Welcome to the first lesson of Unit 1 on parts of speech! In this lesson, we will be discussing the answer key for the exercises in Lesson 1. Understanding parts of speech is crucial for developing strong language skills, as it helps us analyze the function and role of each word in a sentence. By the end of this lesson, you will have a clear understanding of the different parts of speech and their uses.
Before we begin, it is important to note that there are eight main parts of speech in the English language: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each of these parts of speech has its own unique function and purpose within a sentence. In Lesson 1, we focused on nouns and pronouns, discussing their definitions and examples.
Now let’s move on to the answer key for the exercises in Lesson 1. In Exercise 1, you were asked to identify the nouns in the given sentences. The correct answers for Exercise 1 are as follows:
1. “The cat” – cat is a noun.
2. “John and Mary” – John and Mary are nouns.
3. “The book” – book is a noun.
4. “My sister and I” – sister and I are nouns.
5. “The car” – car is a noun.
6. “The table” – table is a noun.
7. “The teacher” – teacher is a noun.
Now that we have covered the answer key for Exercise 1, let’s move on to Exercise 2. In this exercise, you were asked to replace the underlined nouns with pronouns. The correct answers for Exercise 2 are as follows:
1. “It” – replaces “the cat”.
2. “They” – replaces “John and Mary”.
3. “It” – replaces “the book”.
4. “We” – replaces “my sister and I”.
5. “It” – replaces “the car”.
6. “It” – replaces “the table”.
7. “They” – replaces “the teachers”.
Great job! You have successfully completed the answer key for Lesson 1. Understanding and recognizing parts of speech is a fundamental skill in language learning, and it will continue to play a vital role in your English language journey. Make sure to practice identifying and using different parts of speech in your own sentences to strengthen your language skills. Keep up the excellent work!
What are the Parts of Speech?
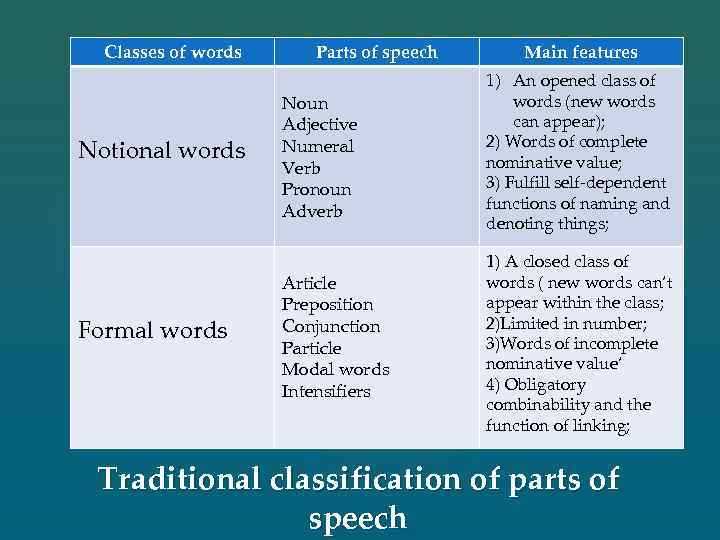
When it comes to understanding and using language effectively, it is crucial to have a solid grasp of the parts of speech. These are the building blocks of sentences and help us to communicate our thoughts and ideas clearly. In English, there are eight main parts of speech, each with its own unique purpose and function. Let’s take a closer look at each one.
Noun: A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. It can be something tangible, like “dog” or “table,” or something abstract, like “love” or “happiness.”
Pronoun: Pronouns are words that are used in place of nouns. They help us avoid repetition and make our sentences flow more smoothly. Common pronouns include “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” and “we.”
Verb: Verbs are action words. They show what someone or something is doing, or the state of being. Examples of verbs include “run,” “eat,” “sleep,” and “is.”
Adjective: Adjectives describe and modify nouns. They give us more information about the qualities or characteristics of a person, place, or thing. Some examples of adjectives are “red,” “happy,” “tall,” and “beautiful.”
Adverb: Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. They provide information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action is performed. Adverbs often end in -ly, such as “quickly,” “happily,” and “carefully.”
Preposition: Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence. They indicate location, time, direction, or manner. Common prepositions include “in,” “on,” “at,” “from,” and “to.”
Conjunction: Conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses together. They can be used to show addition, contrast, cause and effect, or other relationships. Common conjunctions include “and,” “but,” “or,” “because,” and “if.”
Interjection: Interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or sudden bursts of thoughts. They can stand alone or be used within a sentence to add emphasis or show surprise, joy, or pain. Examples of interjections include “wow,” “ouch,” “hurray,” and “oh no!”
In conclusion, understanding the parts of speech is essential for effective communication. By recognizing and correctly using these different elements, we can construct sentences that convey our ideas precisely and accurately.
Nouns: Identifying and Classifying

A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. It is an essential part of any sentence, as it helps us identify and classify the subject or object. There are several types of nouns, each serving a different purpose and providing more information about the entity it represents.
One type of noun is a common noun. Common nouns are general words that refer to everyday objects and concepts. Examples of common nouns include “dog,” “city,” and “happiness.” Common nouns are not capitalized unless they appear at the beginning of a sentence. They can be further classified into concrete nouns, which refer to tangible things like “chair” or “book,” and abstract nouns, which refer to intangible concepts like “love” or “justice.”
Another type of noun is a proper noun. Proper nouns are specific names or titles that refer to particular individuals, places, or organizations. Proper nouns are always capitalized. Examples of proper nouns include “John,” “Paris,” and “Google.” Proper nouns help us differentiate between entities and provide more specific information.
