon. It is an educated guess that can be supported or refuted through experimentation. The hypothesis should be clear, specific, and based on existing knowledge. It is important for scientists to create a hypothesis that can be tested and potentially proven false, as this is the foundation for the scientific method.
After a hypothesis has been formulated, scientists design and conduct experiments to test their hypothesis. These experiments must be carefully planned and controlled to ensure accurate results. Variables are manipulated and measured, and data is collected and analyzed. The results of the experiment are then compared to the initial hypothesis to determine if it is supported or refuted.
The final step in the scientific method is drawing conclusions. Scientists analyze the data collected from their experiments and use statistical analysis to determine the significance of their results. If the results support the hypothesis, then it may be considered valid. If the results do not support the hypothesis, then it may need to be revised, or a new hypothesis may need to be formed.
The scientific method is an iterative process, meaning that scientists often repeat experiments or conduct further research to confirm their findings. It is a rigorous and objective approach that allows scientists to gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and make reliable predictions.
Hypothesis: Is Bigfoot real?
There has been an ongoing debate for years regarding the existence of Bigfoot, also known as Sasquatch. Numerous eyewitness accounts, footprints, and alleged sightings have fueled speculation about the reality of this elusive creature. However, skeptics argue that the evidence presented so far is inconclusive and can be easily explained by natural phenomena or human pranks.
The hypothesis to be tested is whether Bigfoot, a large, hairy, humanoid creature, exists in the wild. This hypothesis assumes that there is a population of undiscovered primates living in remote areas, which has managed to evade scientific detection for centuries. If proven true, the existence of Bigfoot would revolutionize our understanding of the animal kingdom and our relationship with the natural world.
It is important to approach the investigation of Bigfoot’s existence using the scientific method. This involves formulating a hypothesis, designing and conducting experiments, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions based on the evidence gathered. Only through rigorous scientific inquiry can we ascertain whether Bigfoot is a legitimate creature or a product of folklore and imagination.
Evidence for Bigfoot:
- Eyewitness testimonies: There have been numerous reports from credible witnesses who claim to have seen Bigfoot in different parts of the world.
- Footprints: Some alleged Bigfoot footprints have been found, showing a unique morphology and stride pattern that are distinct from known animal tracks.
- Audio recordings: Various audio recordings exist, capturing unidentified vocalizations believed to be emitted by Bigfoot.
Critical analysis and skepticism:
- Hoaxes: Many skeptics argue that the majority of Bigfoot evidence can be attributed to hoaxers seeking attention or monetary gain.
- Misidentification: It is possible that witnesses have mistaken known animals or natural phenomena for Bigfoot due to fear, excitement, or lack of familiarity with the local wildlife.
- Lack of physical evidence: Despite numerous claims and alleged sightings, no conclusive physical evidence, such as DNA, remains, or intact specimens, has been found to definitively prove the existence of Bigfoot.
In order to determine whether Bigfoot is a real creature or a myth, it is essential to conduct rigorous scientific investigations that take into account both the evidence supporting its existence and the skeptical arguments against it. Only by adopting a balanced and objective approach can we hope to uncover the truth behind the mystery of Bigfoot.
Experiment: Gathering Evidence
The scientific method requires gathering evidence to support or refute a hypothesis. In the case of Bigfoot, researchers have devised various experiments to collect evidence of Bigfoot’s existence. These experiments often involve the collection of physical evidence, eyewitness testimonies, and data analysis.
Physical Evidence
In an attempt to gather physical evidence of Bigfoot, researchers have conducted extensive searches in areas where Bigfoot sightings have been reported. These searches involve examining footprints, hair samples, and any other potential traces left behind. The goal is to collect physical evidence that can be analyzed and compared to known species to determine if it belongs to an unidentified primate.
One specific experiment involves setting up camera traps in Bigfoot hotspots. These camera traps are motion-activated and capture images or videos when triggered. Researchers hope that by monitoring these camera traps over an extended period, they will capture clear evidence of Bigfoot’s existence, such as a clear photograph or a video.
Eyewitness Testimonies
Another critical aspect of gathering evidence for Bigfoot involves collecting eyewitness testimonies. Researchers interview individuals who claim to have seen Bigfoot to gather information about the sighting. These testimonies are valuable in determining the location, time, and characteristics of the alleged Bigfoot encounter.
Researchers analyze the testimonies for consistency and conduct follow-up interviews if necessary. By comparing multiple eyewitness testimonies, researchers can look for patterns and similarities that may further support the existence of Bigfoot.
Data Analysis
Data analysis plays a crucial role in gathering evidence for Bigfoot. Researchers analyze collected physical evidence, such as footprints or hair samples, using various scientific techniques. For example, footprint casts can be compared to known primate footprints to identify any similarities or unique characteristics.
Additionally, researchers may employ DNA analysis to examine hair samples found in Bigfoot hotspots. This analysis can help determine if the hair belongs to an unknown primate species or if it can be attributed to a known animal.
All data collected, whether it be physical evidence or eyewitness testimonies, is carefully analyzed, compared, and interpreted using the scientific method. Researchers strive to gather as much evidence as possible to support or refute the hypothesis of Bigfoot’s existence, following the principles of the scientific method.
Analysis of the evidence
When analyzing the evidence surrounding Bigfoot, it is important to consider the scientific method and apply critical thinking skills. One key piece of evidence often cited is eyewitness testimonies. However, eyewitness accounts alone are not considered strong evidence in the scientific community. People can easily be mistaken or influenced by suggestion, and the human memory is notoriously fallible.
Another form of evidence that is often brought forward are blurry photographs or videos of what is claimed to be Bigfoot. These pieces of evidence, known as “blobsquatches,” lack clear detail and can easily be attributed to a misidentification of a known animal, or even a clever hoax. Without verifiable and high-quality visual evidence, these blobsquatches are not considered reliable evidence in scientific analysis.
Physical evidence, such as footprints or hair samples, can provide more concrete evidence. However, these types of evidence are often inconclusive. Footprints can be faked or misattributed to known animals, and hair samples can be contaminated or belong to unknown animals. To truly confirm the existence of Bigfoot, physical evidence would need to be thoroughly examined by experts and shown to be distinct and cannot be attributed to any known species.
In conclusion, while there may be numerous pieces of evidence and testimonies surrounding Bigfoot, it is crucial to approach them with skepticism and adhere to the scientific method. Without clear and verifiable evidence, the existence of Bigfoot remains a subject of speculation and debate.
Interpreting the data
After conducting a comprehensive analysis of the available data on Bigfoot, it is clear that there is insufficient evidence to support the existence of this mythical creature. Despite numerous eyewitness accounts and purported footprints, no concrete scientific evidence has been found to substantiate these claims.
Many of the sightings and photographs can be attributed to misidentifications of known animals, hoaxes, or simple misinterpretations. The lack of clear and credible evidence, such as DNA samples or conclusive photographic evidence, raises significant doubts about the existence of Bigfoot.
Furthermore, the scientific method demands that claims be supported by testable hypotheses and repeatable experiments. Without the ability to subject Bigfoot claims to these scientific standards, it is difficult to justify considering it as a legitimate area of scientific inquiry.
In light of these shortcomings, it is important to approach Bigfoot studies with skepticism and critical thinking. While it is entertaining to speculate about the existence of mysterious creatures, it is essential to rely on scientific evidence and rigorous analysis to form conclusions.
Until concrete evidence emerges, the existence of Bigfoot will remain firmly in the realm of folklore and myth. While it is intriguing to imagine such creatures roaming the forests, it is important to prioritize scientific rigor and critical thinking in our search for the truth.