In addition to common and proper nouns, there are also collective nouns and compound nouns. Collective nouns refer to groups of people or things, such as “team” or “family.” Compound nouns, on the other hand, are made up of two or more words that work together to form a single noun, such as “raincoat” or “birthday cake.”
In conclusion, nouns play a crucial role in our language by helping us identify and classify the people, places, things, and ideas mentioned in a sentence. By understanding the different types of nouns, we can better communicate and convey precise information. So, next time you read or write a sentence, pay attention to the nouns and their classifications!
Verbs: Action Words and More
Verbs are an essential part of any sentence. They are words that describe actions, such as run, jump, and eat. These action verbs show what someone or something is doing. For example, in the sentence “She ran to the store,” the verb “ran” shows the action of running. However, verbs can also do more than just describe actions.
Verbs can also show a state of being or existing. These verbs are called linking verbs. Examples of linking verbs include “is,” “was,” and “were.” These verbs connect the subject of a sentence to a noun or adjective that describes it. For instance, in the sentence “He is a doctor,” the verb “is” links the subject “he” to the noun “doctor.”
Verbs can also indicate a condition or a happening. These verbs are called auxiliary or helping verbs. They assist the main verb in a sentence and provide more information about the action or state. Examples of auxiliary verbs include “have,” “do,” and “will.” In the sentence “I am going to wash the dishes,” the auxiliary verb “am” helps the main verb “going” and indicates the present continuous tense.
Furthermore, verbs can be categorized as transitive or intransitive. Transitive verbs take a direct object, while intransitive verbs do not. For example, in the sentence “She baked a cake,” the transitive verb “baked” has a direct object “cake.” On the other hand, in the sentence “He smiled,” the intransitive verb “smiled” does not have a direct object.
In conclusion, verbs play multiple roles in a sentence. They can describe actions, link subjects to descriptive words, indicate conditions, or provide assistance to the main verb. Understanding the different types of verbs and their functions helps to build clear and effective sentences.
Adjectives: Describing the World Around Us

Adjectives play a crucial role in describing the world around us. They provide additional information about the nouns they modify, helping to create a vivid and detailed picture in the reader’s mind. Whether it’s describing the appearance, size, color, or texture of an object, adjectives allow us to express our observations and perceptions in a concise and impactful manner.
When we encounter a beautiful sunset, we can use adjectives such as “vibrant,” “stunning,” and “breathtaking” to convey the awe-inspiring colors and natural beauty that captivate our senses. Similarly, when describing a tall and majestic tree, we might use adjectives like “towering,” “graceful,” and “majestic” to emphasize its grandeur and elegance.
Appearance: Adjectives related to appearance help us paint a clear picture in our minds. For example, a cute puppy can be described as “adorable,” “fuzzy,” and “playful,” while a sleek sports car can be characterized as “sleek,” “fast,” and “sporty.”
Size: Adjectives related to size enable us to understand the magnitude or scale of an object. A tiny ladybug can be described as “tiny,” “small,” and “minuscule,” while a gigantic mountain can be depicted as “enormous,” “immense,” and “towering.”
Color: Adjectives related to color bring life and vibrancy to our descriptions. For instance, a beautiful sunset can be described as “fiery,” “golden,” and “vibrant,” while a vibrant flower can be depicted as “colorful,” “bright,” and “bold.”
Texture: Adjectives related to texture allow us to convey the feel or touch of an object. For instance, a soft and fluffy pillow can be described as “cozy,” “comfortable,” and “fluffy,” while a rough and jagged rock can be characterized as “rough,” “sharp,” and “crusty.”
In conclusion, adjectives are powerful tools that help us describe and bring to life the world around us. By carefully choosing the right adjectives, we can create vivid and engaging descriptions that captivate the reader’s imagination and leave a lasting impression.
Adverbs: How, When, and Where
In this lesson, we have learned about adverbs and their different functions in a sentence. Adverbs are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide information about how, when, and where an action is performed.
An adverb that describes how an action is performed can answer the question “How?” For example, in the sentence “She sings beautifully,” the adverb “beautifully” describes how she sings.
An adverb that describes when an action is performed can answer the question “When?” For example, in the sentence “He always arrives late,” the adverb “always” describes when he arrives.
An adverb that describes where an action is performed can answer the question “Where?” For example, in the sentence “They are going there,” the adverb “there” describes where they are going.
It is important to remember that adverbs can also modify adjectives and other adverbs. They can add more detail and precision to the sentence.
Overall, adverbs play a crucial role in conveying information about how, when, and where an action takes place. By understanding the different functions of adverbs, we can enhance our writing and communication skills to express ourselves more effectively.
Now that we have a better understanding of adverbs, we can begin to recognize and use them in our own sentences. Practice identifying adverbs and experimenting with different adverb placements to create more dynamic and descriptive writing.
Q&A:
What is an adverb?
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, adjective, or other adverb.
How do adverbs modify verbs?
Adverbs modify verbs by answering the question “how?” For example, “She ran quickly.”
How do adverbs modify adjectives?
Adverbs modify adjectives by answering the question “to what degree?” For example, “He is extremely tall.”
How do adverbs modify other adverbs?
Adverbs modify other adverbs by answering the question “to what extent?” For example, “She sings very beautifully.”
When do adverbs come before a verb?
Most adverbs come before the verb in a sentence. For example, “They often visit their grandparents.”
What is an adverb?
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It provides more information about how, when, or where an action or event takes place.